Application Portfolio Assessment Introduction and Best Practices
An application portfolio is a collection of an organization's software applications. It includes both the applications that are developed in-house as well as the ones that are purchased from external sources.
Managing this portfolio effectively is crucial for organizations to optimize their resources, improve efficiency, and align their IT investments with business goals. With rapid technological advancements, regular application portfolio assessment has become imperative to stay competitive in the ever-evolving market.
What is an Application Portfolio?
Understanding the concept of application portfolio
An application portfolio comprises all the software applications in an organization, serving various functions, departments, and business processes. It provides a comprehensive view of the application landscape and helps evaluate the effectiveness and suitability of each application for the organization's needs.
Components of an application portfolio
The first component of an application portfolio is the strategic roadmap, which outlines the overall direction and priorities for the applications within the portfolio. This helps organizations identify which applications are necessary for their operations and which can be retired or replaced.
The second component is the application inventory, which provides a comprehensive list of all the applications within the portfolio. This includes the application name, version, vendor, and the business function it supports. The inventory also contains details on the application lifecycle, including its planned retirement or replacement date.
The third component is the application architecture, which describes how the applications within the portfolio are structured and how they integrate. This includes information on the underlying technologies, the data flows between applications, and any interfaces or integration points that must be maintained.
The fourth component is the application performance and usage data, which provides insights into how the applications perform and are used. This includes metrics such as response time, system availability, and user adoption rates. This data can help organizations identify areas for improvement and optimize their application portfolio.
The fifth component is the application governance framework, which outlines the policies, processes, and procedures for managing and maintaining the applications within the portfolio. This includes guidelines for application development, testing, deployment, and support. It also includes protocols for monitoring and controlling application access and security.
Benefits of Managing Your Application Portfolio
One of the main reasons why managing an application portfolio is essential is that it enables organizations to make informed decisions about which applications to invest in, maintain, or retire. By regularly reviewing and assessing the applications in their portfolio, organizations can identify redundant or outdated applications that no longer provide value or support their business needs. This allows them to reallocate resources and investments toward more strategic applications that drive innovation and growth.
Also, by managing an application portfolio, organizations can proactively address security vulnerabilities, implement necessary patches and updates, and minimize the risk of data breaches or other security incidents.
Why is Application Portfolio Assessment Important?
Managing an application portfolio is crucial for organizations to prioritize, analyze, and align their software applications with their overall business goals and objectives.
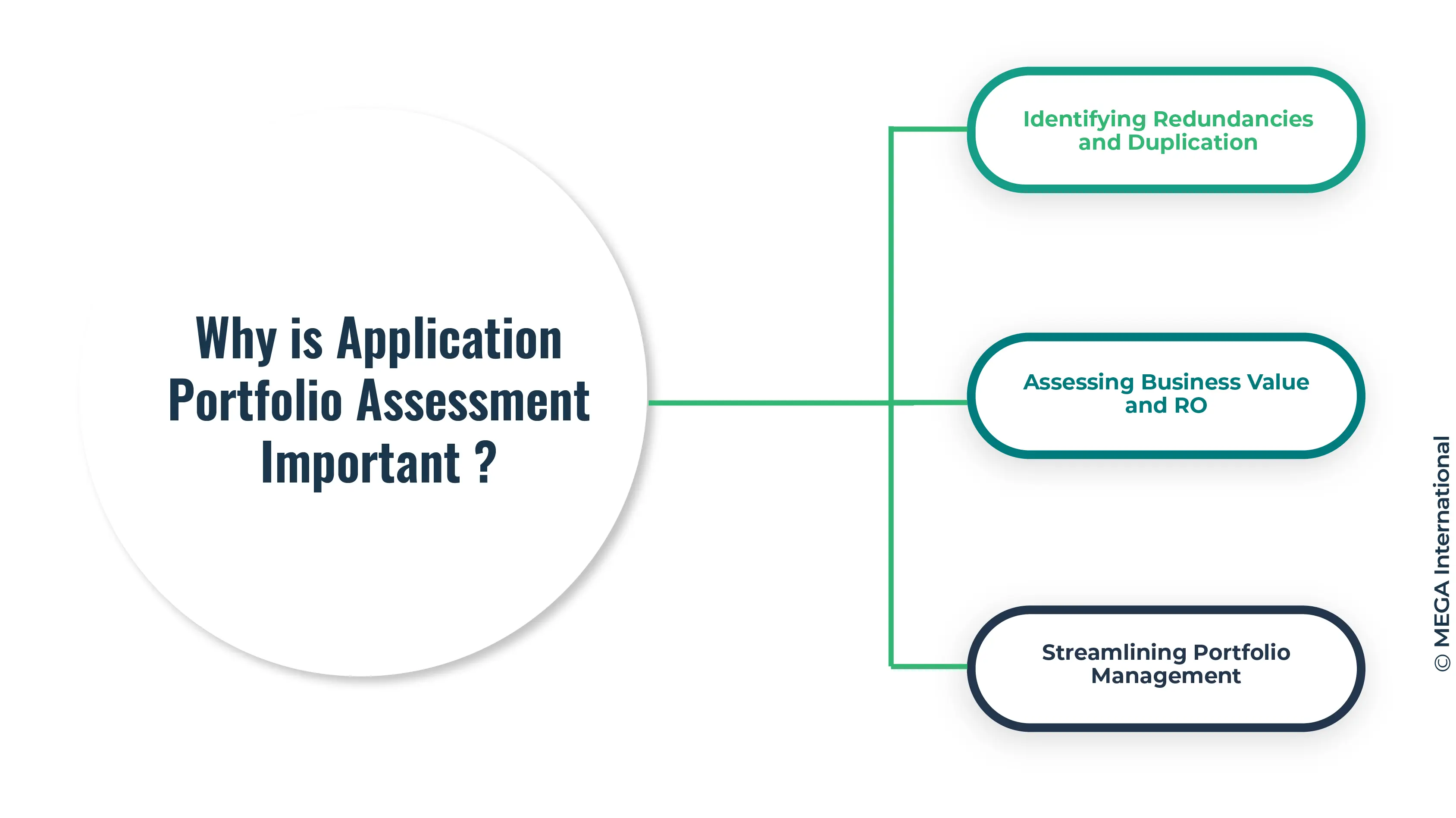
Identifying Redundancies and Duplication
One critical reason for conducting an application portfolio assessment is to identify redundancies and duplications in the application landscape. Organizations can eliminate unnecessary applications by evaluating each application's functionality and usage, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
Assessing Business Value and ROI
Another critical aspect of application portfolio assessment is evaluating each application's business value and return on investment (ROI). By understanding the business capabilities supported by each application, organizations can prioritize their assets and ensure that the applications deliver value in line with their strategic objectives.
Streamlining Portfolio Management
An application portfolio assessment gives organizations a clear view of their application landscape. This enables them to streamline their portfolio management activities by categorizing applications based on usage, criticality, and modernization potential. It helps organizations decide which applications to prioritize for further investment, modernization, or retirement.
How to Perform an Application Portfolio Assessment?
The application portfolio assessment starts by systematically evaluating an organization's application landscape to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and areas for improvement. This journey comprises several interconnected steps that guide the assessment from initiation to actionable insights.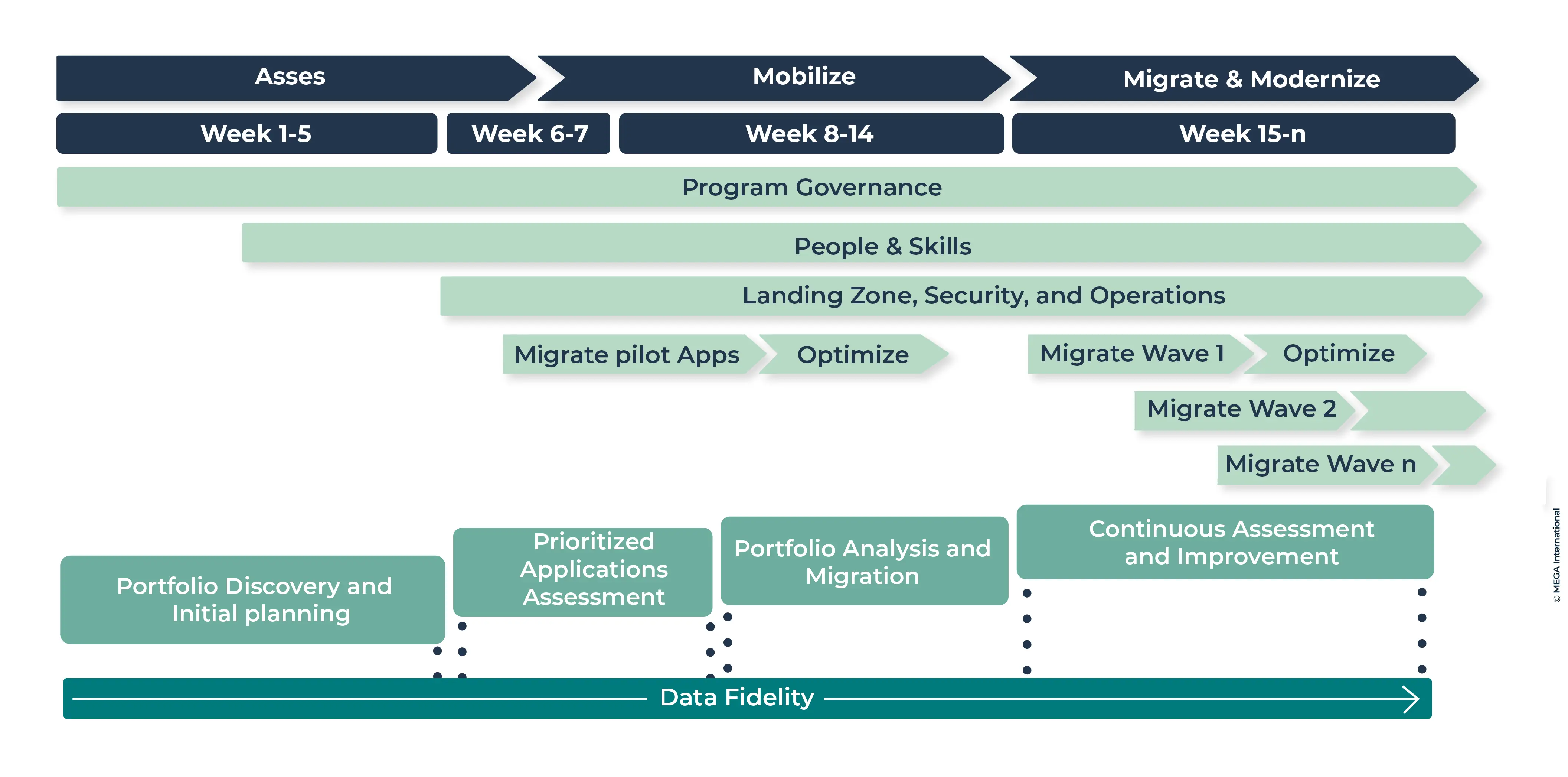
1. Define Assessment Objectives
Clearly articulate the goals and objectives of the assessment. Determine whether the focus is on cost reduction, alignment with business goals, technical health, or a combination of factors.
2. Establish a Cross-Functional Team
Form a diverse team with representatives from IT, business units, development, operations, and other relevant departments. This ensures comprehensive insights and diverse perspectives.
3. Inventory Applications
Compile a comprehensive list of all applications within the portfolio. This includes large systems, small tools, custom applications, and third-party solutions. This inventory should contain detailed information about each application, including its functionality, usage, dependencies, and ownership.
4. Conducting a Portfolio Analysis
Once the application inventory is created, organizations can conduct a portfolio analysis to evaluate each application's business value, costs, risks, and modernization potential, including its purpose, functionality, user base, technical architecture, dependencies, integration points, and usage patterns. This analysis helps identify redundant, outdated, or underperforming applications that can be rationalized or retired.
5. Assess Technical Health
Evaluate the technical health of applications, including their architecture, performance, security, scalability, and maintenance requirements.
6. Prioritize Applications
Rank applications based on business value, technical complexity, security vulnerabilities, and alignment with strategic objectives.
7. Identify Pain Points
Pinpoint bottlenecks, redundancies, inefficiencies, and challenges within the application portfolio must be addressed.
8. Assessing the Modernization Potential
As part of the portfolio analysis, organizations should assess the modernization potential of their applications. This involves evaluating whether the application supports the latest technology standards and aligns with the organization's future needs. Organizations can plan their modernization roadmap and allocate resources by identifying applications that require modernization.
9. Quantify Business Value
Assign quantifiable metrics to measure the business value of each application, such as revenue generation, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.
10. Develop Optimization Strategies
Formulate strategies for optimizing the application portfolio, which may include retiring obsolete applications, consolidating functionalities, migrating to the cloud, or enhancing user experience.
11. Create an Implementation Roadmap
Design a roadmap that outlines the actions to be taken, along with timelines, resource allocation, and expected outcomes.
12. Engage Stakeholders
Communicate assessment findings, recommendations, and the implementation roadmap to key stakeholders, garnering their buy-in and support.
13. Implement Changes
Execute the optimization strategies according to the roadmap, ensuring each step is carefully planned, communicated, and monitored.
14. Monitor Progress
Continuously monitor the progress of optimization efforts, track key performance indicators, and make necessary adjustments based on real-time insights.
15. Iterate and Improve
Periodically revisit the application portfolio assessment process, incorporating feedback, adapting to changing business needs, and ensuring continuous improvement.
Recap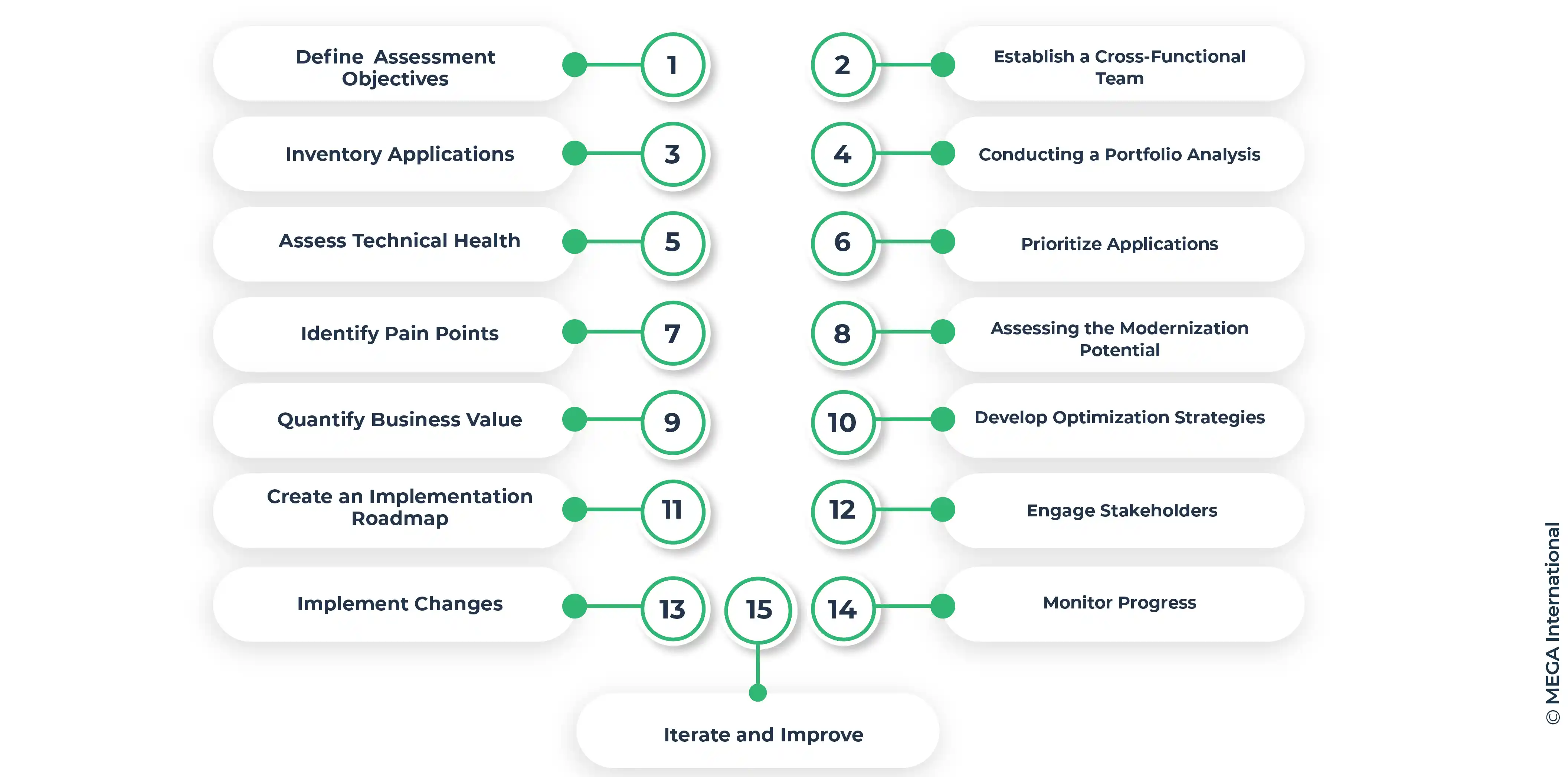
How Does Application Portfolio Assessment Help Reduce IT Costs?
Identifying Costly Dependencies
An application portfolio assessment helps organizations identify costly dependencies between applications. By understanding the interdependencies, organizations can adopt strategies to minimize these dependencies and reduce the associated costs.
Streamlining and Optimizing Applications
Through application portfolio assessment, organizations can identify opportunities for streamlining and optimizing applications. By consolidating similar applications, organizations can eliminate redundancies and achieve cost savings by reducing licensing, maintenance, and support costs.
Validating the Rationalization Process
Application portfolio assessment provides organizations with data-driven insights that validate the rationalization process. By assessing each application's business value, costs, and risks, organizations can justify their rationalization efforts and gain stakeholder support for optimizing the application portfolio.
How Can HOPEX Assist in Application Portfolio Assessment?
The HOPEX platform provides various tools and features to assist in application portfolio assessment. Here are some ways HOPEX can help with this:
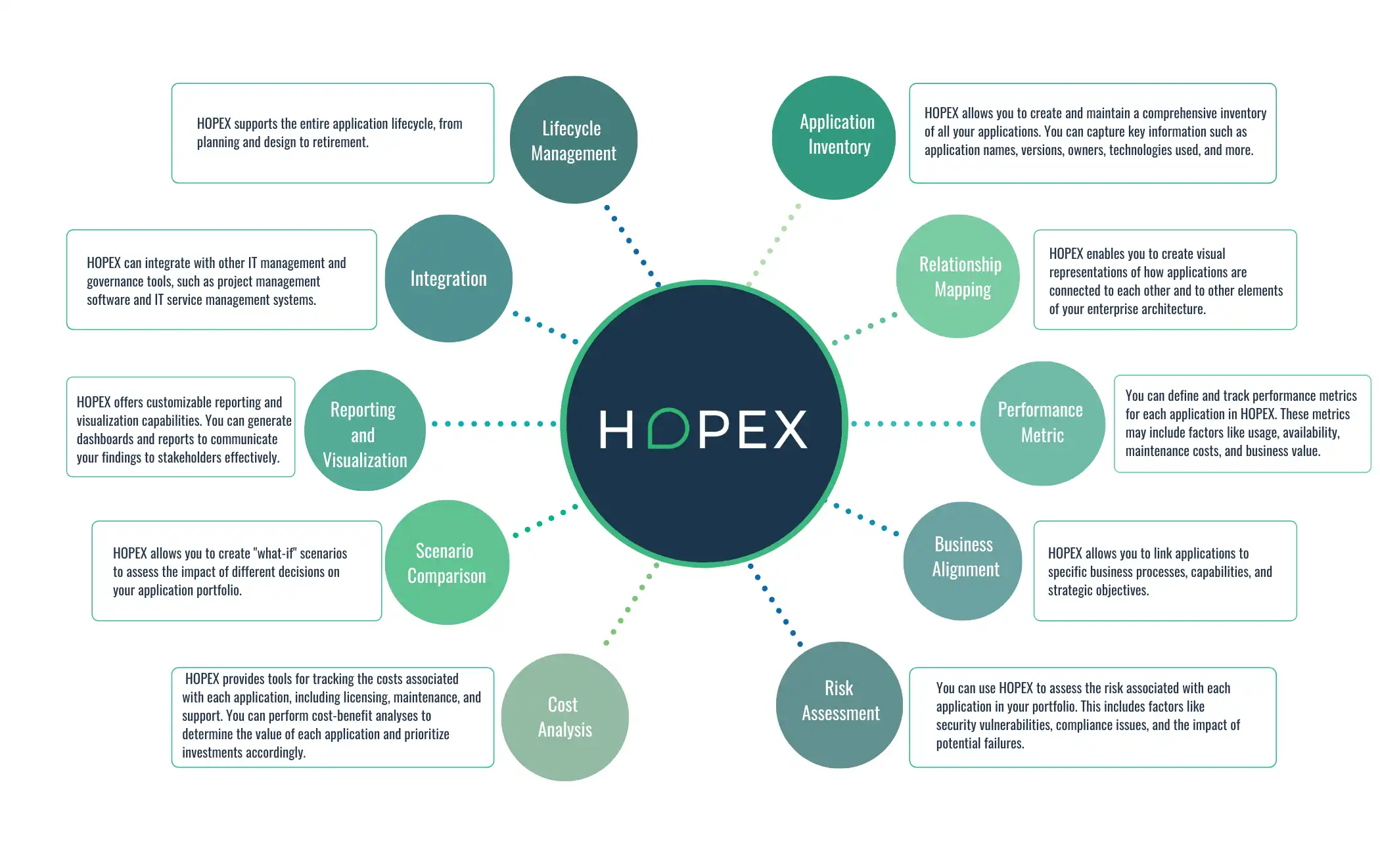
Application Inventory:
HOPEX allows you to create and maintain a comprehensive inventory of all your applications. You can capture critical information such as application names, versions, owners, technologies, etc. This inventory forms the foundation for your application portfolio assessment.
Relationship Mapping:
HOPEX lets you visualize how applications are connected to other elements of your enterprise architecture. This helps you understand the dependencies between different applications and their relationships with processes, capabilities, technologies, and data, which is crucial for portfolio assessment.
Performance Metrics:
You can define and track performance metrics for each application in HOPEX. These metrics may include usage, availability, maintenance costs, and business value. By collecting and analyzing this data, you can assess the performance of each application in your portfolio.
Business Alignment:
HOPEX allows you to link applications to specific business processes, capabilities, and strategic objectives. This helps you evaluate how well your application portfolio aligns with your business goals and identify gaps or redundancies.
Risk Assessment:
You can use HOPEX to assess the risk associated with each application in your portfolio. This includes security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and potential failure impact. Identifying and mitigating these risks is a critical part of portfolio assessment.
Cost Analysis:
HOPEX provides tools for tracking the costs associated with each application, including licensing, maintenance, and support. You can perform cost-benefit analyses to determine each application's value and prioritize investments accordingly.
Scenario Comparison:
HOPEX allows you to create "what-if" scenarios to assess the impact of different decisions on your application portfolio. For example, you can simulate the effects of retiring or replacing specific applications to make informed decisions.
Reporting and Visualization:
HOPEX offers customizable reporting and visualization capabilities. You can generate dashboards and reports to communicate your findings effectively to stakeholders, and visualizations can help convey complex information in a digestible format.
Integration:
HOPEX can integrate with other IT management and governance tools, such as project management software and IT service management systems. This integration streamlines data exchange and ensures your application portfolio assessment is based on up-to-date information.
Lifecycle Management:
HOPEX supports the entire application lifecycle, from planning and design to retirement. This means you can assess your current portfolio and plan for the future by aligning application investments with your organization's strategic goals.
HOPEX provides comprehensive tools and features to assist in application portfolio assessment. It helps you capture, analyze, and visualize data about your applications and their relationships with other elements of your enterprise architecture.
Start today with the HOPEX Platform.
Why should you assess your application portfolio?
Assessing your application portfolio is crucial to effectively managing and optimizing your technology investments. By periodically evaluating the applications within your portfolio, you can gain valuable insights into their performance, cost, and alignment with your business goals.
Assessing your application portfolio allows you to identify consolidation, standardization, and modernization opportunities. By consolidating similar applications and reducing redundancies, you can streamline your operations and reduce costs. Standardization helps to improve interoperability and simplify maintenance, while modernization enables you to leverage the latest technologies and enhance overall performance.
Signs that your application portfolio needs assessment
There are several signs that your application portfolio may need evaluation. Let's cover the main ones:
- Performance Issues: Frequent crashes, slow response times, or other performance problems can indicate that your applications are not functioning optimally.
- Outdated Technology: If your applications are built on outdated technology or rely on obsolete frameworks, they may need help to keep up with modern security and functionality standards.
- Security Concerns: Increasing cybersecurity threats requires regular assessment of your applications' security measures to ensure they are robust against potential breaches.
- User Complaints: If users are consistently reporting issues, complaints, or difficulty using your applications, it's a sign that there might be usability or functionality problems that need attention.
- Lack of Integration: Inefficient communication between applications or difficulty sharing data between them can hinder business processes and productivity.
- High Maintenance Costs: If maintenance costs are escalating due to frequent bug fixes and updates, it might be time to assess whether a redesign or replacement is more cost-effective.
- Incompatibility with Devices: With the various devices available today, applications should be compatible and responsive across different platforms and screen sizes.
- Poor User Experience: A clear or updated user interface can decrease user satisfaction and engagement.
- Business Strategy Changes: If your organization's goals, objectives, or business strategies have shifted, your applications may need to be aligned accordingly.
- Market Trends: Keeping up with industry trends and competitors is essential. If your applications meet the evolving needs of your target audience, you can retain market share.
- Scalability Issues: If your applications struggle to handle increased loads or demand, it might be time to assess their scalability and optimize accordingly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Changes in regulations or compliance standards may require updates to your applications to ensure they meet the necessary legal requirements.
- Redundant Functionality: If you have multiple applications with overlapping features, consolidating or streamlining them could be more efficient.
- Data Management Challenges: Difficulties in managing, processing, or extracting insights from application data can hinder decision-making processes.
- Vendor Support: If the vendors providing tools, frameworks, or components for your applications no longer offer support or updates, it could threaten your application's stability and security.
Bottlenecks and pain points in your application portfolio
Identifying bottlenecks and pain points in your application portfolio ensures optimal performance and user satisfaction. In an ever-evolving technological landscape, organizations continuously strive to enhance their application portfolios to meet the changing needs of their customers.
However, without a thorough understanding of the underlying bottlenecks and pain points, any attempts at improvement may prove futile. One of the first steps in identifying these issues is conducting a comprehensive application portfolio assessment.
This assessment involves evaluating the performance and functionality of each application in the portfolio and identifying any areas of inefficiency or user dissatisfaction. It is important to include stakeholders from various departments to gather a holistic perspective on the pain points experienced by different user groups.
Once the pain points are identified, the next step is to prioritize them based on their impact on the overall user experience and business goals.
This involves analyzing various metrics such as response times, error rates, and user feedback.
Organizations can allocate their resources effectively by prioritizing the bottlenecks and pain points, ensuring that the most critical issues are addressed first.
After prioritization, a detailed root cause analysis is essential to understand the underlying reasons for these pain points.
This analysis may examine the applications' architecture, infrastructure, codebase, or user interface. It is also essential to consider external factors such as network congestion or hardware limitations that may contribute to these issues.
Once the root causes are identified, organizations can implement targeted solutions to mitigate these bottlenecks. This may involve optimizing performance, refactoring code, upgrading hardware, or redesigning user interfaces. Regular monitoring and ongoing assessment of the application portfolio are crucial to identify any new bottlenecks or pain points that may arise.
By proactively addressing these issues, organizations can ensure that their application portfolio remains current and meets users' expectations.
Read More about APM
Common challenges in application portfolio assessment
Challenges that organizations often encounter during application portfolio assessment, shedding light on the complexities and offering insights to overcome them effectively:
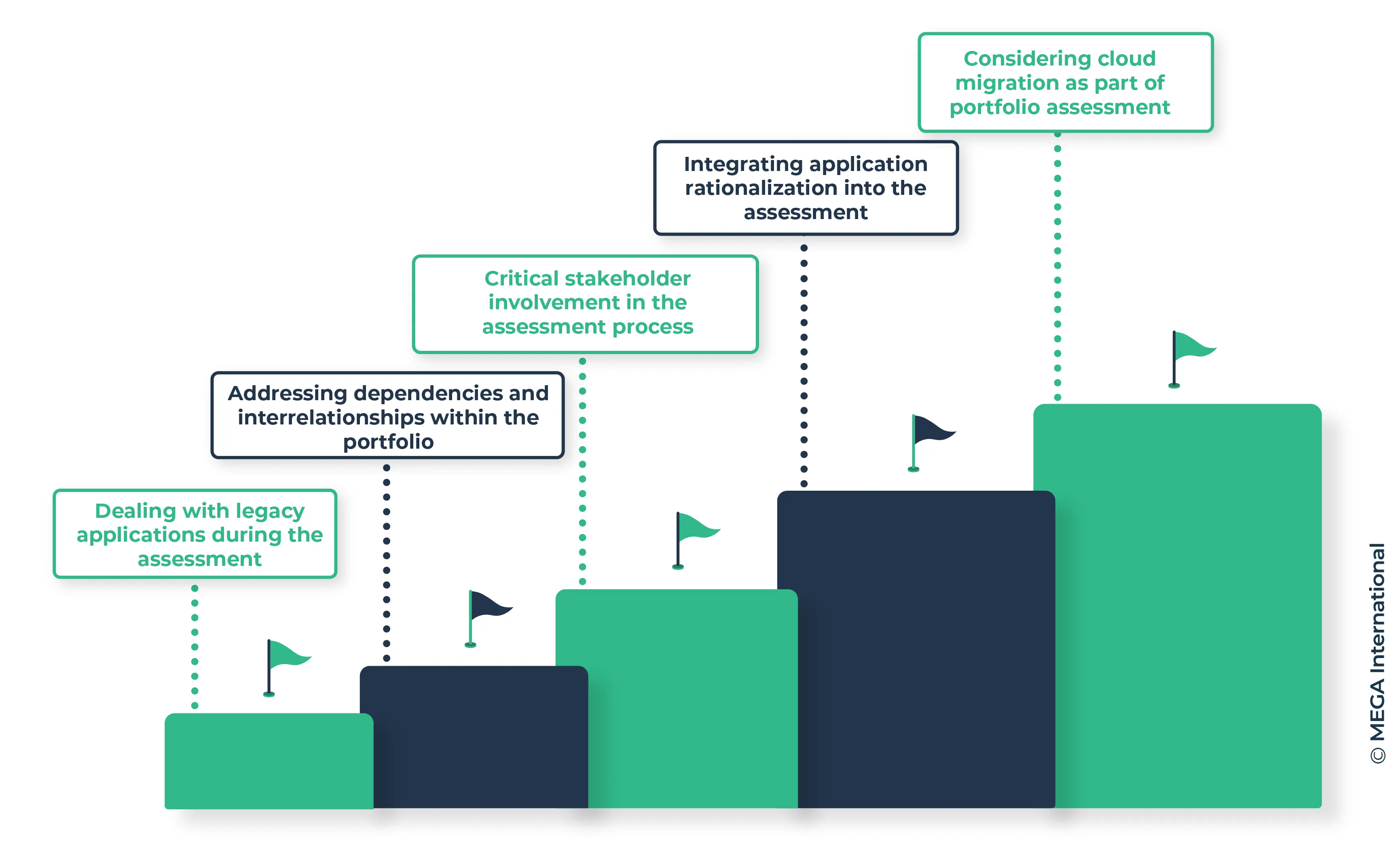
Dealing with legacy applications during the assessment
When assessing legacy applications, it is essential to approach the process systematically and thoroughly. Legacy applications are often outdated and complex and can contain hidden issues or vulnerabilities. It is crucial to begin the assessment by gathering all relevant documentation and information about the application, such as its purpose, design, and any known issues.
This will help identify potential areas for improvement or modernization. The assessment should also include a comprehensive analysis of the application's codebase, looking for outdated programming languages, deprecated libraries, or security loopholes.
Assessing the application's overall performance and scalability is crucial to determining whether it can handle current and future demands.
Lastly, documenting the assessment findings, including a prioritized list of areas needing attention, will help the development team upgrade or replace the legacy application.
Addressing dependencies and interrelationships within the portfolio
Application portfolios often comprise a complex web of dependencies and interrelationships between various software systems. Understanding and managing these connections is crucial for a comprehensive assessment.
In a portfolio, projects often have interdependencies, where the success of one project depends on the outcome or progress of another project. By understanding and addressing these dependencies, project managers can mitigate risks and ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget. Dependencies can be classified as either internal or external.
Internal dependencies occur between projects within the same portfolio, while external dependencies exist between projects in different portfolios or with external stakeholders. Identifying dependencies requires thoroughly analyzing project requirements, objectives, and milestones.
Once dependencies are identified, project managers can develop a strategy to manage them effectively. This may involve adjusting project timelines, allocating additional resources, or prioritizing specific projects to minimize delays or bottlenecks.
Critical stakeholder involvement in the assessment process
Stakeholder involvement is a crucial factor in the success of any application portfolio assessment. Ensuring that the right stakeholders are engaged throughout the assessment process can be challenging, but it is essential for gaining diverse perspectives, gathering valuable insights, and making well-informed decisions.
Including them in the process allows for their input, concerns, and perspectives to be considered, which can result in more comprehensive and accurate assessments.
Engaging stakeholders also promotes transparency and legitimacy of the assessment, as it demonstrates a commitment to including a range of voices and viewpoints.
Involving stakeholders early in the process can help identify relevant issues and potential impacts, which can inform the assessment scope and methodology.
Integrating application rationalization into the assessment
Application rationalization is a strategic process that involves evaluating and streamlining the application portfolio to optimize costs, improve efficiency, and align with business goals.
Integrating application rationalization into the application portfolio assessment can be challenging, but it's a critical step toward ensuring a cohesive and well-organized software ecosystem.
Considering cloud migration as part of portfolio assessment
The growing adoption of cloud computing has prompted organizations to consider cloud migration as part of their application portfolio assessment. While moving applications to the cloud offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that need careful consideration.
Best practices for Application Portfolio Assessment
To conduct a successful application portfolio assessment, businesses must follow best practices that streamline the assessment process and deliver accurate and actionable insights. Next, we will explore some of the best practices for application portfolio assessment and how they can benefit organizations in optimizing their application landscape and driving business success:
Regularly updating and maintaining the application inventory.
An accurate and up-to-date application inventory is the cornerstone of a successful application portfolio assessment. Regularly updating and maintaining this inventory ensures your organization understands its software ecosystem, enabling informed decision-making, optimization, and alignment with business objectives.
Establishing clear goals and objectives for the assessment
A successful application portfolio assessment begins with well-defined goals and objectives. Clearly outlining what you aim to achieve through the assessment sets the direction for the entire process and ensures that efforts are focused and aligned with organizational priorities.
Aligning the assessment with the organization's business strategy
For a comprehensive and impactful application portfolio assessment, it is essential to ensure that the assessment's goals, methodologies, and outcomes are closely aligned with the organization's overarching business strategy. This alignment not only enhances decision-making but also enables the identification of opportunities to optimize the application portfolio in line with strategic objectives.
Using business value as a key factor in assessing applications
Effective application portfolio assessment goes beyond technical considerations; it involves understanding the business value that each application brings to the organization. By prioritizing applications based on their alignment with business goals, revenue generation, customer satisfaction, and overall strategic impact, organizations can optimize their portfolios for maximum value.
Considering modernization and optimization opportunities
An effective application portfolio assessment identifies current challenges and unveils opportunities for modernization and optimization. By evaluating applications to enhance performance, user experience, and alignment with emerging technologies, organizations can ensure their portfolios remain competitive and responsive to changing business needs.
Identify Regulatory Requirements
Understand the regulatory landscape relevant to your industry and geography. Identify specific compliance standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific regulations.
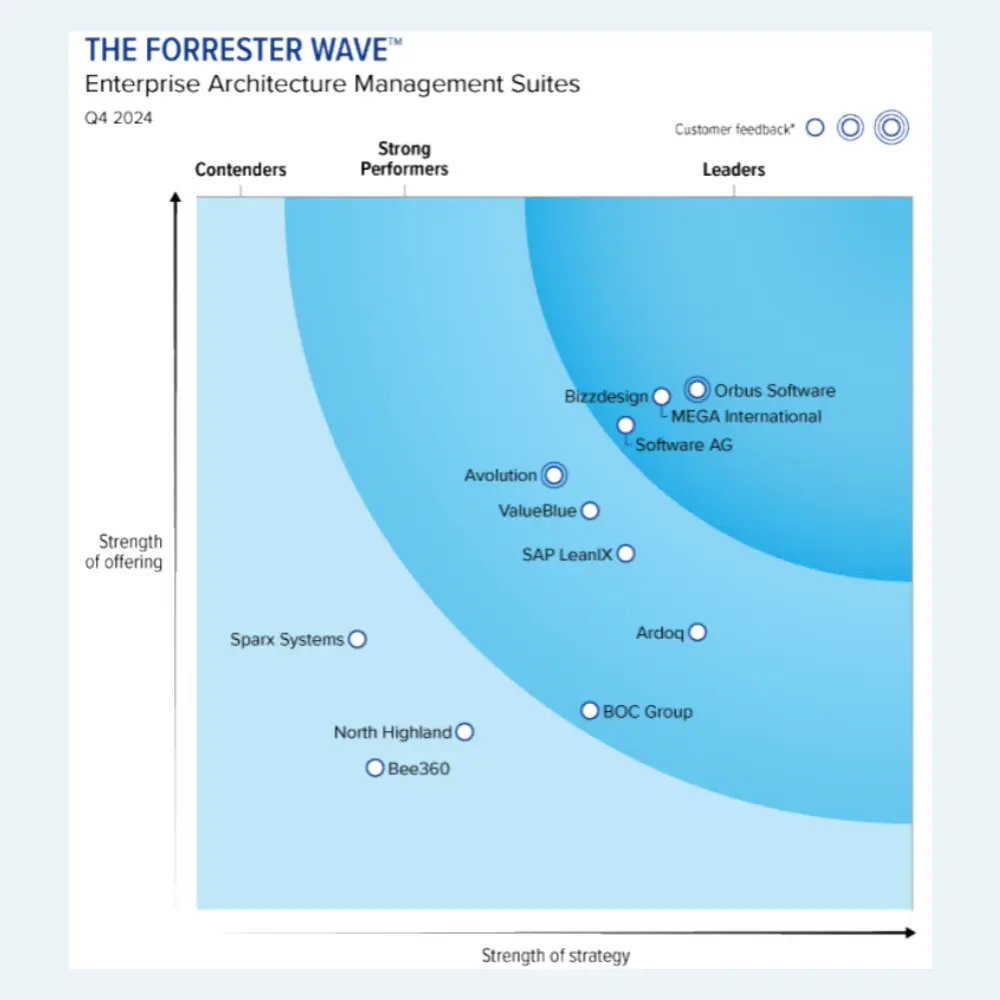
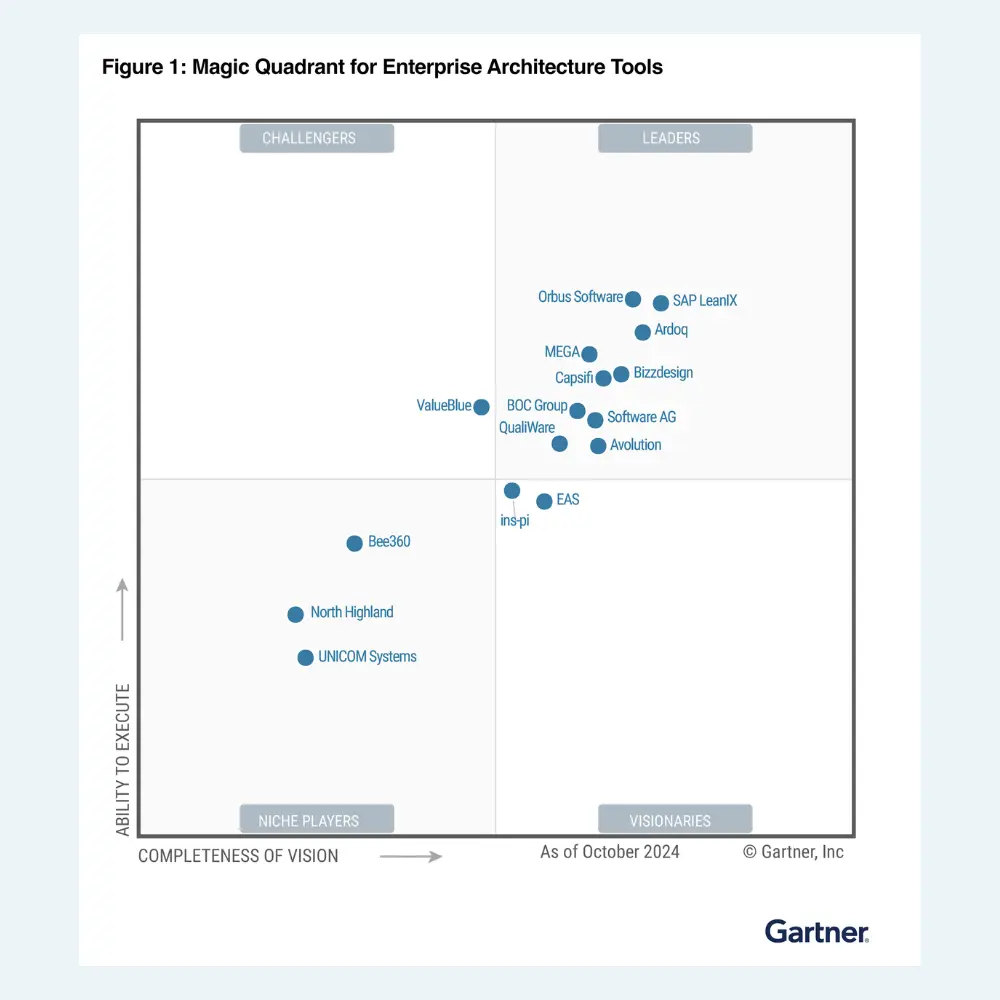
Get a complimentary copy: 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Enterprise Architecture Tools
Assess Data Handling
Evaluate how each application handles sensitive data, including personally identifiable (PII) and financial data. Ensure data encryption, access controls, and proper storage.
Conduct Vulnerability Assessment
Perform application vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify potential security vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit.
Review Authentication and Authorization
Examine applications' authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure only authorized users can access sensitive functionalities and data.
Consider Data Privacy
Assess how applications handle user privacy, including data collection, consent mechanisms, and retention policies.
Evaluate Third-Party Integrations
Review integrations with third-party services and APIs to ensure they follow security best practices and not introduce vulnerabilities.
Implement Secure Development Practices
Ensure that applications are developed using secure coding practices and that developers are trained in security awareness.
Monitor and Respond to Threats
Implement monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. Develop incident response plans to mitigate the impact of breaches.
Secure Data Transfer and Storage
Evaluate how applications transfer and store data, ensuring that encryption protocols are used to protect data both in transit and at rest.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Perform regular security audits on applications to identify potential weaknesses and proactively address them before they can be exploited.
Maintain Patching and Updates
Regularly update applications and underlying components to apply security patches and protect against known vulnerabilities.
Collaborate with Security Teams
Involve your organization's cybersecurity experts in the assessment process to evaluate security risks comprehensively.
Educate Stakeholders
Communicate the importance of security and compliance to all stakeholders, emphasizing the shared responsibility in maintaining a secure application environment.
Develop a Security Roadmap
Based on assessment findings, create a roadmap for addressing security gaps and improving the overall security posture of the application portfolio.
Ensure Compliance Documentation
Document compliance efforts, including policies, procedures, and audit reports, to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
Summary
Implementing an Application Portfolio Assessment is vital for companies and businesses in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape.
This strategic practice offers many benefits, including driving efficiency, enhancing competitiveness, and aligning technology with overarching business goals.
By comprehensively evaluating their application ecosystem, organizations can make informed decisions, optimize resources, and position themselves for sustained growth and success. Learn more about IT Governance.
FAQs
An application portfolio assessment is a process of evaluating and analyzing an organization's collection of applications, commonly known as the application portfolio. It involves reviewing the applications and assessing their business value, performance, dependencies, and alignment with the organization's goals and objectives.
Application portfolio assessment is crucial because it helps organizations understand the current state of their application landscape and identify redundancies, vulnerabilities, and opportunities for optimization or modernization. It provides insights into the overall health of the application portfolio and enables informed decision-making regarding future investments, rationalization, and migration strategies.
Application portfolio assessment provides critical information for effective portfolio management. By evaluating and analyzing the application portfolio, organizations can identify areas for consolidation, rationalization, or migration, resulting in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced alignment with business objectives.
The value of Enterprise Architecture to accelerate business transformation
Access this white paper to learn:
- The evolution of the enterprise architecture practice
- How to Deliver Value through a Connected Enterprise Architecture Practice
- Strategies for Adopting a Business-Outcome-Driven Approach
- How to Use Data-Driven Tools to Enhance Your Enterprise Architecture Connectivity
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.