The Impact of DORA Regulation on Compliance and IT Departments
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) introduces a comprehensive framework to ensure financial entities' IT systems are robust, secure, and resilient to cyber threats and other IT-related disruptions. This regulatory environment significantly impacts IT departments within these entities, necessitating enhanced security measures and the implementation of resilience strategies. Below, we explore how DORA regulations shape these areas.
The Objectives of DORA
As a critical initiative to safeguard financial institutions and their consumers against digital threats and disruptions, DORA ushers in a new era of stringent operational requirements.
But what does this mean for these institutions' Compliance and IT departments? DORA is not just another regulatory hurdle to clear; it is a clarion call for a systemic overhaul of the existing cybersecurity, risk management, and operational resilience frameworks. For Compliance departments, it presents a complex matrix of compliance requirements, advising mandates, and the management of potential breaches and penalties.
It is crucial to understand the multifaceted challenges and opportunities DORA represents for Compliance and IT departments.

READ: What is DORA?
The Compliance Implications of DORA
DORA's implications are far-reaching, impacting many entities, including banks, insurance companies, investment firms, and critical third-party service providers such as cloud computing services. Here are some essential implications of compliance with DORA:
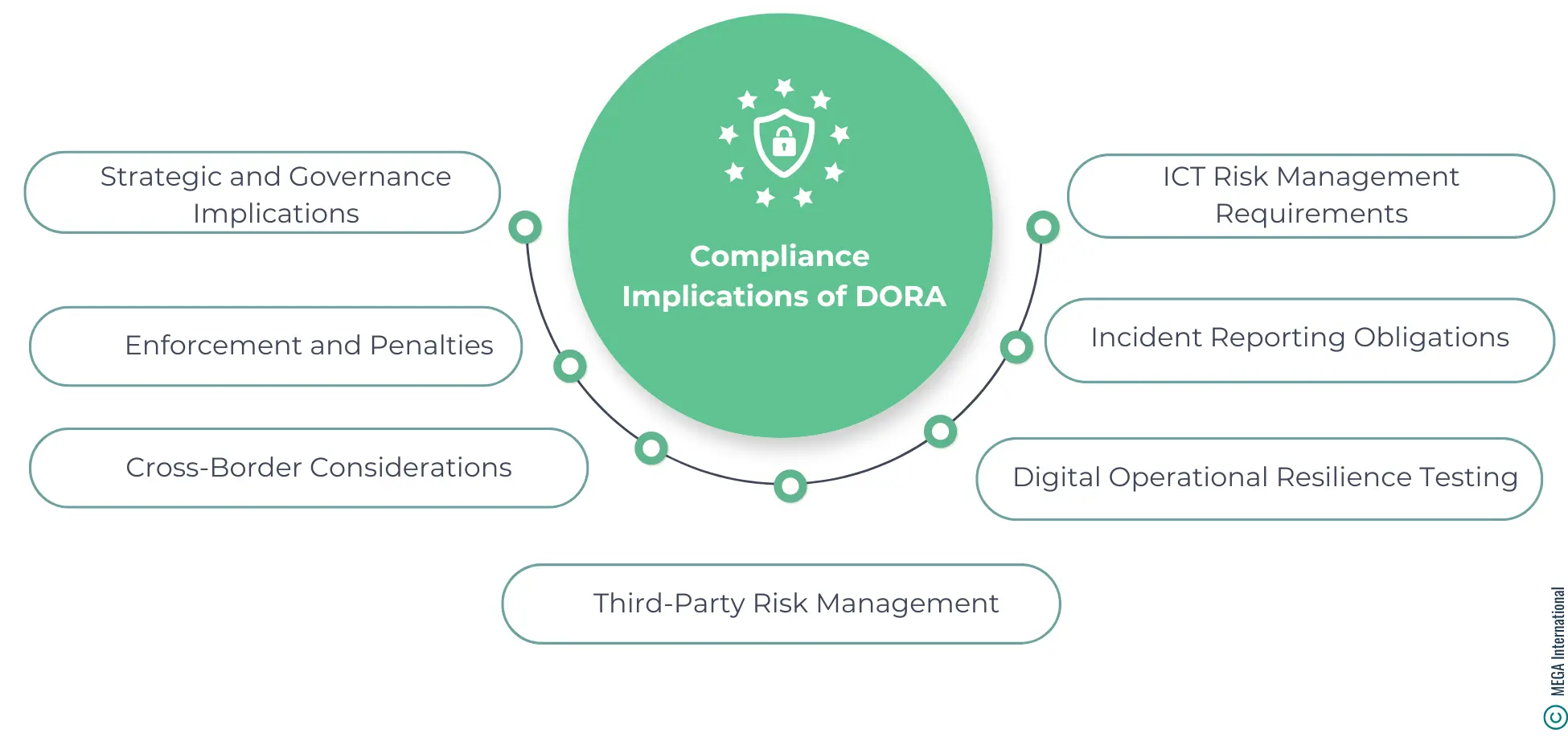
1. ICT Risk Management Requirements
DORA mandates strict requirements for financial entities to establish and maintain robust ICT risk management frameworks. These frameworks must cover risk identification, protection, prevention, detection, response, recovery, learning and evolving mechanisms, and communication strategies. This means entities must reassess and potentially overhaul their current ICT risk management strategies to ensure compliance.
READ: Cybersecurity Compliance
2. Incident Reporting Obligations
Under DORA, financial entities must establish mechanisms to detect and report significant ICT-related incidents to relevant authorities. This imposes a proactive duty on entities to monitor ICT systems continuously and report incidents that could impact financial stability or customer interests, which may require substantial investments in detection and reporting technologies.
3. Digital Operational Resilience Testing
DORA introduces mandatory resilience testing for financial entities, including advanced testing like threat-led penetration testing. These tests evaluate the effectiveness of an entity's measures to withstand ICT disruptions and breaches. Entities must, therefore, engage in regular testing and potentially invest in more sophisticated testing procedures than currently employed.
4. Third-Party Risk Management
Given the reliance on third-party service providers for critical ICT services, DORA emphasizes the importance of managing risks stemming from these relationships. Financial entities must ensure that contracts with third parties include robust compliance clauses and retain the ability to audit these providers for compliance with DORA requirements. This may lead to contract renegotiation and enhanced due diligence processes.
5. Cross-Border Considerations
DORA aims to harmonize digital operational resilience requirements for entities operating across multiple EU jurisdictions, simplifying compliance efforts to some extent. However, entities must navigate the nuances of DORA implementation in different Member States and manage coordination with numerous national authorities.
6. Enforcement and Penalties
DORA sets out specific enforcement mechanisms and potential penalties for non-compliance, including substantial fines. Financial entities must, therefore, prioritize compliance to avoid regulatory sanctions, reputational damage, and financial losses.
7. Strategic and Governance Implications
Implementing DORA will likely require significant strategic planning and investment from financial entities. Senior management and boards will need to be directly involved in overseeing the adaptation to these regulations, ensuring compliance is integrated into the entity's overall strategic objectives and governance structures.
The Impact on IT Departments
IT departments are now at the forefront of managing and implementing technology and ensuring the security and resilience of their organization's digital infrastructure. This responsibility encompasses enhancing IT security measures and implementing comprehensive resilience strategies.
Enhancing IT Security Measures
Under DORA, IT departments must improve security protocols to protect the digital infrastructure and sensitive data from cyber threats. This involves several key actions:
- Advanced Security Solutions: To protect against sophisticated cyber threats, it is imperative to deploy advanced cybersecurity technologies. These include next-generation firewalls, endpoint security solutions, and anomaly detection systems tailored to identify and mitigate threats in real-time.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: DORA mandates regular security assessments and audits to identify vulnerabilities within the IT infrastructure. IT departments must conduct these evaluations systematically to ensure compliance and fortify their security posture.
- Enhanced Access Controls: Implementing stringent measures ensures only authorized personnel can access sensitive information and systems. This may involve multifactor authentication, role-based access controls, and continuous monitoring of access logs.
- Cybersecurity Training: Regular training programs for all employees, focusing on cybersecurity awareness and data protection best practices. DORA emphasizes the need for an informed workforce to prevent data breaches and cyber incidents.
Implementing Resilience Strategies
Operational Resilience
Operational resilience under DORA involves ensuring that the IT systems can withstand and recover from disruptions, maintaining the continuity of critical functions. Key elements include:
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Developing comprehensive disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity plans (BCP) that detail procedures for maintaining and restoring IT operations during a disruption. DORA expects these plans to be tested regularly and updated based on lessons learned.
- Infrastructure Redundancy: Building redundant systems and data backups in geographically diverse locations to ensure that services can continue even if one area is compromised or experiences a failure.
Cyber Resilience
Cyber resilience focuses on the ability to prevent, respond to, and recover from cyberattacks:
- Incident Response Plans: IT departments must have detailed incident response plans that outline steps to be taken in the event of a cyberattack. These plans should include notification procedures for internal teams and external authorities, as DORA requires.
- Continuous Monitoring and Detection: Implement systems for constantly monitoring IT infrastructure to detect and respond to cyber threats in real-time. DORA encourages using automated tools and services to identify unusual activity that may indicate a cyberattack.
- Learning and Adaptation: Post-incident analyses are crucial for understanding the nature and impact of cyberattacks. IT departments are expected to learn from these incidents and adapt their cybersecurity strategies accordingly, continuously improving their resilience.
READ: DORA Five Pillars
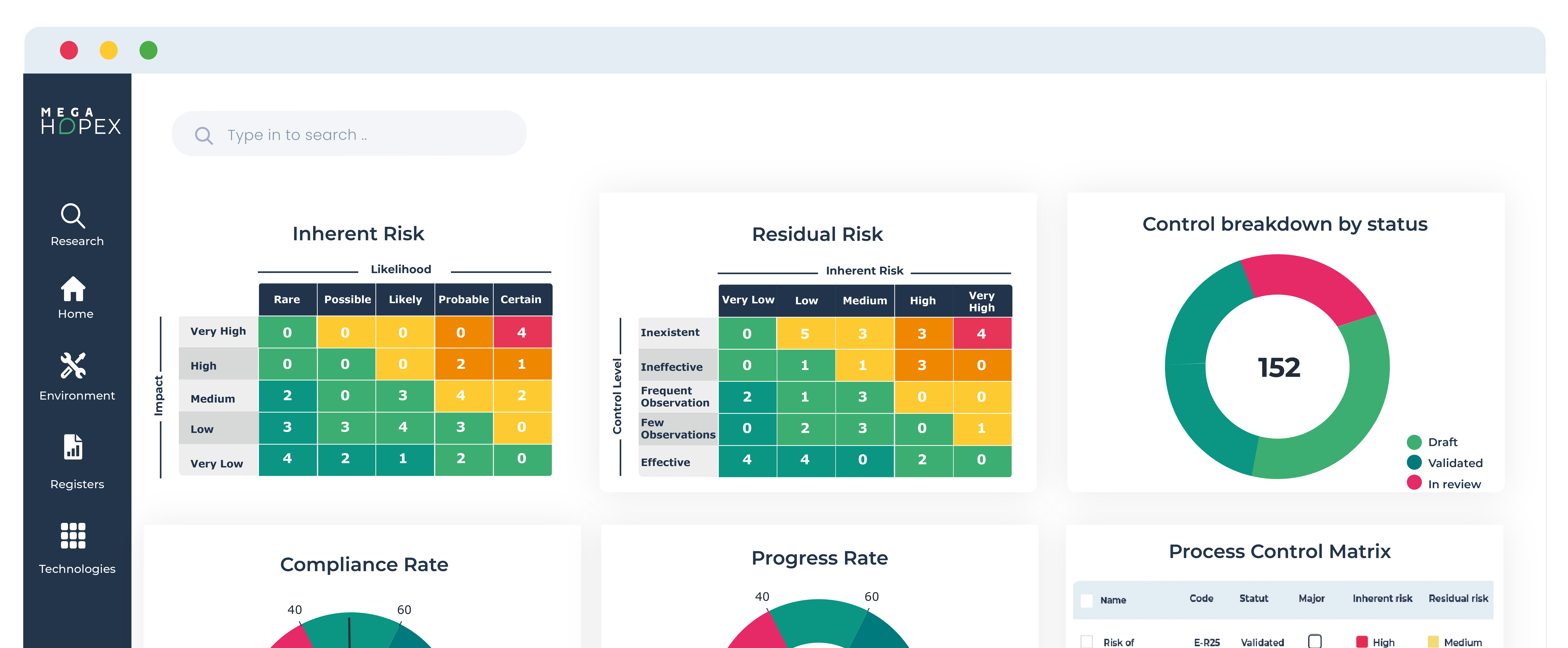
The Role of HOPEX in Supporting Compliance and IT Departments
HOPEX, a comprehensive suite of integrated software solutions designed for Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC), can significantly mitigate the impact of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) regulation on both Compliance and IT departments within financial entities.
By leveraging HOPEX's capabilities, organizations can enhance their compliance posture, streamline risk management processes, and fortify their operational resilience.
Here’s how HOPEX can support these departments in addressing the challenges posed by DORA:
For Compliance Departments
Regulatory Compliance Management
HOPEX provides tools that enable Compliance departments to stay updated on regulatory changes, including those related to DORA. It helps map applicable regulations to business processes and IT supporting assets, assess compliance levels, and identify gaps that need addressing. This ensures that the organization complies with DORA requirements, reducing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
Gap Assessment and Remedial Progress Monitoring:
| HOPEX enables real-time gap assessment analysis across the organization to pinpoint where it deviates from DORA's standards. Once areas for improvement have been identified, HOPEX's strong action plan management allows for implementation and monitoring of necessary actions to rectify these deviations. the |
For IT Departments
1. IT Risk Management
HOPEX enables IT departments to identify, assess, and manage ICT risks in alignment with DORA's risk management framework. It offers tools for conducting risk assessments, defining risk mitigation strategies, and monitoring risk levels over time. This proactive approach to IT risk management helps ensure that ICT systems are resilient to disruptions and cyber threats.
2. Incident Management and Reporting
DORA mandates timely detection, management, and reporting of significant ICT-related incidents. HOPEX's incident management module allows IT departments to record, investigate, and resolve incidents efficiently. It also facilitates mandatory reporting to regulatory authorities, ensuring compliance with DORA's incident reporting requirements.
3. Operational and Cyber Resilience
HOPEX supports the development of operational and cyber resilience strategies by providing a framework for documenting business processes, IT assets, and dependencies. This visibility enables IT departments to conduct thorough resilience testing, including scenario analysis and disaster recovery planning, in line with DORA's resilience testing requirements. Additionally, HOPEX can help plan and implement measures to enhance cyber resilience, including data backup and recovery solutions.
4. Third-Party Risk Management
Given DORA's focus on managing risks related to third-party service providers, HOPEX offers capabilities for third-party risk assessment and monitoring. It enables organizations to assess the resilience of their third-party providers, ensuring they comply with DORA regulations and thereby reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions.
Integrating Compliance and IT Efforts
By providing a centralized platform for managing compliance, risk, and resilience, HOPEX facilitates collaboration between Compliance and IT departments. This integrated approach ensures that both departments work synergistically to address DORA's requirements, streamlining efforts and enhancing the organization's overall operational resilience. HOPEX's dashboards and reporting tools offer executives and senior management real-time insights into compliance status, risk levels, and resilience capabilities, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Summary
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) ushers in a new era for Compliance and IT departments within financial institutions, challenging them to elevate their game in the face of stricter compliance and resilience demands.
As these departments navigate the complexities of adhering to DORA's stringent regulations, they find an ally in HOPEX. This powerful suite of software solutions becomes a beacon, guiding organizations through the murky waters of compliance, risk management, and operational resilience. By fostering a symbiotic relationship between Compliance and IT teams, HOPEX helps institutions comply with DORA and empowers them to strengthen their defenses against cyber threats.
With HOPEX, the journey towards achieving digital operational resilience under DORA's watchful eyes becomes less daunting, transforming regulatory challenges into opportunities for strategic enhancement.
FAQs
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is an EU regulation that enhances operational resilience for the financial sector. It imposes requirements on financial institutions and ICT systems, aiming to ensure the resilience of critical functions by January 2025. Read: DORA EU
Third-party ICT service providers must ensure compliance with the provisions of DORA to support critical or essential functions for financial institutions and manage ICT risks effectively.
DORA sets requirements for ICT risk management and operational resilience in the financial sector, necessitating robust governance practices and risk management processes to enhance digital operational resilience.
Compliance and IT departments should focus on understanding the scope of DORA, the digital operational resilience testing requirements, and the obligations for compliance with EU legislation related to network and information systems.
Strengthen cyber resilience with an integrated solution

A five-step approach to strengthen your company's cyber resilience, offering key benefits:
- Protect organizations from cyber disruptions
- Comply with cyber resilience regulations
- Align cyber resilience management with business objectives
- Maintain a proactive cyber resilience stance
Governance, Risk and Compliance Related Content
Enhance operational resilience using integrated risk management
MEGA HOPEX for GRC
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for GRC, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.