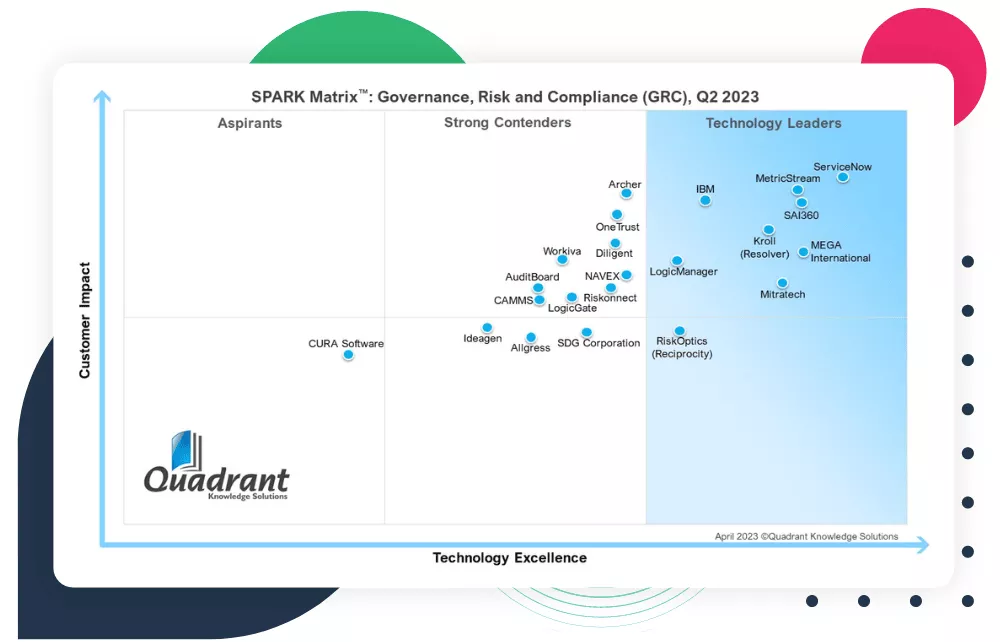
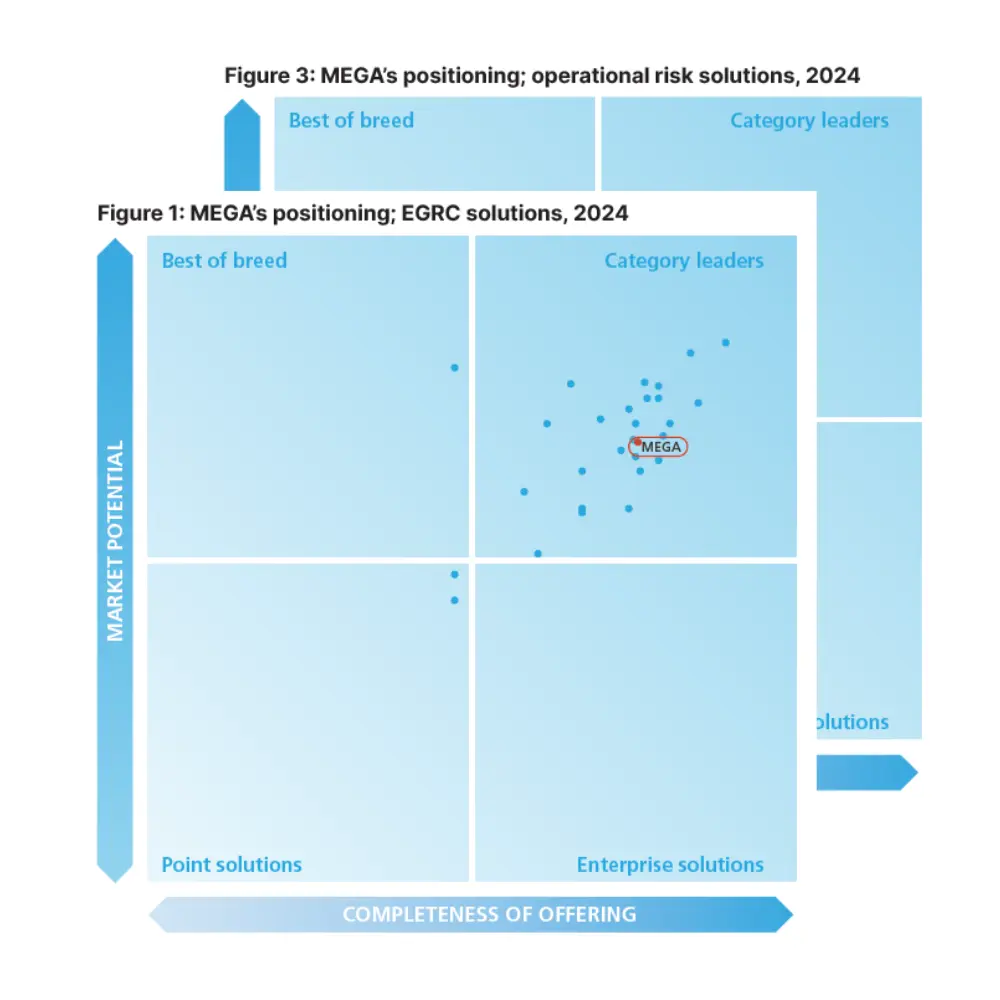
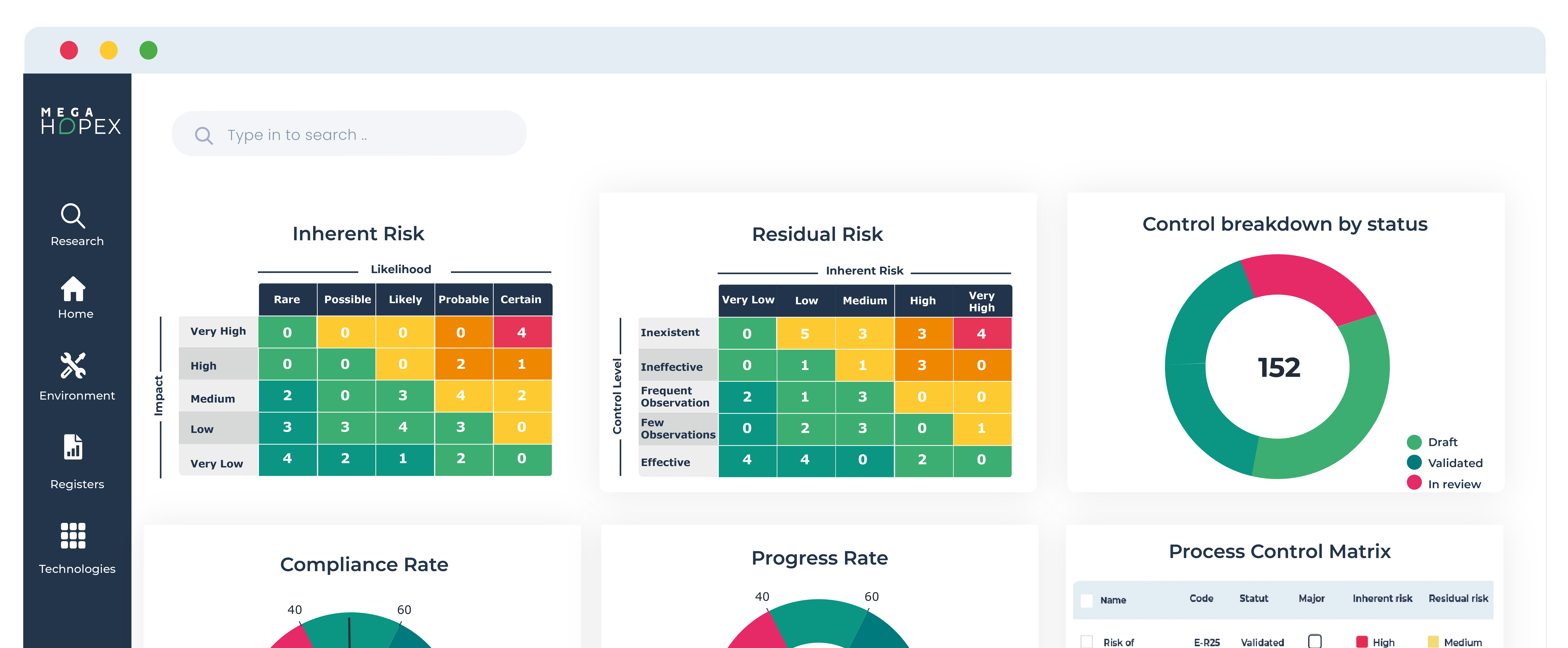
Risk Management: An Essential Practice for Success
Effective risk management is essential for any business or organization to thrive and succeed. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that may impact achieving objectives. This article will explore the concept of risk management, its importance, and how to manage risk effectively.
What is Risk Management?
According to ISO 31000, risks are the effect of uncertainty on objectives. Therefore, the primary aim of risk management is to enhance decision-making processes, protect assets, and reduce potential losses or adverse consequences to reach organizational goals.
It encompasses a systematic and proactive approach to identifying, assessing, responding to, and monitoring risks across various areas such as finance, operations, environment, safety, and reputation. Effective risk management involves establishing risk management strategies, implementing risk control measures, and regularly reviewing and updating risk management processes.
Why is Risk Management Important?
Effective risk management is crucial in various industries and sectors to ensure the success and sustainability of businesses. It helps organizations proactively identify potential threats and take appropriate measures to avoid or minimize their impact. By managing risks effectively, businesses can safeguard their reputation, enhance stakeholder confidence, improve decision-making, and increase long-term profitability.
Risk Management Techniques
There are several techniques and strategies used to mitigate risks. Risk avoidance involves eliminating activities or situations that may pose significant risks. Risk reduction focuses on minimizing the likelihood or impact of identified risks through implementing control measures.
Risk transfer involves transferring the financial burden of a risk to a third party, such as through insurance. Deploying appropriate risk management techniques is essential to safeguard an organization's interests effectively.
How to Manage Risk
Managing company risks involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring potential risks that could impact the organization's operations, finances, reputation, and other aspects. Here's a step-by-step summary of how to manage risks effectively:
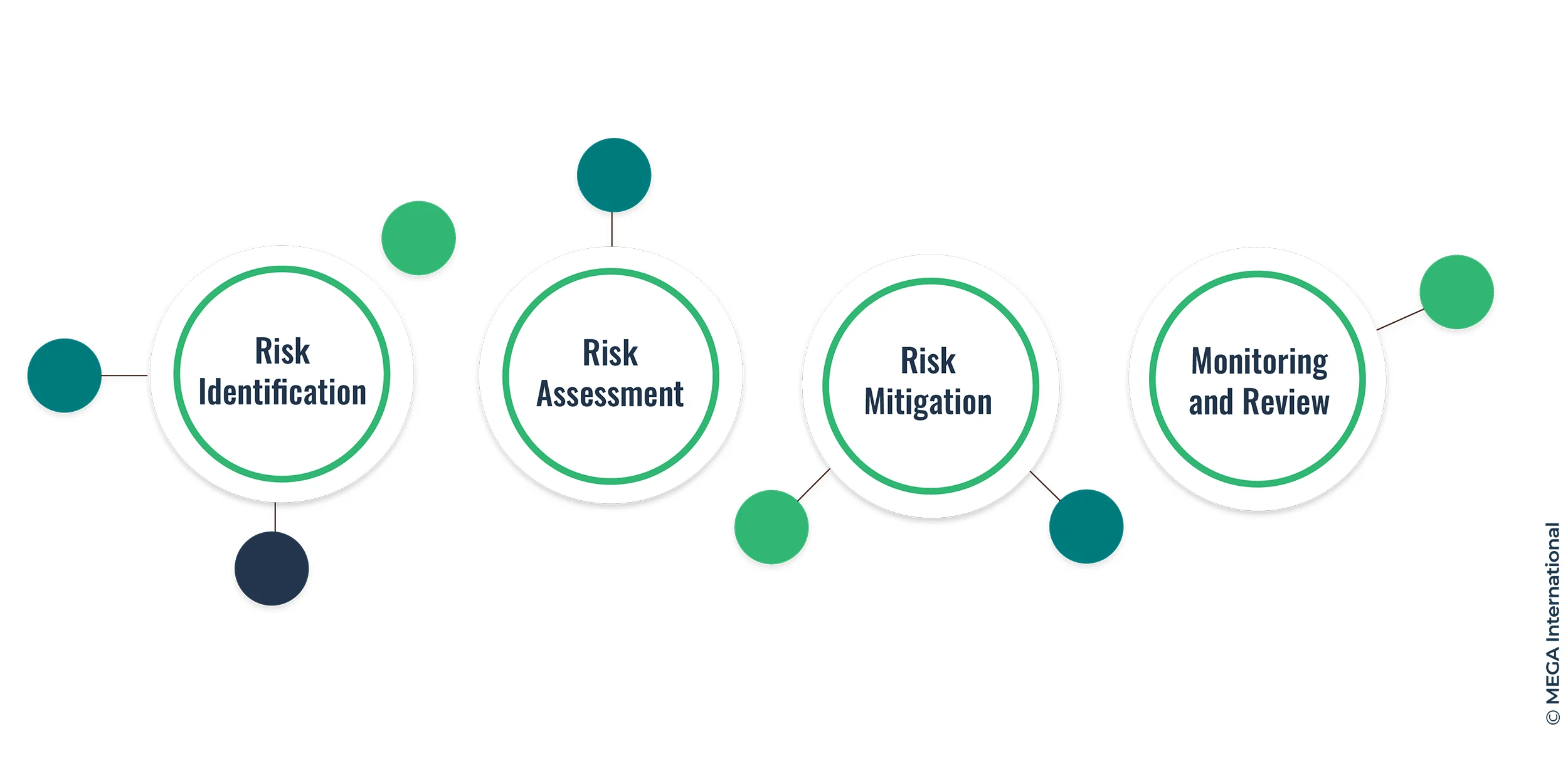
1. Risk Identification
The first step in managing risk effectively is identifying potential risks your organization might face. This involves thoroughly analyzing internal and external factors that could disrupt your business operations. Conducting regular risk assessments, brainstorming sessions, and utilizing data analytics can aid in recognizing these risks.
This process helps understand the organization's risk profile and enables decision-makers to allocate resources accordingly.
2. Risk Assessment
Once you've identified potential risks, the next step is to assess their potential impact and likelihood. This helps prioritize risks based on their severity and the probability of occurrence. A risk matrix or similar tools can assist in categorizing risks as high, medium, or low priority, enabling you to allocate resources appropriately.
3. Risk Mitigation
Mitigation strategies involve developing plans to minimize the impact of identified risks. This could include implementing preventive measures, creating contingency plans, or transferring the risk through insurance. By having a well-defined mitigation strategy, you can effectively reduce your organization's vulnerabilities.
4. Monitoring and Review
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires constant monitoring and review. Regularly assessing the effectiveness of your risk management strategies allows you to adapt to changing circumstances and identify new risks that may emerge over time.
What are the different types of risk?
Risks can manifest in various forms and can be categorized into different types. For example, operational risk refers to the potential losses arising from internal or external operational failures, such as process errors or system malfunctions. Financial risk encompasses risks associated with financial transactions and market fluctuation. Strategic risk involves risks related to an organization's long-term goals and plans…
Organizations can tailor their risk management strategies by understanding the different types of risks.
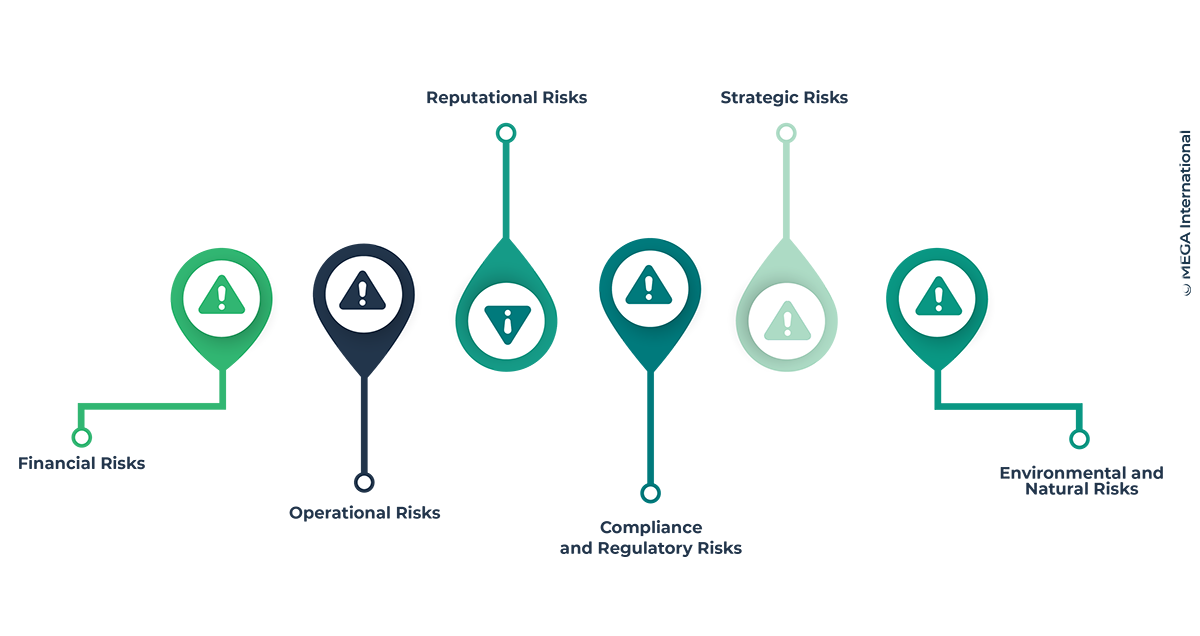
1. Financial Risks
Financial risks pertain to the potential for financial loss due to market fluctuations, economic downturns, or poor financial management. These risks include:
- Market Risk: The risk of financial losses due to changes in market prices of assets, such as stocks, commodities, and currencies.
- Credit Risk: The risk of loss arising from the failure of a customer, supplier, or other counterparty to fulfill their contractual obligations. This can lead to non-payment for goods or services provided.
- Interest Rate Risk: The risk that fluctuations in interest rates can impact borrowing costs and investment returns.
- Liquidity Risk: The risk of being unable to meet short-term financial obligations due to a lack of available funds or the inability to convert assets into cash quickly.
2. Operational Risks
Operational risks arise from inadequate internal processes, systems, and human errors. These risks include:
- Process Failures: Inefficiencies or breakdowns in operational processes that can impact service delivery or product quality.
- Human Error: Mistakes made by employees that can lead to operational disruptions or financial losses.
- Technological Failures: Malfunctions or breakdowns in technology systems, leading to service interruptions and data breaches.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters, geopolitical events, or supplier failures.
3. Reputational Risks
Reputational risks relate to damage to an organization's reputation, brand image, or public perception. These include:
- Public Relations Crises: Negative publicity, scandals, or controversies that can tarnish an organization's image.
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Poor customer experiences lead to negative reviews, reduced loyalty, and potential brand erosion.
- Social Media Backlash: Viral negative feedback or misinformation spread through social media platforms.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Risks
Compliance and regulatory risks emerge from failure to adhere to laws, regulations, and industry standards. These risks encompass:
- Legal Penalties: Financial or legal consequences due to non-compliance with laws and regulations.
- Data Privacy Breaches: Violation of data protection laws, leading to fines and reputational damage.
- Ethical Violations: Actions that go against ethical norms and values, leading to public outrage and legal consequences.
5. Strategic Risks
Strategic risks arise from poor strategic decisions, changes in market dynamics, or inadequate adaptation to industry trends. These risks include:
- Competitor Risks: The impact of aggressive competition or the emergence of disruptive competitors.
- Market Shifts: Changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, or economic shifts that render existing strategies obsolete.
- Innovation Failure: Investing in unsuccessful innovation efforts that don't yield anticipated results.
6. Environmental and Natural Risks
Environmental and natural risks are associated with the impact of environmental factors on an organization. These risks include:
- Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires that can damage facilities and disrupt operations.
- Climate Change Impact: Risks arising from changing climate patterns, resource scarcity, and regulatory changes related to environmental concerns.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
Let's outline the best practices that organizations should adopt to ensure they are well-prepared to navigate the ever-changing landscape of risks.

- Establish a Risk-Aware Culture
Cultivating a risk-aware culture is the cornerstone of effective risk management. All organization members, from leadership to employees, should be encouraged to identify and report potential risks without fear of repercussions. Open communication channels foster early risk detection and enable timely intervention.
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Regular and thorough risk assessments are vital for identifying potential threats. These assessments involve evaluating internal and external factors that could impact the organization. Collaborate with cross-functional teams to comprehensively understand risks across all departments.
- Prioritize Risks Strategically
Not all risks are created equal. Prioritization is critical to resource allocation. Implement a risk scoring system that considers each risk's potential impact and likelihood. This allows organizations to focus on addressing high-priority risks that could have the most significant consequences.
- Develop Clear Mitigation Strategies
Mitigation strategies are the backbone of risk management. Develop detailed plans to address identified risks. These plans should outline preventive measures, contingency plans, and risk transfer strategies. Each strategy should have clear action steps, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Monitor and Review Continuously
Risk management is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your mitigation strategies and update them as needed. Stay attuned to changes in the business environment and emerging risks that may require adjustments to your approach.
- Embrace Technology
Leverage technology to enhance risk management capabilities. Utilize risk management software, data analytics tools, and predictive modeling to identify patterns, forecast potential risks, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Risks often transcend departmental boundaries. Encourage collaboration among different departments to gain diverse perspectives on risks. This ensures a more comprehensive understanding of potential threats and effective implementation of mitigation strategies.
- Provide Ongoing Training
Equip your employees with the knowledge and skills needed for effective risk management. Regular training sessions on risk identification, assessment, and response ensure that everyone in the organization is proactive in mitigating risks.
- Encourage Scenario Testing
Simulating potential risk scenarios allows organizations to test the effectiveness of their mitigation plans. Scenario testing helps identify gaps, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement in your strategies.
- Engage Leadership Support
Leadership buy-in is critical for successful risk management implementation. When leaders prioritize risk management and allocate necessary resources, it reinforces the importance of this practice throughout the organization.
- Stay Informed About Industry Trends
Stay updated about industry trends, regulatory changes, and emerging risks specific to your sector. This knowledge enables you to address risks that could impact your organization proactively.
- Learn From Past Incidents
Analyze past incidents and near misses to understand their root causes. Use these insights to refine your risk management strategies and prevent similar incidents in the future.
Benefits of Effective Risk Management
Implementing robust risk reduction strategies offers a range of advantages:
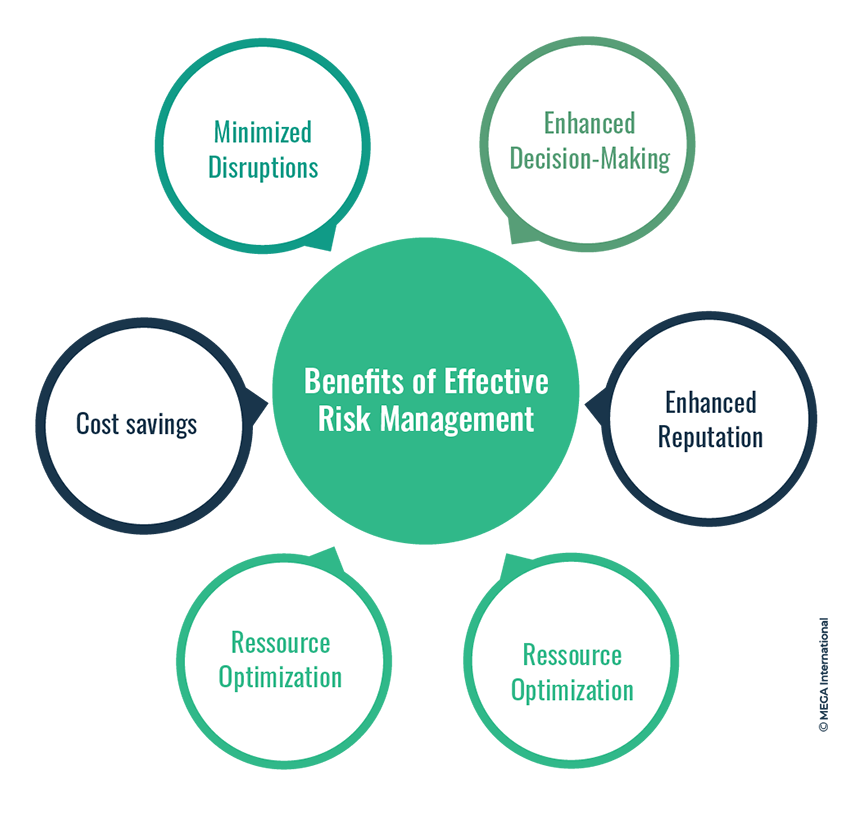
- Minimized Disruptions: Proactive measures reduce the likelihood of disruptions to your operations.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: A thorough understanding of risks allows companies to make informed decisions. They can better assess the potential outcomes of different choices and allocate resources more effectively.
- Cost Savings: Preventing risks is often more cost-effective than dealing with their consequences.
- Enhanced Reputation: Effective risk reduction demonstrates your commitment to safeguarding stakeholders' interests.
- Operational Continuity: Well-prepared organizations can maintain business continuity even when facing challenges.
Summary
Embracing effective risk management is a proactive investment in the resilience and longevity of your organization. You can strategically navigate potential risks and uncertainties through a comprehensive approach, including risk identification, assessment, mitigation, and monitoring.
Incorporate risk management as an integral aspect of your organizational culture. Doing so will bolster your market position, foster stakeholder confidence, and confidently navigate the intricate business landscape. A robust risk management strategy empowers you to make well-informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and seize growth opportunities while preserving your assets and upholding your reputation.
FAQs
Risk management identifies, assesses, and prioritizes risks to minimize their adverse impacts on a project or organization.
Operational risk refers to the potential loss or harm that can arise from an organization's internal processes, systems, or procedures.
Some risk management techniques include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, risk acceptance, and risk sharing.
Risk management can reduce risk by implementing preventive measures, creating an action plan, and implementing controls and safeguards to minimize the likelihood and impact of a risk event.
A risk event is a specific occurrence or incident that can potentially cause harm, loss, or damage to an organization.
While risks can be identified and assessed, not all risks can be managed. Some risks may be beyond an organization's control or have significant consequences that cannot be mitigated.
Risk managers are responsible for identifying, assessing, and managing organizational risks. They develop risk management strategies and work with stakeholders to implement and monitor risk management practices.
Risk management requires a systematic and structured approach involving identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. It also requires effective communication and collaboration among project teams and stakeholders.
A risk officer oversees and coordinates an organization's risk management activities. They develop risk management policies, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and advise senior management on risk-related matters.
Ensure efficient risk management and operational resiliency
Governance, Risk and Compliance Related Content
Enhance operational resilience using integrated risk management
MEGA HOPEX for GRC
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for GRC, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.