Business Process Improvement: The Expert Business Guide
In the rapidly evolving landscape of today's corporate environment, the pursuit of enhanced efficiency and heightened productivity stands as a paramount objective. Within this context, the significance of business process improvement becomes evident. Simply put, business process improvement is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and improving business processes within an organization.
Businesses aim to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce errors, and optimize workflow by analyzing various methods. This results in increased effectiveness, higher quality work, and enhanced profitability. However, the business improvement process can be complex, requiring careful planning, implementation, and evaluation. While many organizations may hesitate to accept the challenge, the potential benefits are worth the effort. In this article, we'll explore the concept of business process improvement in more detail, including strategies and techniques that can help you optimize your operations and achieve your business goals.
What is Business process improvement?
Business process improvement is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and improving a business process's efficiency, effectiveness, and flexibility.
It involves identifying areas where a process can be improved, analyzing the root causes of the inefficiencies, and implementing changes to optimize the process. Business process improvement aims to improve performance, reduce costs, increase profitability, and enhance customer satisfaction.
This may include workflow redesign, process automation, optimization of resource utilization, and continuous monitoring and improvement of the process.
Importance of Business Process Improvement
Business process improvement is a crucial aspect of any organization's success. It involves identifying and optimizing existing business processes for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. By improving these processes, companies can eliminate unnecessary tasks, reduce errors, and automate repetitive tasks.
This can help businesses save time and money while improving the quality of their products and services. Streamlining workflows can help businesses respond quickly to market changes and improve competitiveness. Various business process improvement methodologies, such as Lean Six Sigma, can provide a structured approach to identifying and implementing process improvements.
Continuous business process improvement can lead to a culture of innovation and efficiency within an organization, resulting in better business performance and increased success in the marketplace. Investing in business process improvement can be a valuable tool for organizations to achieve their long-term goals and objectives.
Goals of Business Process Improvement
The main goals of business process improvement are to increase efficiency, reduce costs, enhance quality, and increase customer satisfaction. By analyzing and streamlining existing processes, organizations can identify areas of waste, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies that can be addressed to improve overall performance. This can involve automating certain tasks, eliminating unnecessary steps, reorganizing workflows, improving communication and collaboration, and implementing new technologies.
By doing so, businesses can lower costs, speed up production times, reduce errors, and provide a better experience to their customers, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
Business process improvement is an ongoing effort that requires ongoing monitoring and continuous improvement. Implementing these goals can create a sustainable competitive advantage for organizations, ensuring long-term success.
Steps for Implementing a business process improvement strategy
Achieving successful Business Process Improvement requires a structured approach and a clear roadmap. The following steps outline the process:
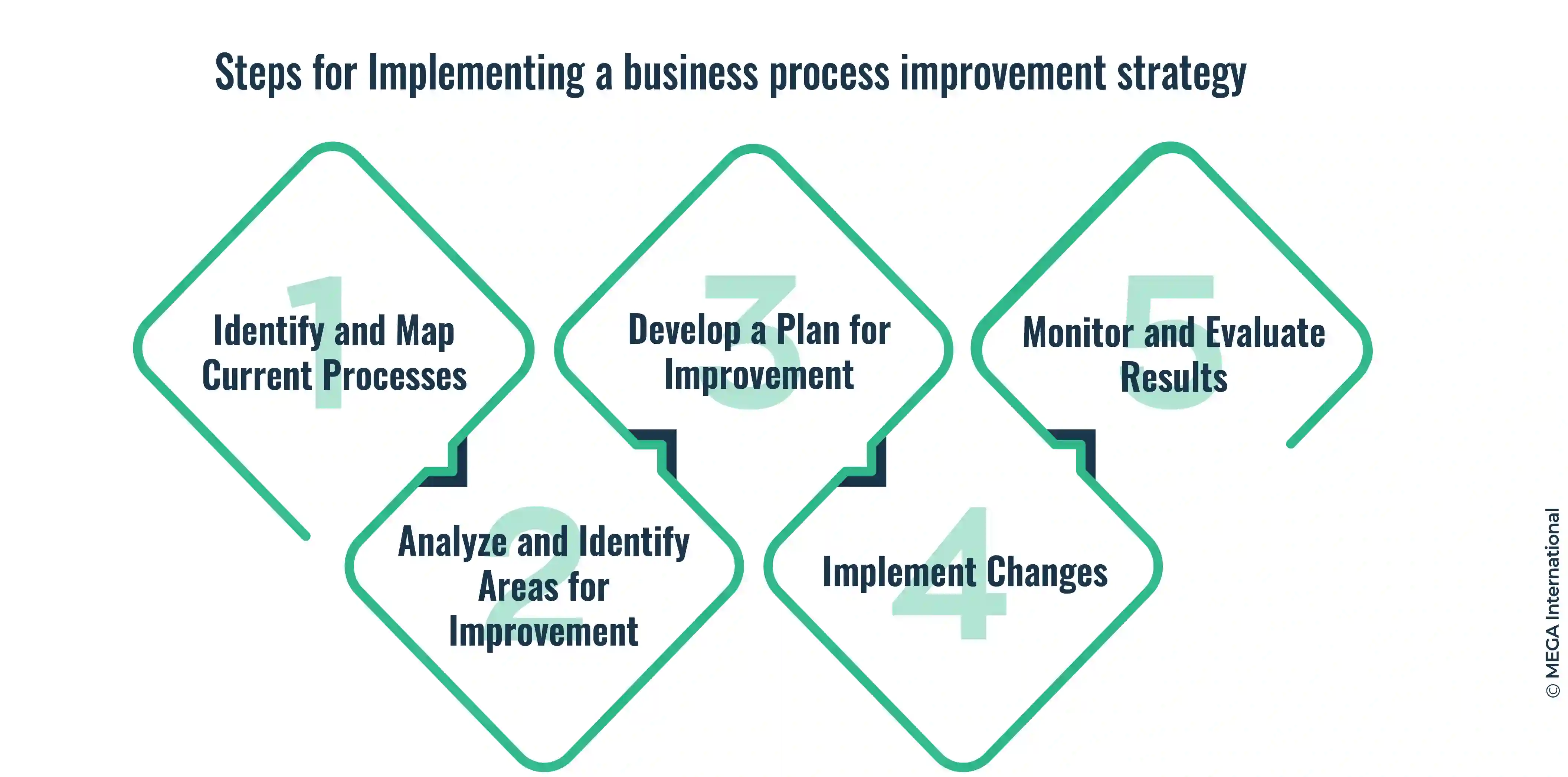
Step 1: Identify and Map Current Processes
The first step in BPI is identifying and documenting the organization's current processes. This involves mapping out each process's steps, inputs, outputs, and dependencies, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the existing workflow.
Step 2: Analyze and Identify Areas for Improvement
Once the current processes are mapped, it is crucial to analyze them thoroughly. This involves identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas with high error rates or delays. By conducting root cause analysis, organizations can pinpoint the underlying issues that hinder process performance.
Step 3: Develop a Plan for Improvement
Based on the analysis, organizations need to develop a well-defined plan for process improvement. This includes setting specific goals, establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), and outlining the strategies and tactics required to achieve the desired improvements.
Step 4: Implement Changes
With a well-crafted improvement plan, organizations can implement the necessary changes. This may involve redesigning workflows, reallocating resources, leveraging technology, or introducing new tools and methodologies.
Step 5: Monitor and Evaluate Results
After implementing the changes, monitoring and evaluating the results is essential. This involves measuring performance against defined KPIs, gathering stakeholder feedback, and making necessary adjustments to ensure sustained improvements.
Benefits of Implementing a Business Process Improvement Strategy
Implementing Business Process Improvement initiatives offers numerous benefits to organizations:
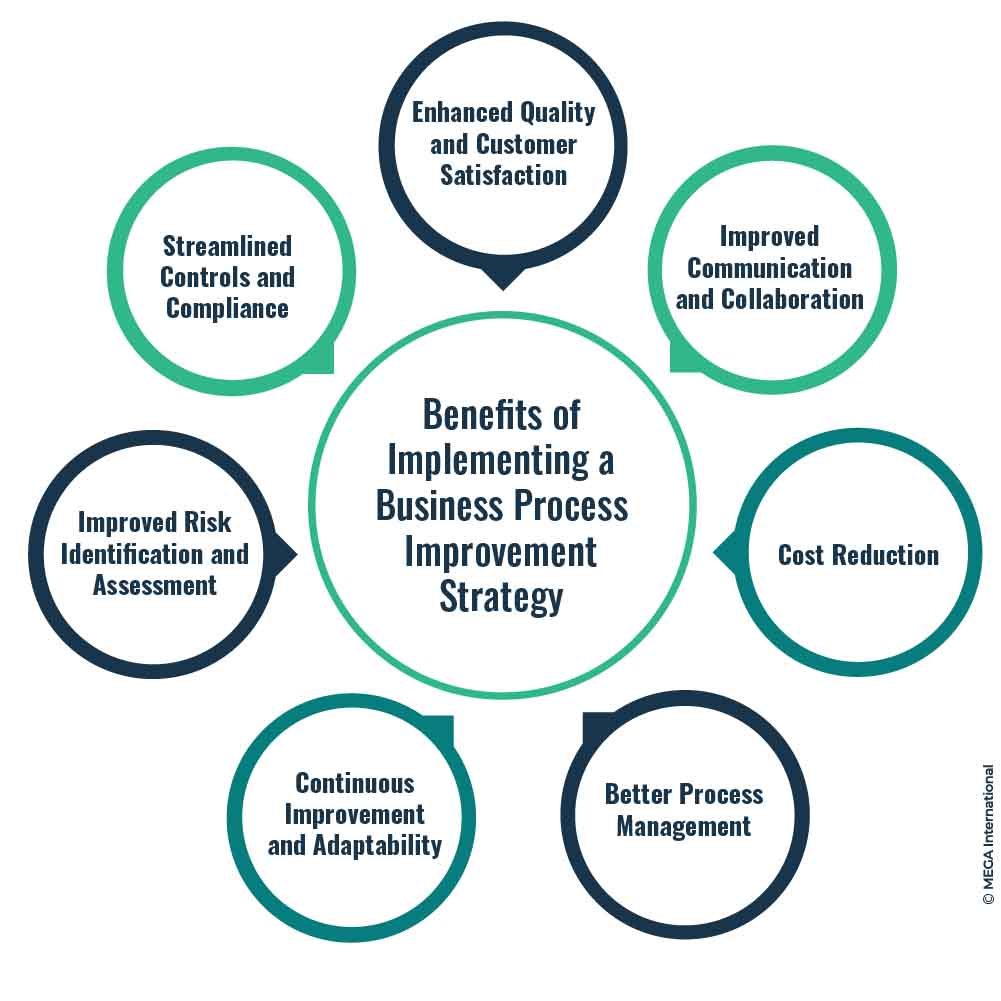
Enhanced Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Business Process Improvement aims to enhance quality standards and customer satisfaction by identifying and addressing inefficiencies and bottlenecks. Improved processes result in better products and services, increasing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
BPI encourages better communication, collaboration, and coordination among departments. By mapping and analyzing processes, organizations can identify areas for improvement in cross-functional workflows, leading to improved teamwork and smoother operations.
Cost Reduction
Process optimization often reduces costs by eliminating wasteful activities, reducing rework, and streamlining resource utilization. Organizations can allocate resources more effectively, minimizing costs and improving profitability.
Better process management
One of the primary benefits of BPI is the increased visibility it provides in organizational processes. Organizations comprehensively understand how different activities and tasks are interconnected through process mapping and analysis. This visibility enables organizations to identify potential risk points, bottlenecks, and process dependencies.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptability
BPI fosters a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability, which is vital for effective risk management. By embedding risk management practices into the BPI framework, organizations can proactively identify emerging risks, changing market conditions, and evolving regulatory requirements.
Organizations can detect potential risks or deviations from desired outcomes through ongoing process monitoring and performance evaluation. This allows for timely adjustments and process updates, ensuring that risk management practices remain effective and aligned with the organization's goals.
Improved Risk Identification and Assessment
During the BPI journey, organizations conduct thorough analyses of their existing processes. This includes identifying process inefficiencies, gaps, and vulnerabilities. As a result, organizations gain a deeper understanding of the risks associated with these processes.
Organizations can systematically evaluate risks at different process stages by integrating risk identification and assessment into the BPI framework. This proactive approach allows for identifying potential risks early on and the implementation of appropriate risk mitigation strategies. Organizations can reduce the likelihood and impact of potential disruptions by addressing risks during process improvement initiatives.
Streamlined Controls and Compliance
Business processes often involve multiple control points and compliance requirements. Organizations can streamline and strengthen these controls through BPI, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards, industry best practices, and internal policies.
By mapping and analyzing processes, organizations can identify control gaps, redundancies, or inefficiencies that may lead to compliance breaches or increased risk vulnerability. BPI enables organizations to implement standardized and optimized controls that mitigate risks, improve compliance, and enhance overall governance.
Methodologies and Tools Used in Business Process Improvement
In Business Process Improvement (BPI), several tools and techniques are available to support organizations in analyzing, optimizing, and enhancing their business processes. These tools and techniques provide valuable insights into process inefficiencies, help identify root causes of problems, and enable data-driven decision-making. Here are some commonly used BPI tools and techniques:
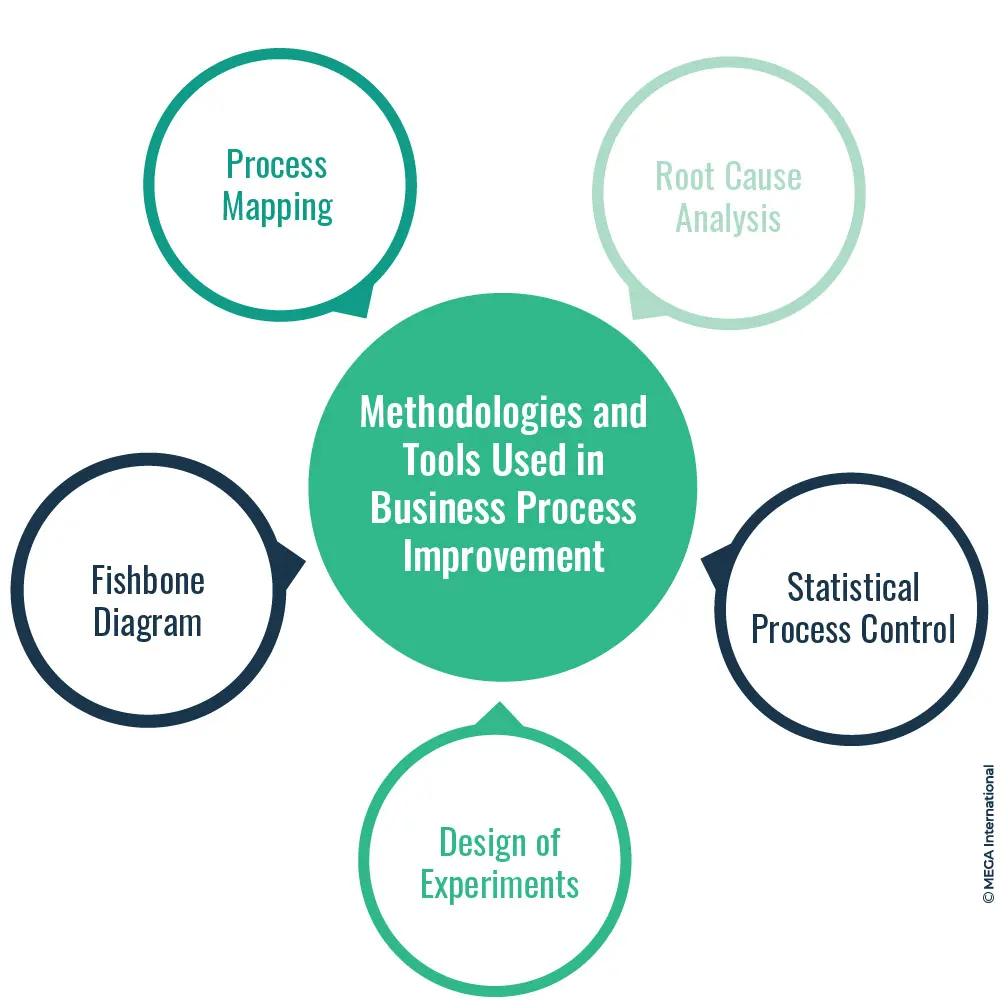
Process Mapping
Process mapping, also known as process flowcharting, is a visual tool that allows organizations to document and analyze their business processes. It involves visualizing the sequence of activities, decision points, inputs, outputs, and interactions within a process.
Process maps provide a clear understanding of the current state of a process, including its steps, dependencies, and potential bottlenecks. They help stakeholders visualize the activities' end-to-end flow and identify improvement areas. Process maps serve as a foundation for further analysis and optimization efforts.
Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach to identifying the underlying causes of process issues or problems. It aims to uncover the fundamental reasons behind process inefficiencies, errors, or failures rather than merely addressing symptoms.
RCA involves asking "why" multiple times to delve deeper into the causes of a problem. By identifying the root causes, organizations can implement targeted solutions that address the source of the issue, leading to more sustainable process improvements.
Fishbone Diagram
A Fishbone Diagram, also known as a Cause-and-Effect or Ishikawa Diagram, is a visual tool that helps identify the potential causes of a problem or process variation. It provides a structured approach for brainstorming and categorizing the factors contributing to a specific outcome.
The Fishbone Diagram consists of a central problem statement or effect, with branches representing different categories of potential causes. These categories include people, processes, equipment, materials, measurement, and environment. Organizations can identify potential causes and prioritize improvement actions by systematically analyzing each category.
Statistical Process Control
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is a technique used to monitor and control process performance. SPC involves collecting and analyzing data over time to identify process variations and ensure that the process remains within acceptable control limits.
SPC utilizes control charts to visualize and analyze process data. These charts display process data points, control limits, and trends, allowing organizations to identify when a process deviates from its desired performance. By implementing SPC, organizations can proactively detect process variations, identify potential causes, and take corrective actions to maintain process stability and consistency.
Design of Experiments
Design of Experiments (DOE) is a systematic approach used to optimize processes and identify the most influential factors that impact process performance. DOE involves conducting carefully planned experiments by varying input factors and measuring their impact on the process output.
By systematically manipulating process variables and analyzing the results, organizations can identify the optimal parameter settings, maximize process performance, and minimize variations. DOE helps organizations understand the relationships between process variables and outcomes, enabling them to make informed decisions for process improvement.
Tools
MEGA HOPEX
MEGA HOPEX is a powerful platform that enables organizations to visualize, analyze, and optimize their business processes. It offers various features and modules supporting various aspects of BPI. With MEGA HOPEX, organizations can:
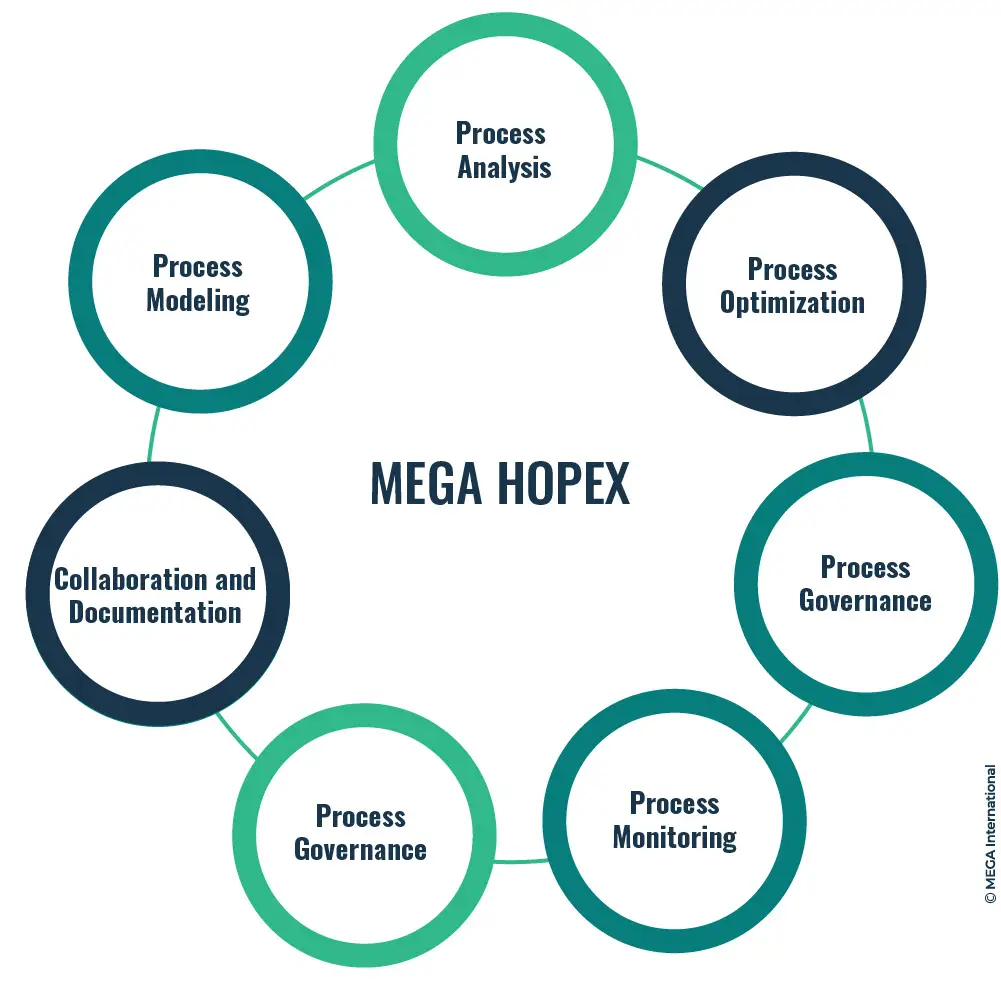
- Process Modeling: Create visual process models using industry-standard notations such as BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation). These models represent the current processes and serve as a basis for process analysis and improvement.
- Process Analysis: Analyze process performance, identify bottlenecks, and assess the impact of proposed process changes. MEGA HOPEX offers capabilities for conducting process simulations, scenario analysis, and process mining to gain insights into process efficiency and effectiveness.
- Process Optimization: Design and optimize processes to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. MEGA HOPEX enables organizations to identify improvement opportunities, test alternative process designs, and evaluate the impact of proposed changes before implementation.
- Process Governance: Establish process governance frameworks to ensure adherence to standards, policies, and regulatory requirements. MEGA Process allows organizations to define and enforce process-related rules, guidelines, and control mechanisms.
- Process Monitoring: Continuously monitor process performance and track key process metrics. MEGA Process provides real-time dashboards and reporting capabilities to visualize process performance, identify deviations, and take proactive action to address issues.
- Collaboration and Documentation: Facilitate stakeholder collaboration by providing a centralized platform for capturing process-related information, documenting process improvements, and enabling real-time collaboration on process models.
MEGA Architecture
While primarily known for its Business Process Management (BPM) capabilities, MEGA also offers robust Enterprise Architecture (EA) solutions. These solutions enable organizations to align their business processes with their overall enterprise architecture, ensuring coherence and consistency across the organization. The MEGA Architecture tools offer features such as:
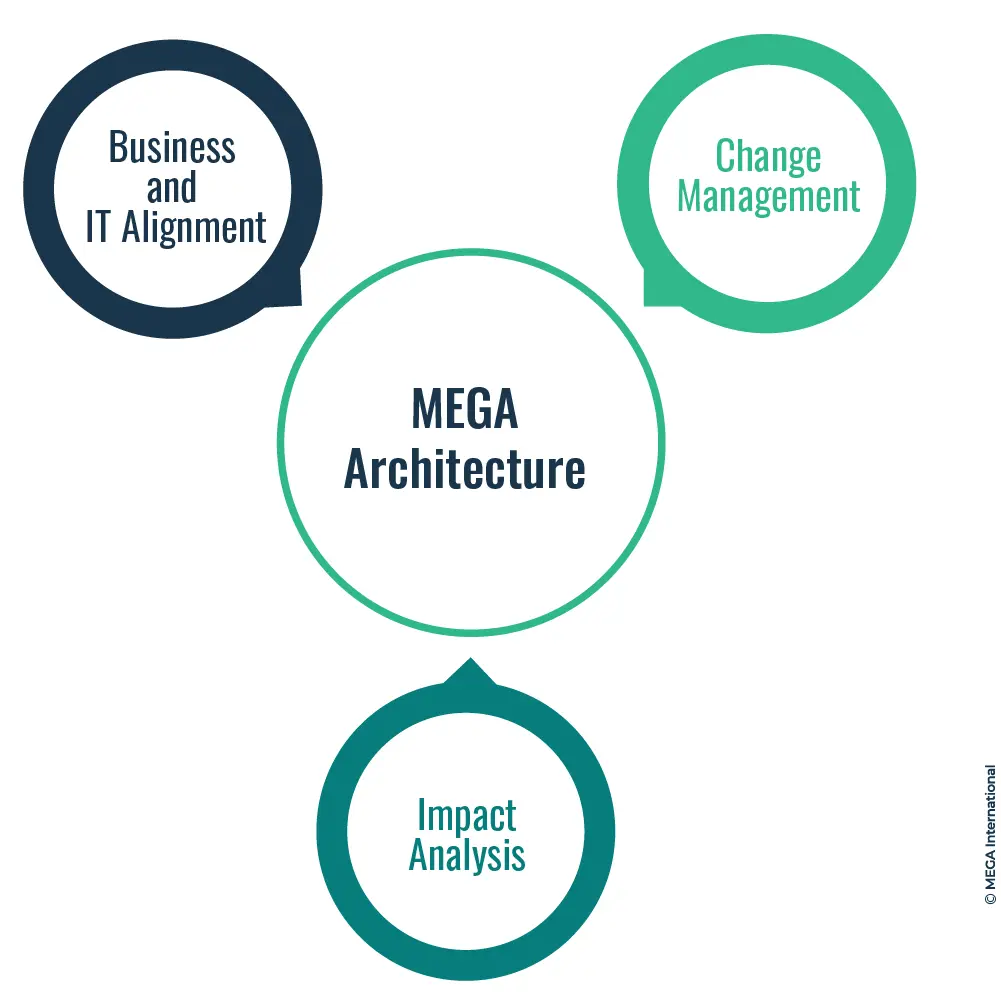
- Business and IT Alignment: Align business processes with IT systems, applications, and infrastructure. MEGA Architecture allows organizations to visualize and analyze the dependencies and interactions between business processes and IT components.
- Impact Analysis: Assess the impact of process changes on the enterprise architecture. MEGA Architecture enables organizations to model and simulate the impact of process modifications on the underlying IT landscape, ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing disruption.
- Change Management: Facilitate change management by providing a holistic view of the enterprise architecture and its relationships with business processes. MEGA Architecture helps organizations manage the complexity of process changes and ensure that the overall architecture remains aligned with business objectives.
Challenges in Business Process Improvement
While Business Process Improvement offers significant benefits, organizations often encounter challenges during implementation. Some common challenges include:
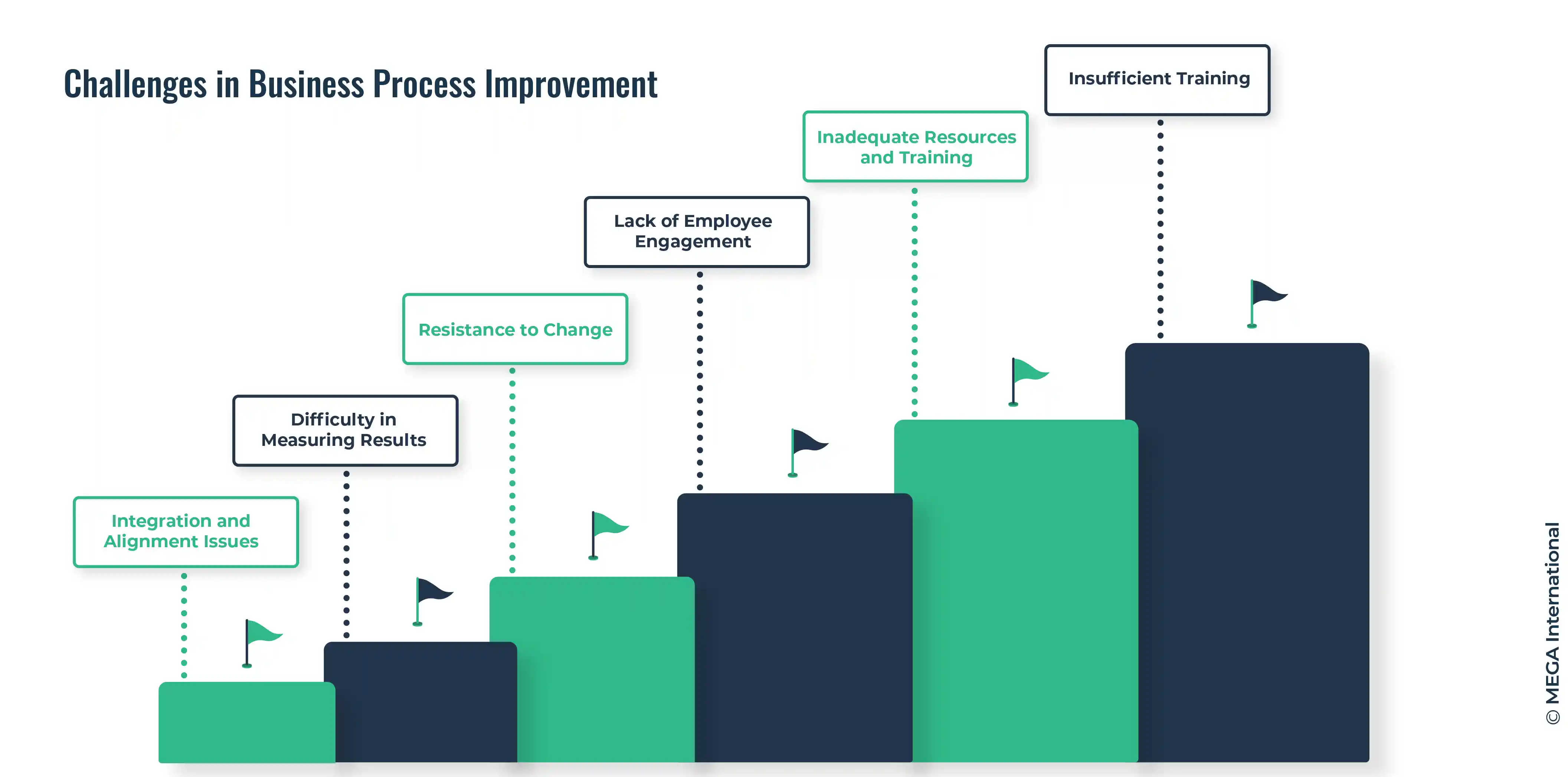
Integration and Alignment Issues
Business Process Improvement often involves changes across departments and functions. Ensuring integration and alignment can be complex, especially in large organizations. Effective communication and collaboration are essential to address integration challenges.
Difficulty in Measuring Results
Measuring the impact of process improvements can be challenging. Organizations need to establish clear metrics and performance indicators to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented changes. Data-driven decision-making and regular monitoring are essential for measuring results accurately.
Resistance to Change
Change can be resisted by employees who are comfortable with existing processes. Overcoming resistance requires effective change management strategies, clear communication, and the involvement of employees in the improvement process.
Lack of Employee Engagement
Engaging employees in the improvement process is crucial for success. Lack of employee buy-in and involvement can hinder the effectiveness of improvement initiatives. Organizations should foster a culture of continuous improvement and provide training and support to empower employees.
Inadequate Resources and Training
Insufficient financial and human resources can impede the progress of Business Process Improvement initiatives. Organizations must allocate the necessary resources and provide training to employees to ensure successful implementation.
Insufficient Training
Insufficient training is a common challenge organization face when implementing Business Process Improvement (BPI) initiatives. Without proper training, employees may struggle to understand and adapt to the changes introduced through process improvement efforts. This can hinder the successful implementation of BPI and limit the effectiveness of the improvements.
Best practices in business process improvement
To achieve successful Business Process Improvement, organizations should follow these best practices:

Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Create a culture that values continuous improvement and encourages employees to seek opportunities for enhancement. Recognize and reward innovative ideas and successful improvements.
Establish Clear Goals and Metrics
Set clear goals and objectives for improvement initiatives. Define measurable metrics to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of implemented changes.
Use Data-Driven Decision Making
Base decisions on data and facts rather than assumptions. Collect and analyze relevant data to identify areas for improvement and measure the impact of implemented changes.
Regularly Review and Update Processes
Business processes should not be static. Regularly review and update processes to align with organizational goals and industry best practices. Solicit feedback from stakeholders and make necessary adjustments.
Engage and Empower Employees
Engage employees at all levels of the organization in the improvement process. Encourage their participation, provide training, and empower them to take ownership of the changes.
Pitfalls to Avoid in Business Process Improvement
While Business Process Improvement (BPI) can benefit organizations significantly, several pitfalls can hinder its success. It is important to be aware of these pitfalls and take proactive measures to avoid them. Here are some common pitfalls to avoid in BPI initiatives:
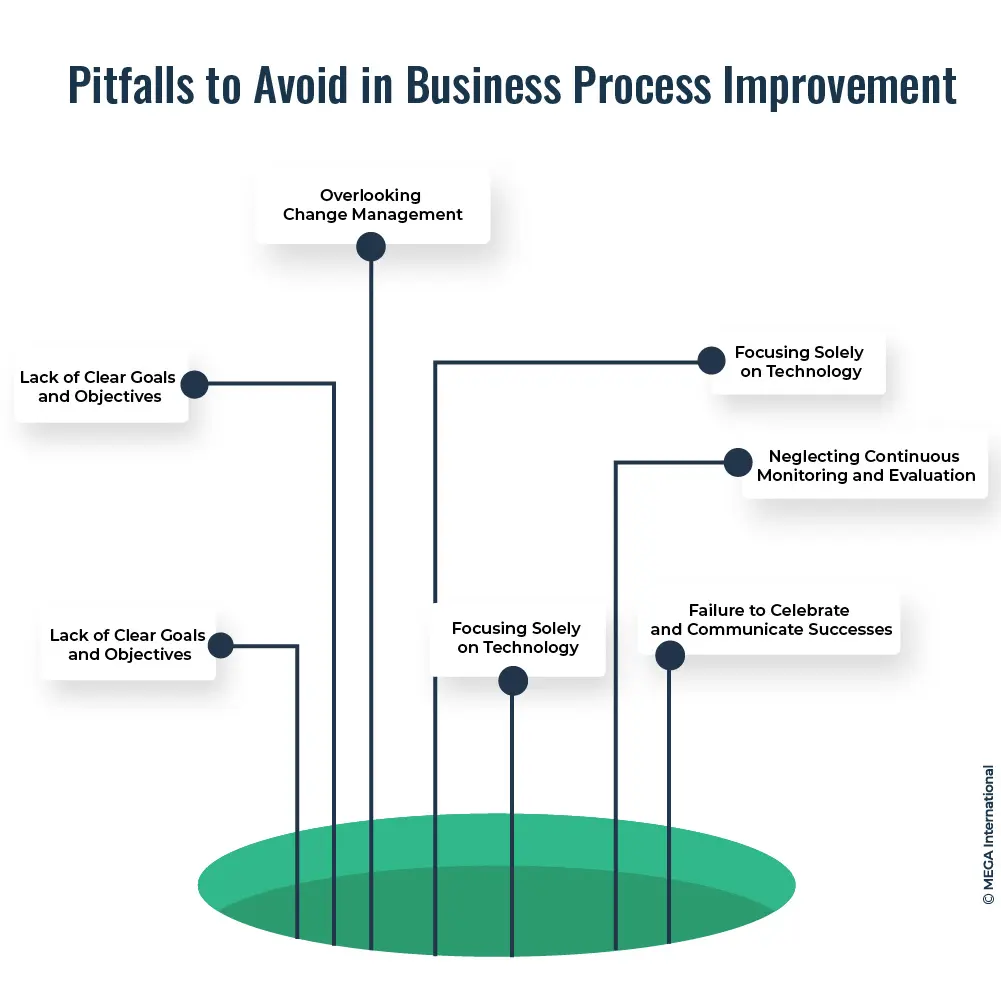
- Lack of Clear Goals and Objectives: Without clear goals and objectives, BPI initiatives can lose focus and direction. Defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for process improvement is important. Clear objectives provide a roadmap and help align efforts toward desired outcomes.
- Ignoring Stakeholder Involvement: Excluding stakeholders from the BPI process can lead to resistance, lack of buy-in, and, ultimately, the failure of improvement efforts. It is crucial to involve stakeholders at every stage, including process analysis, solution design, and implementation. Engaging stakeholders fosters ownership, improves acceptance of changes, and ensures that the improvements align with their needs and expectations.
- Overlooking Change Management: BPI often requires significant processes, roles, and responsibilities changes. Neglecting change management can lead to resistance, confusion, and a lack of adoption. To avoid this pitfall, developing a comprehensive change management plan that includes clear communication, stakeholder engagement, training programs, and ongoing support is important to facilitate smooth transitions and maximize acceptance.
- Focusing Solely on Technology: While technology can enable and enhance BPI, relying solely on technology without considering the human aspect can undermine the success of improvement efforts. It is essential to strike a balance between technology and human factors. Organizations should focus on aligning people, processes, and technology to drive sustainable improvements.
- Neglecting Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: BPI is an ongoing process, and it is crucial to monitor and evaluate the improvements' effectiveness continuously. Failing to establish mechanisms for monitoring and evaluation can lead to a lack of accountability, missed opportunities for further enhancement, and a decline in performance over time. Regularly review key performance indicators (KPIs), collect feedback, and use data-driven insights to identify areas for further improvement.
- Becoming Overly Complex: BPI initiatives should aim to simplify and streamline processes, but there is a risk of overcomplicating the improvement efforts. Complex methodologies, excessive documentation, or unnecessary bureaucracy can hinder progress and create resistance. Keep the improvement approach simple, focus on practical solutions, and avoid unnecessary complexity that may impede adoption and execution.
- Failure to Celebrate and Communicate Successes: Recognizing and celebrating successes along the BPI journey is crucial for sustaining momentum and maintaining employee motivation. Failing to communicate and celebrate achievements can lead to a lack of awareness and enthusiasm for further improvements. Regularly share success stories, acknowledge contributions, and highlight the improvements' positive impact to foster a continuous improvement culture.
Clear goals, stakeholder involvement, effective change management, balanced technology-human focus, continuous monitoring, simplicity, and celebration of successes are key elements to navigate the BPI journey successfully and drive meaningful and sustainable process improvements.
FAQs
Business Process Improvement (BPI) is a methodology that analyzes and improves business processes to increase efficiency, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
BPI helps organizations identify inefficiencies in their existing processes and implement changes to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Continuous improvement is essential for long-term business success.
Some process improvement methodologies include Six Sigma, Total Quality Management (TQM), Business Process Management (BPM), Kaizen, and the PDCA cycle.
The first step is to map out the current process and identify any bottlenecks or areas with waste or inefficiency. This can be done using process mapping, flowcharting, and value stream analysis techniques.
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to process improvement that aims to reduce process defects and variations. It involves a structured problem-solving methodology called DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control).
Kaizen is a Japanese term that means "continuous improvement". It involves making small, incremental process changes over time to achieve improvement.
There are many ways to improve business processes, such as automating manual tasks, reducing cycle time, optimizing workflows, eliminating waste, and improving quality. The key is identifying the areas needing improvement and implementing changes that increase efficiency and effectiveness.
The steps typically include identifying the problem, analyzing the current process, developing an improvement plan, implementing the changes, and monitoring the results. Evolving all stakeholders and using data-driven analytics to track progress and measures is essential.
Related Content to Business Process Management
Get a clear understanding of how your operation runs, identify areas of improvement, and build scenarios to optimize and transform business processes;
MEGA HOPEX for BPM
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for BPM, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.