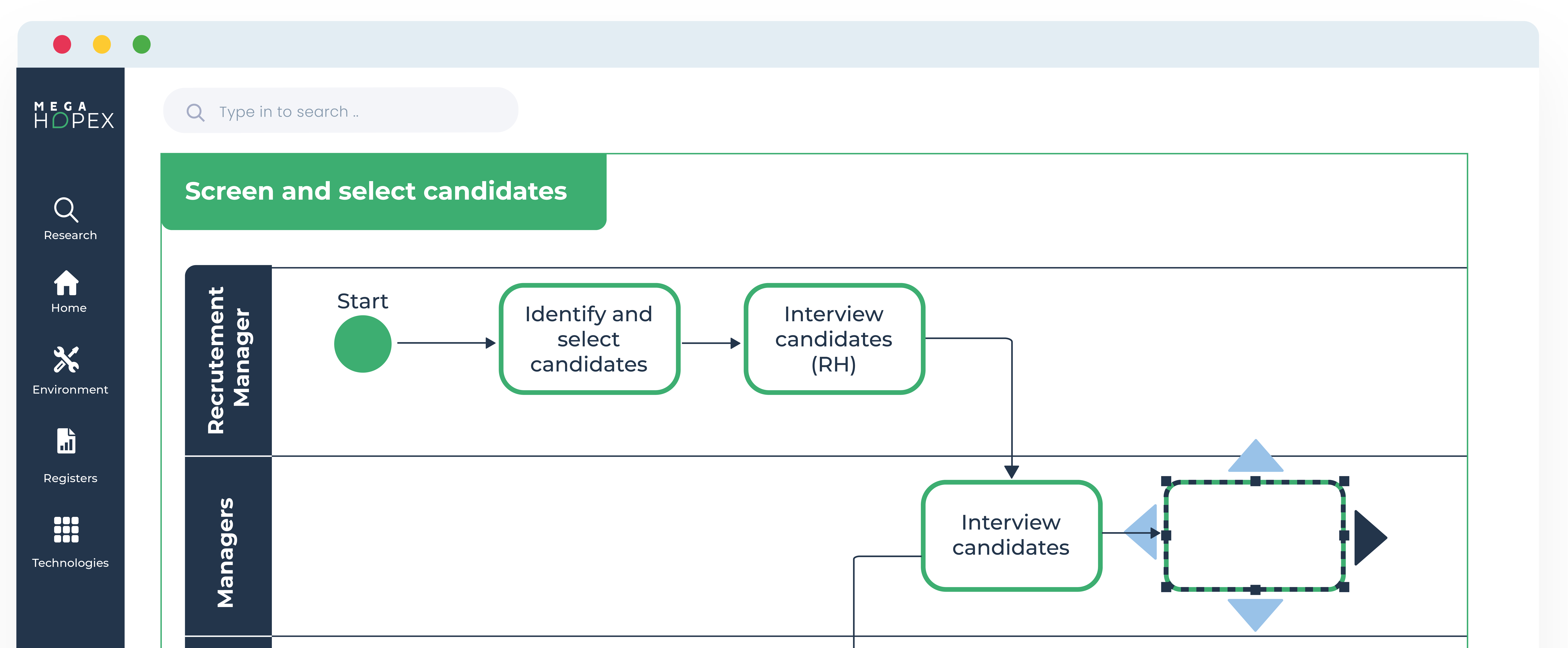
Guide to Business Process Mapping: Creating Effective Process Maps
In today's fast-paced business environment, efficiency and productivity have become crucial factors for organizations to remain competitive. Business process mapping is a technique that can be used to help streamline operations and increase efficiency. It is a visual representation of the steps involved in a particular process, designed to identify improvements that can be made to reduce waste, increase productivity, and improve quality. This article explores the importance of business process mapping and how it can revolutionize how organizations function.
What is business process mapping?
Business process mapping is essential for organizations to understand, analyze, and improve their internal processes. It visually represents a company's operational activities from beginning to end while outlining the steps involved in each process.
The process map is a flowchart that displays how workflows within an organization, identifying the inputs required for each step and the outputs generated by each stage.
Business process mapping aims to increase efficiency and productivity by identifying and removing inefficiencies, redundancies, and bottlenecks. It also helps create a shared understanding of the organization's workflow and maintains consistency in the process.
Definition of process map
A process map visualizes a workflow that displays the steps involved in a particular process, emphasizing the flow of materials, information, and activities. It is an essential tool for understanding how work is done, identifying potential areas of improvement, and implementing process improvement initiatives.
A process map visually depicts the activities, inputs, and outputs involved. It enables a team to align their understanding of the process, communicate more effectively, and make better-informed decisions about process improvement initiatives.
Different Types of Business Process Maps
Business process mapping is essential for analyzing and optimizing critical business processes. Business process maps include flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, value streams, and cross-functional maps.
Flowcharts are ideal for representing high-level processes in a simple and easy-to-understand format. Swimlane diagrams are helpful for operations that involve multiple departments or stakeholders. Value stream maps help identify and eliminate waste in an entire process, from start to finish.
Cross-functional maps are a more detailed version of swimlane diagrams showing how each department interacts.
The difference between flowcharts and process maps
Flowcharts and process maps visually represent a process or series of steps. However, there are distinct differences between the two. Flowcharts contain more detail and define decision-making points and rules.
They are typically used for complex processes with multiple paths and variables. Process maps are more straightforward and focus on the overall flow of a process. They are used to identify improvement areas and communicate process changes to stakeholders. Choosing the appropriate tool for a given situation can increase efficiency and effectiveness in process management.
How does business process mapping fit into business process management?
Business process mapping is an essential component of business process management. It involves identifying and documenting all the steps and activities in a business process. This detailed description serves as a basis for analyzing and optimizing the said process by identifying potential inefficiencies and gaps that can be addressed.
The insights generated from this exercise help organizations to achieve process optimization, reduce errors, and improve the quality of their deliverables.
Why is business process mapping important?
Business process mapping is crucial in organizations' quest to improve performance, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. It is a powerful tool that allows enterprises to meticulously analyze and optimize their operational processes, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity. By visually mapping out the intricacies of business processes, companies can gain a comprehensive understanding of the activities and tasks involved, thus enabling them to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Subsequently, organizations can devise effective strategies to resolve these issues and streamline their operations.
How to Create a Process Map?
A process map visually represents a business process, outlining the steps and actions required to achieve a particular goal. Creating a process map involves thoroughly understanding the process and the individuals and departments involved in its execution.
To create a practical process map, one must first identify critical steps, map out the flow of activities, and review and refine the map until it accurately reflects the process. The resulting process map can identify inefficiencies, prioritize improvements, and streamline operations.
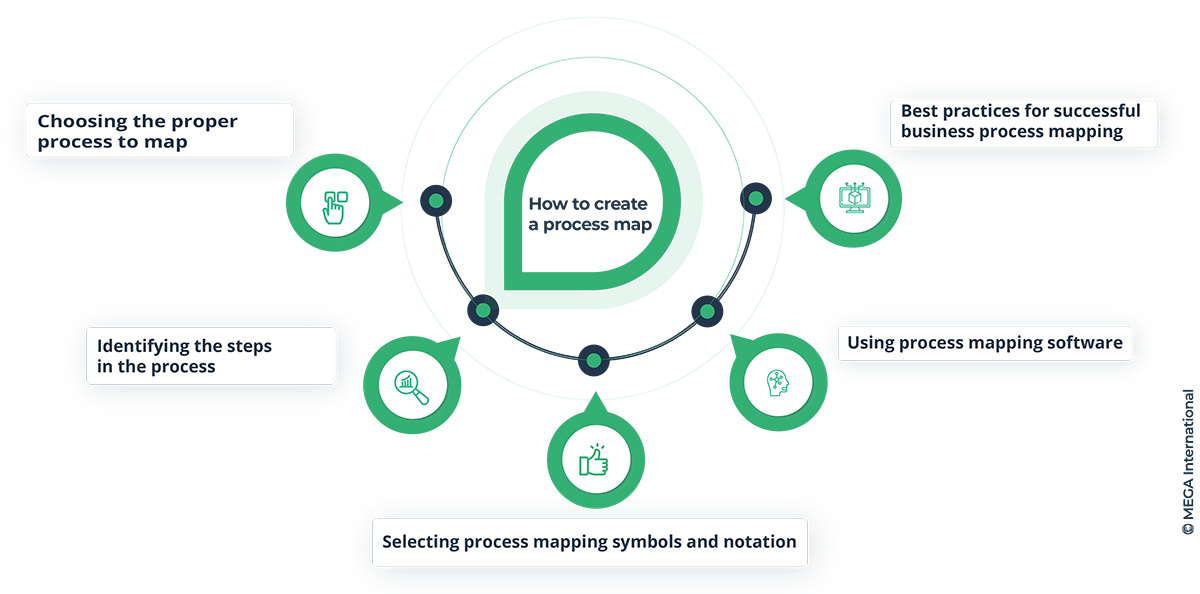
Choosing the proper process to map
When determining which process to map, it is crucial to consider the purpose and objectives of the mapping exercise carefully. The chosen method should be central to the organization's overall goals and can provide insight into areas of improvement.
Additionally, it is essential to ensure adequate data and feedback are available to map the process accurately. Evaluating these factors before the mapping process will increase the likelihood of producing meaningful and actionable results.
Identifying the steps in the process
To effectively and efficiently complete a task, it is essential to identify the steps in the process. This involves breaking down the overall objective into smaller, manageable steps that can be quickly followed and executed. Once the steps have been defined, it helps to prioritize them based on their importance and sequence.
Identifying the steps in the process simplifies the task and increases accuracy and productivity. It is a crucial aspect of project management and enables organizations to achieve their goals promptly and effectively.
Selecting process mapping symbols and notation
When selecting process mapping symbols and notation, it is essential to choose those that are universally recognized and easily understood. The signs should accurately represent the mapped process, making it clear and concise for the individuals reviewing the map.
Consistency in the selected characters is also vital, as it ensures that all parties involved can easily interpret and understand the map. It is advisable to review the industry standards for process mapping and the specifics of the process being mapped before making any decisions on symbols and notation.
Using process mapping software
Employing process mapping software can significantly enhance the productivity and efficiency of a business. This software can visualize and analyze complex business processes by documenting every operation step, identifying inefficiencies, and suggesting opportunities to optimize performance. It can also assist in simplifying the evaluation of various solutions, comparing them side-by-side with precise data, and determining the best course of action. Utilizing process mapping software can not only save time and resources but can also make a substantial contribution to meeting customer and business goals.
Best practices for successful business process mapping
When implementing business process mapping, certain best practices can significantly enhance the chances of success. First and foremost, involving all stakeholders – from executives to front-line employees – is crucial in the process.
Secondly, the team responsible for mapping the process should be well-versed in the organization's goals and values and the processes involved in achieving those goals.
Finally, regular review and updating of the process map are essential to ensure it remains relevant over time. By following these best practices, businesses can streamline operations and improve their bottom line.
Benefits of Business Process Mapping
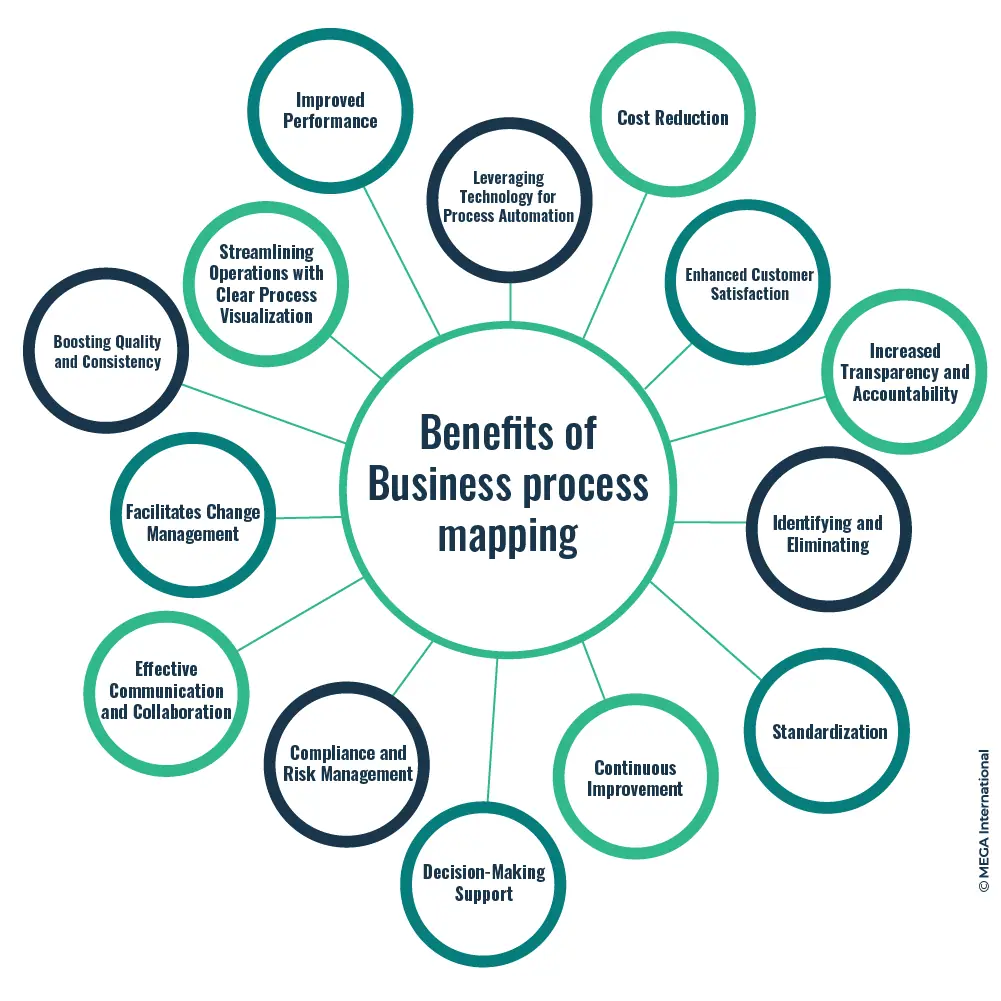
- Streamlining Operations with Clear Process Visualization: One of the primary benefits of business process mapping is its ability to clearly and concisely visualize the various steps involved in a particular process. By mapping out the flow of activities, decision points, and dependencies, organizations can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. This holistic view enables companies to streamline their operations, eliminate redundant steps, and optimize their processes for maximum efficiency.
- Improved Performance: Business process mapping enables organizations to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and redundancies. By streamlining operations and optimizing workflows, companies can enhance their overall performance and achieve higher productivity.
- Cost Reduction: Mapping business processes allows organizations to identify areas where costs can be minimized. Companies can achieve cost savings and improve their bottom line by eliminating unnecessary steps, reducing manual effort, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Business process mapping enables organizations to deliver better customer products and services. Companies can provide faster response times, reduce errors, and enhance customer experience by improving operational efficiency.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: Mapping out business processes provides a clear and transparent view of how work is being done within an organization. This transparency promotes accountability as employees understand their roles and responsibilities, leading to improved collaboration and a sense of ownership.
- Standardization: Business process mapping allows organizations to standardize their procedures and ensure consistency in their operations. Standardization helps eliminate variations in processes, reduces errors, and improves the quality of outputs, leading to excellent reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: Through the visualization of processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement and implement changes iteratively. Business process mapping fosters a culture of continuous improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics, enhance efficiency, and remain competitive.
- Compliance and Risk Management: Mapping business processes helps organizations identify and understand risks, regulatory requirements, and compliance obligations. By aligning processes with legal and industry standards, companies can mitigate risks, avoid penalties, and maintain a strong reputation for integrity and trustworthiness.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for the smooth functioning of any organization. Business process mapping facilitates better communication among team members and departments by providing a shared understanding of how different processes interconnect. Employees can easily comprehend their roles and responsibilities with a visual workflow representation, fostering a collaborative work environment. This improved communication reduces errors, eliminates misunderstandings, and enhances overall productivity.
- Facilitates Change Management: Business process mapping becomes a valuable tool for managing the transition when organizations change, such as process redesign or technology implementation. It allows stakeholders to visualize the impact of changes, identify potential risks or challenges, and plan for successful implementation.
- Decision-Making Support: Business process mapping gives organizations a comprehensive view of their operations, enabling data-driven decision-making. Organizations can make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, process improvements, and strategic planning by analyzing process maps and performance metrics.
- Identifying and Eliminating Inefficiencies can plague the most well-established organizations, hindering their growth and profitability. Business process mapping helps identify these inefficiencies by uncovering bottlenecks, redundant activities, and waste areas. With a detailed process map, organizations can analyze each step and identify opportunities for improvement. Businesses can significantly enhance operational efficiency by eliminating unnecessary steps, automating tasks, and implementing best practices.
- Boosting Quality and Consistency: Consistency is critical to delivering high-quality products and services. Business process mapping ensures that processes are executed consistently across the organization, reducing variations and errors. By defining clear guidelines and standard operating procedures, organizations can achieve a higher level of quality control. Process mapping also allows companies to identify critical control points and implement quality checks, ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Leveraging Technology for Process Automation: In an era of digital transformation, leveraging technology is vital for achieving operational excellence. Business process mapping provides organizations with a clear understanding of their existing processes, making it easier to identify areas suitable for automation. By embracing automation technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA) or workflow management systems, companies can streamline their operations, reduce manual effort, and increase overall efficiency.
Process Mapping Symbols and Notation
Process mapping symbols and notation are essential for businesses to visualize and understand their operational processes effectively. Consistent usage of symbols and notation in process mapping provides clarity and accessible communication for employees and stakeholders.
Understanding the meaning behind each character and note ensures accurate workflow representation and assists in identifying areas of improvement. Businesses can optimize operations and increase efficiency by utilizing process mapping symbols and notation.
An overview of standard symbols used in process mapping
Using symbols to represent different activities and stages is a common practice regarding process mapping. These symbols help to create a visual representation of the process, making it easier to understand and analyze.
The most commonly used characters include circles to represent events, squares or rectangles for activities, diamonds for decisions, arrows to describe flow and direction, and parallel lines for multiple process paths. By understanding and utilizing these symbols, process maps can be created that are clear, concise, and effective in conveying information.
Business process modeling notation (BPMN)
Business process modeling notation (BPMN) is a formal methodology used to depict a business process's steps and interactions visually. It is a graphical notation language that aids in creating and communicating business process flow diagrams. Standardizing the symbols used in BPMN allows for straightforward interpretation and understanding across different organizations. BPMN provides a comprehensive representation of complex process models, making it an essential tool for process improvement, optimization, and analysis in various organizations.
Tips for effectively using symbols and notation
When effectively using symbols and notation, it is imperative to maintain consistency and clarity. Choosing characters that are concise and understandable to a broader audience is crucial. Establishing a key to interpret the signs used in the notation is also essential to avoid confusion.
Lastly, it is critical to stick to the base notation throughout the document rather than introducing new characters or notes, which may lead to inconsistency and complexity. These simple tips ensure easy comprehension and effective communication of an idea or concept.
The importance of consistent notation and symbols
Consistent notation and symbols are crucial when conveying information accurately and quickly, particularly in technical fields. Using standardized notes and symbols ensures clarity and minimizes the risk of misinterpretation or confusion. It also facilitates communication between professionals in the same area. In addition, uniform notation and symbols enable easy reading and understanding of technical drawings, models, and diagrams across different organizations and regions. Therefore, consistent notation and symbols are essential for precise and efficient communication in specialized settings.
Common mistakes to avoid in process mapping
Several common errors should be avoided in process mapping to facilitate smooth and efficient operations.
One critical mistake is failing to keep track of all the relevant details, leading to incomplete or inaccurate process maps. Another pitfall to be mindful of is being overly prescriptive in outlining the process, which can stifle creativity and constrain the flexibility often necessary for adapting to changing circumstances. In addition, it is crucial to ensure that sufficient time and resources are dedicated to the mapping process, including soliciting input and feedback from stakeholders.
Types of Business Process Maps
There are various types of business process maps that organizations use to establish and improve their operations. The most common ones include flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and Value Stream Maps.
Flowcharts detail the steps and decisions involved in a circle—swimlane diagrams show which departments or individuals perform certain parts of a process. Value Stream Maps provide an overview from start to finish, highlighting areas of waste and potential for improvement. Choosing the correct type of map depends on the purpose of the analysis and the complexity of the process.
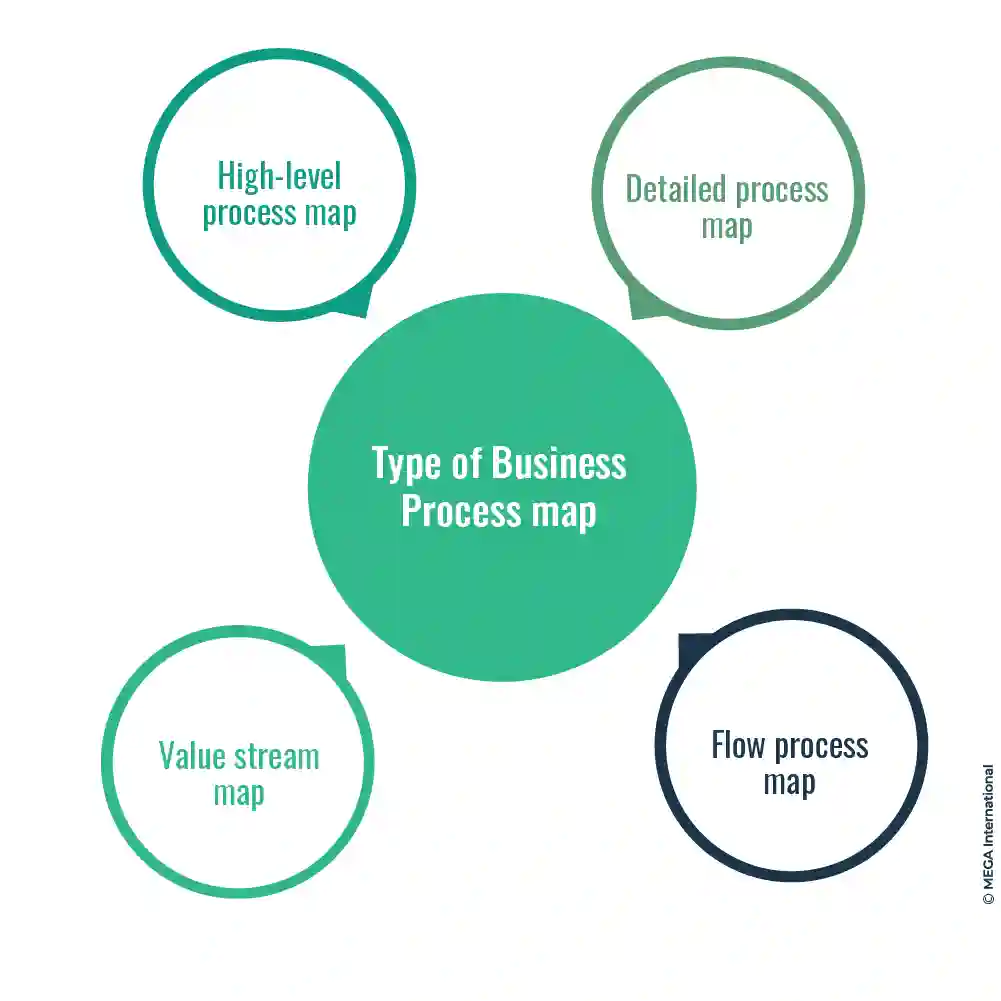
High-level process map
A high-level process map is a visual representation of a company's workflow, which helps to identify critical stages in a process and the interdependencies between them. This map typically includes the main steps involved and any sub-processes and can help identify areas of improvement or inefficiencies. A high-level process map can make assessing risks and identifying potential issues easier, helping businesses streamline operations and improve overall efficiency.
Detailed process map
A detailed process map comprehensively illustrates the steps in completing a particular process. It provides a clear and concise visual representation of all the tasks, activities, and decision points required to complete the process.
This map type is often used in project management to identify areas where improvements can be made or standardize procedures across multiple projects. The detailed process map allows team members to optimize workflows, reduce errors, and improve productivity. Its thorough approach helps to identify inefficiencies and areas that require additional resources or training.
Flow process chart
A flow process chart is a tool used in business process management to represent the steps involved in a process visually. It outlines the process flow from start to finish, identifying the decision points and activities involved.
The chart provides a clear overview of the process and can help identify areas for improvement or optimization. It is commonly used in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare to streamline processes and increase efficiency. Overall, a flow process chart effectively communicates and analyzes complex operations in a structured and formal manner.
Value stream map
A Value Stream Map is a visual tool that identifies and analyzes all the activities involved in a specific process. It depicts the activities undertaken by each team member and the sequence in which they occur. By mapping value streams, organizations can better understand the waste in their processes and identify areas for improvement. It provides data and actionable insights that help organizations streamline activities and optimize workflows. Value Stream Mapping is essential for organizations seeking to enhance their operational efficiency and improve their bottom line.
Steps to Create a Business Process Map, with example
Creating a business process map is a systematic approach that involves several key steps. By following these steps, organizations can effectively document and visualize their processes, leading to improved understanding, analysis, and optimization. Here are the steps:
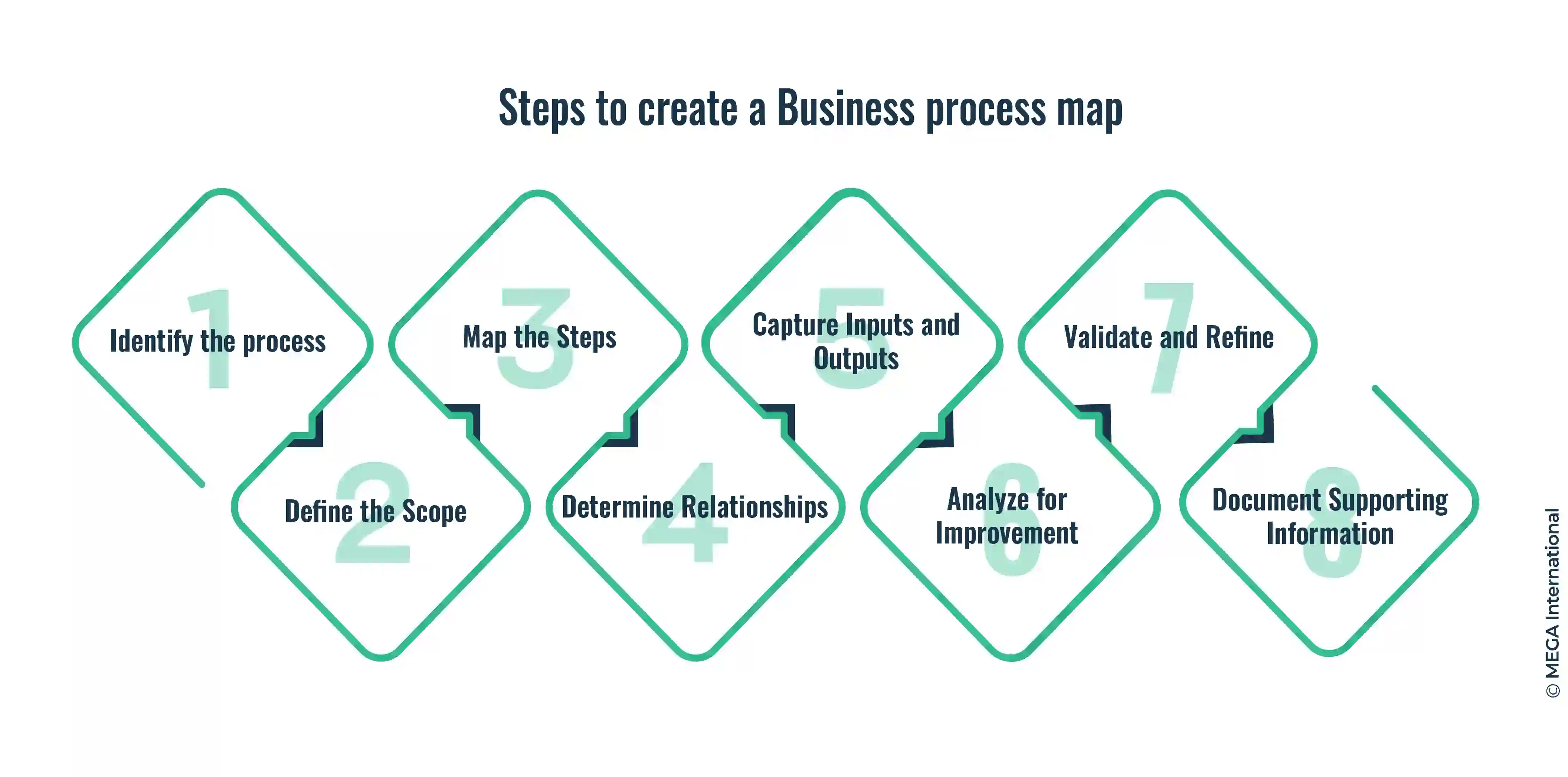
- Identify the Process: Select the specific process you want to map. It could be a core business process, such as order fulfillment or customer service. For example, consider the "Purchase Order Processing" process.
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the boundaries and scope of the process you're mapping. Identify the inputs, outputs, and the stakeholders involved. In our example, the content might include receiving purchase orders, verifying information, generating invoices, and updating inventory.
- Map the Steps: Break down the process into individual steps or activities. Use clear and concise language to describe each step. You can use symbols and icons to represent activities, decisions, and data flows. For instance, in the Purchase Order Processing example, measures might include "Receive Purchase Order," "Verify Information," "Generate Invoice," and "Update Inventory."
- Determine Relationships: Identify the relationships and dependencies between the steps. This helps visualize the process's information, materials, or decision flow. Use arrows or connectors to illustrate these connections. For example, the "Generate Invoice" step might depend on completing the "Verify Information" step.
- Capture Inputs and Outputs: Document the inputs required for each step and the outputs produced. Information can include documents, data, or materials needed to initiate or complete a degree. Outputs represent the results or deliverables produced at each stage. In the Purchase Order Processing example, inputs might include purchase order forms, customer information, and product specifications, while outputs could include invoices, updated inventory records, and order confirmation emails.
- Analyze for Improvement: Once the process map is complete, analyze it for potential improvements. Look for bottlenecks, redundancies, or areas of inefficiency. Identify opportunities to streamline the process, eliminate unnecessary steps, or automate specific tasks. For instance, in our example, you might discover that introducing an automated invoice generation system can reduce processing time and improve accuracy.
- Validate and Refine: Share the process map with stakeholders and subject matter experts to validate its accuracy. Incorporate their feedback and make necessary refinements. Ensure that the map reflects the actual process as closely as possible.
- Document Supporting Information: Provide additional details, such as process metrics, roles and responsibilities, and relevant documentation, to supplement the process map. This information helps users understand the context and requirements of each step.
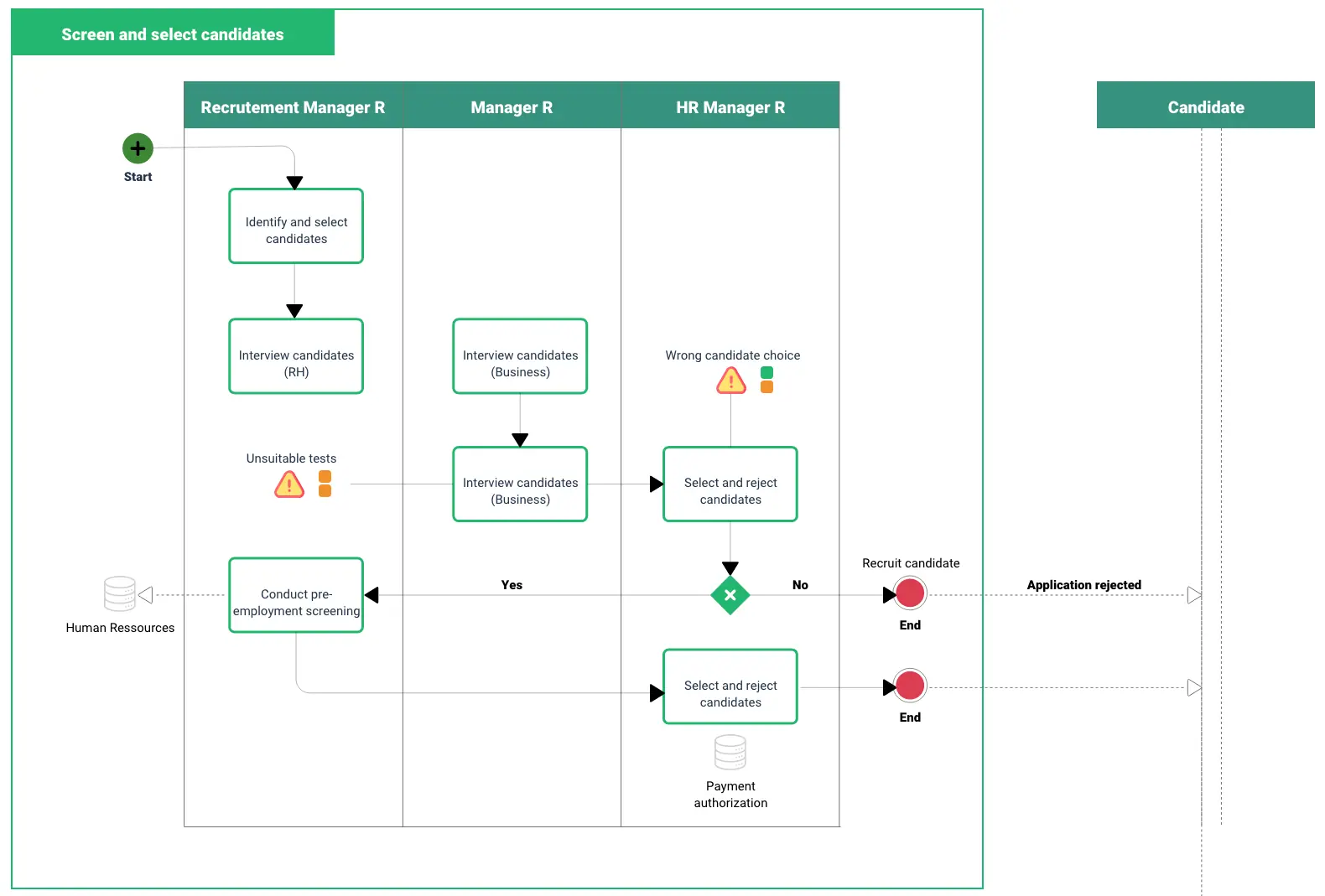
Example:
Let's consider an example of a business process map for the KYC (Know your customer” process in the banking industry:
- Step 1: Identify the customer
- Step 2: Verify the client's information
- Step 3: Understand client activities and fund origin
- Step 4: Conduct a risk assessment
- Step 5: Apply risk rating
- Step 6: Monitor and review regularly
Involving stakeholders in the process of mapping
A formal communication plan should be created and shared with all stakeholders, including the mapping objectives, timelines, and expected outcomes. The selection of stakeholders to participate in the process should be based on their knowledge of the process, expertise, and ability to influence the success of the mapping project.
The stakeholders' training should occur before the process mapping begins, ensuring that they understand the mapping process, their role in it, and how it relates to the organization's larger goals. Engaging stakeholders in the process allows them to provide their insights, experience, and knowledge of the process, thus enabling a better understanding of potential issues and improvement opportunities. This engagement should continue throughout the mapping process, culminating in monitoring and evaluating the outcomes achieved.
Presenting Process Maps Effectively
When presenting your process maps, it is essential to approach the task professionally and formally. First and foremost, ensure that your maps are accurate and up-to-date, as presenting outdated or incorrect maps will confuse and undermine your credibility. Consider creating a visual representation of your maps using flowcharts or other diagramming tools, making them more accessible and easier to understand.
When presenting your maps, providing context and explaining their rationale is essential. This could include detailing the process objectives, identifying potential bottlenecks, or highlighting areas for improvement. Additionally, be prepared to answer questions and address concerns during the presentation.
The tone of the presentation should be respectful and considerate of the audience, avoiding technical jargon and complex terminology that may be unfamiliar to them. Use clear and concise language, and focus on the critical aspects of the maps that are most relevant to the audience.
Finally, consider providing a copy of the maps to the audience in electronic or printed format to enable them to reference them later. This will demonstrate your commitment to transparency and openness and allow further questions or discussions after the presentation.
Following these guidelines ensures that your process maps are presented professionally and effectively, providing valuable insights and driving improvements throughout your organization.
Process Mapping Tools and Software
Business process mapping software facilitates this methodology and provides businesses with a structured approach to mapping their processes. Numerous process mapping tools and software are available in the market, each with its features and benefits.
The essential elements of process mapping software include the ability to document processes, create flowcharts, and analyze data. The more advanced tools offer additional features such as notifications, real-time collaboration, process monitoring, and integration with other software systems.
In addition, process mapping tools software also provides businesses with a visual representation of their processes, making it easier to understand how different departments and functions fit together.
FAQs
Business mapping is a process that helps organizations visually represent their business processes; data flows, organizational structures, and communication channels. The primary purpose of business mapping is to identify inefficiencies and areas where processes can be improved. Through mapping, organizations can better understand their operations and how various departments and systems are connected.
The critical elements of a business process map include identifying the inputs and outputs of a process, the flow of activities and decision points, the roles and responsibilities of the people involved, and the systems or technology used. It also includes metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of a process and identifying areas for improvement. A successful business process map should be clear, concise, and easy to understand, providing a comprehensive view of how a process works and how it could be improved.
Process mapping is an essential tool businesses use to identify areas needing improvement and optimize their operations. Effective process mapping involves four basic steps. Firstly, companies need to define and document their processes in detail, which helps identify waste, redundancies, and inefficiencies. Secondly, they should analyze the process and identify the areas that need improvement. Thirdly, businesses should map the improved process, considering all the changes made. Companies can achieve effective process mapping by following these four steps, significantly improving efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Process mapping is a valuable tool used in business process improvement. It visually depicts the various steps involved in a process, allowing for greater understanding and identification of areas for improvement. The features of process mapping include the ability to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, the ability to analyze and optimize workflows, and the ability to standardize processes throughout an organization.
A process map comprises three main components: inputs, activities, and outputs. Inputs depict the raw materials or resources required to initiate the process, while activities represent the steps taken to carry out the operation. Finally, outputs illustrate the completed product or service and its quality. A well-defined process map enhances organizational efficiency and provides a clear understanding of the workflow. It also enables businesses to identify areas where improvements can be made to optimize performance.
Related Content to Business Process Management
Get a clear understanding of how your operation runs, identify areas of improvement, and build scenarios to optimize and transform business processes;
MEGA HOPEX for BPM
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for BPM, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.