Migrate & Enjoy the Benefits of Cloud Computing

Migrate & Enjoy the Benefits of Cloud Computing
In this article, we will explore the benefits of moving to the Cloud and provide a list of those advantages. Whether you're just learning about the Cloud's potential or considering moving, this article will help you understand all it offers.
Cloud-based technology is becoming an increasingly popular choice for businesses worldwide. The Cloud can help businesses streamline their processes and operations, allowing them to focus more on their core business.
Why is cloud migration important?
- The past 2+ years have seen a massive shift to the Cloud as companies adopted remote or hybrid work environments (many of which are now permanent) and sought to develop more agile operating capabilities.
- Today, nearly two-thirds (72%) of IT decision-makers say their organizations default to the cloud when adopting new technologies, and 69% say they've accelerated their cloud migration plans over the past 12 months.
- Gartner Research estimates that 45% of IT spending in 2024 will go toward cloud-based solutions. These investments support technological and organizational changes to enable and continuously improve digital business models contingent on cloud infrastructures.
- Behind this trend are multiple market drivers, but since last year, the COVID-19 pandemic has proven that cloud-hosted services can deliver resilient, scalable, and reusable IT environments. 2020 was the year that enterprises invested more funds in cloud infrastructure services than in on-premises data centers and hardware, a victory for cloud proponents borne of years of enterprise acceptance and evidence of its value.
- What is less well known to the enterprise audience are the requirements for implementing and governance decentralized IT environments. Prospectively, on-premises applications that can be migrated to the cloud may come with heavy technical collateral. The slightest change in their functional composition can disrupt interconnected business processes and formal compliance-related procedures. Inevitably, trade-offs must eventually be made when migrating these services. If a transition is not tied to a concrete business objective, decisions will be delayed, if taken at all.
Explore the Benefits of Cloud Migration
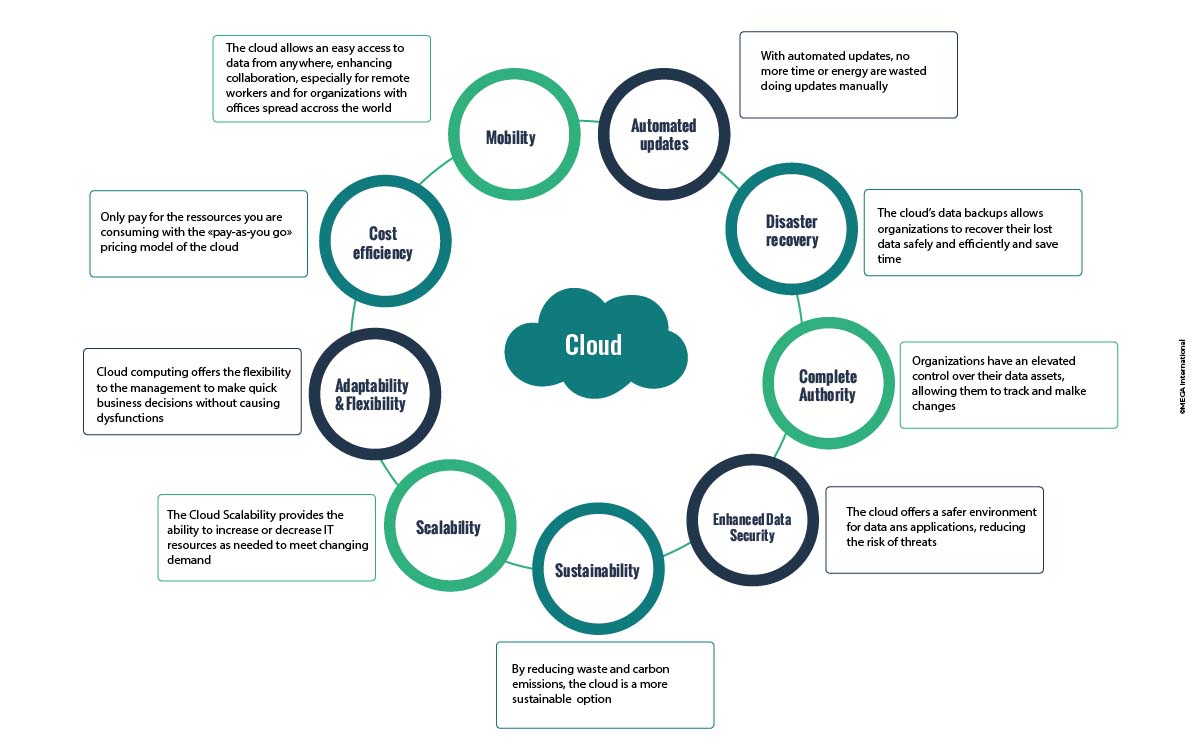
Cloud computing is revolutionizing how companies do business, and the benefits of moving to the cloud are becoming increasingly apparent. Whether you're a small business or a large corporation, this modern technology has plenty of advantages worth considering. Cloud computing is cost-effective, offering increased flexibility, scalability, and improved team collaboration.
 Learn the best strategy for successful cloud migration here↗
Learn the best strategy for successful cloud migration here↗
If you haven't moved your applications to the cloud yet, check out the many benefits of moving and adopting a SaaS solution below:
Most significant benefits of moving to the Cloud:
Tailored & cost-effective software solutions
Cloud service resources offer cost-effective solutions, as businesses only pay for their services. They can reduce costs when demand decreases without worrying about wasted hardware investments.
Moving from the capital-heavy expense of installing, maintaining, and upgrading on-premises IT infrastructure to the operational cost of a SaaS subscription provides greater clarity on the costs of using a software solution (license, maintenance, and infrastructure costs).
Indeed, the historical complaint about enterprise software has been the unknown cost to deploy, operate, and archive. With SaaS, the total cost of managing the application is fixed and transparent from the start, so there aren't any surprises or unexpected costs; in other words, it is a pay-as-you-go model.
Scalability
Cloud resources can provide businesses the flexibility to adjust to changing needs. With cloud resources, companies can quickly scale up or down depending on their current requirements.
This is especially beneficial for businesses that have unpredictable peaks and troughs in their demand, as they don't have to invest heavily in infrastructure that becomes redundant during quieter periods.
In summary, cloud computing provides a highly scalable solution for businesses looking for greater flexibility and cost savings per their changing business needs.
Flexibility Remote work
With cloud adoption, you only need an internet connection to work on your daily tasks and projects the same way as desktop applications. Your work is automatically saved and safely stored in the cloud.
You can also easily collaborate with your peers using modern embedded features such as review notes and validation workflows, improving teamwork efficiency and providing faster results. This enables your workforce to work remotely without productivity taking a hit.
Automated backups and disaster recovery
Cloud solutions generally include automated backups that are out of the box. Cloud vendors can perform daily backups and weekly and monthly backups so that you are sure that your data is safe.
In addition to backups, cloud vendors can offer advanced disaster recovery programs to protect you from unexpected disruption. Production data are synchronized regularly to a secure server in a remote location. In the event of a disaster, the production server is updated with the latest backup of the remote server.
Up-to-date software
Cloud systems provide higher uptime than on-premises systems. Cloud systems help reduce technology complexity and rely on an enhanced and secure cloud infrastructure.
With SaaS, there’s also no need to plan for costly IT upgrades. It eliminates the hassle of managing upgrades or any other IT expansion as your business grows. By letting the software vendor manage upgrades, it ensures that your software solution is always up-to-date.
Enhanced Data security
Last but not least, cloud solutions are even more secure than on-premise solutions, enabling you to store your strategic data on a secure infrastructure. Cloud providers are large companies with high technical expertise and hire certified professionals.
They comply with many international regulations and use the most recent technologies. Cloud providers also run powerful cybersecurity software to prevent attacks and protect your data.
Furthermore, cloud resources offer increased security as data is stored securely off-premise, keeping it safe from any potential damage caused by natural disasters or malicious attacks.
Types of Cloud
When it comes to cloud computing, there are different types of clouds available to choose from, each with advantages and disadvantages. Cloud storage offers incredible convenience when accessing files from any device with an internet connection, making it a valuable tool for businesses and individuals.
There are four types of clouds: private clouds, public clouds, hybrid clouds, and multi-clouds. The main two types are public and private cloud storage. Public cloud storage is open to anyone with an account, allowing users to store and access data from any device connected to the internet.
Private cloud storage offers more secure options for those needing extra data security, as it requires unique authentication before allowing access. Users can select the best choice for their needs with both public and private options.
HOPEX Cloud Benefits
HOPEX Cloud offers excellent tools for businesses to streamline operations, accelerate growth, and optimize their IT infrastructure. HOPEX Cloud is a powerful cloud-based platform that provides users a wide range of benefits.
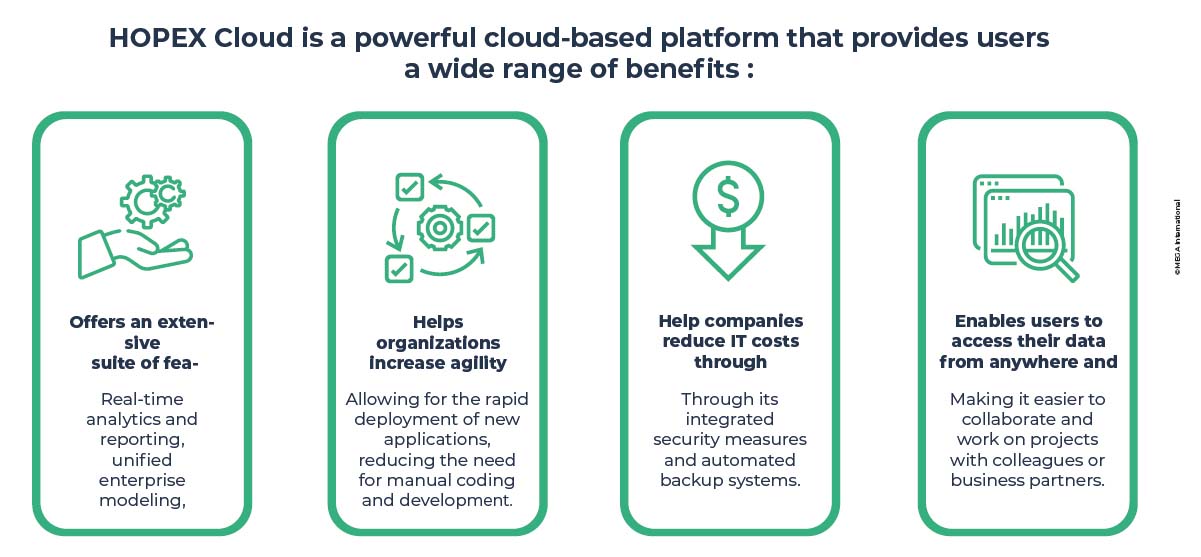
The platform enables users to access their data anywhere and anytime, making it easier to collaborate with colleagues or business partners on projects.
It also offers an extensive suite of features such as real-time analytics and reporting, unified enterprise modeling, process orchestration, and more. Additionally, HOPEX Cloud helps organizations increase agility by allowing for the rapid deployment of new applications, reducing the need for manual coding and development. Finally, the platform can help companies reduce IT costs through its integrated security measures and automated backup systems.
At MEGA, we provide a flexible cloud offering that relies on the Microsoft Azure infrastructure, available in two configurations, depending on your needs:
- HOPEX Cloud Essentials is based on a multi-tenant architecture. It offers an affordable, full-featured cloud infrastructure built for ease of use and performance.
- HOPEX Cloud Enterprise uses a single-tenant architecture. It is best suited for custom configurations and advanced security needs. It has completed the SOC 2 Type 2 examination based on the trust principles of security, availability, and confidentiality. With HOPEX Cloud Enterprise, you can configure multiple settings, including security access options, SSO, and advanced disaster recovery. Additional management services, such as sandboxes and extended services, are available upon request.
Want to learn more about our HOPEX Cloud program? Please download our HOPEX Cloud datasheet.
In conclusion, migrating to the Cloud offers many business advantages. From cost savings and improved scalability to enhanced security and higher performance, cloud computing solutions are undoubtedly the way of the future.
The time to move is now, and the benefits are too great to ignore. Furthermore, with various options from various providers, companies can find the perfect solution for their unique needs. Make the switch today and experience all that cloud computing has to offer!
FAQs
Moving to the cloud is worth it, as it can save businesses money, time, and resources. It can also improve a business's efficiency and scalability, allowing it to focus on its core operations.
Cloud computing offers several benefits to businesses and individuals alike. The three primary benefits of cloud computing include cost savings, scalability, and reliability.
The cloud has become increasingly popular and is now used by many businesses and individuals. There are three common reasons to use the cloud - cost savings, scalability, and flexibility.
Maximize the ROI of Your Enterprise Architecture Initiative
Frédéric Fourquet
Data Governance Product Marketing Manager, Frédéric started his career in 1997.
Prior to joining MEGA as Product Marketing Manager for Data Governance, Frederic was previously Product Director in Artificial Intelligence & Data Intelligence for Banking & Insurance - Strategy, Marketing, Business Development, Consulting & Partnerships (4 years), Consulting Director in Regulations, Compliance, Data Governance & Data Innovation (16 years), and Sales/Presales Executive and Consultant in US/EMEA Software Companies (4 years).

Latest Blog Posts
Cyril Amblard-Ladurantie
Cyril Amblard-Ladurantie is GRC (Gouvernance, Risque & Conformité) and BPA (Business Process Analysis) Product Marketing Manager at Mega International with more than 15 years of experience focusing on GRC technology. Prior to joining MEGA International, he was a manager at a major Advisory firm (EY) focusing on advising clients on their digital GRC journey, coordinating implementation projects, and providing project management assistance. Before his experience at EY, Cyril held pre-sales and support positions at a major international GRC and regulatory intelligence provider (Thomson Reuters).

Latest Blog Posts
Paul Estrach
Paul Estrach is Product Marketing Director at MEGA International, with over 15 years of experience in the Enterprise Architecture practice. Prior to this role, he worked with a large number of organizations on their transformation projects, from process optimization to the evolution of their information systems, first as consultant then as Services Director for over 7 years.

Latest Blog Posts
The Growing Role of the Enterprise Architect as a Business Partner

The Growing Role of the Enterprise Architect as a Business Partner
In the ever-changing world of digital transformation, the enterprise architect role is becoming increasingly important.
In agile environments at the core of most businesses, enterprise architects become business partners who facilitate digital business transformation.
They have sometimes been considered as being disconnected from reality. To prove business value derived from enterprise architecture, the role of the enterprise architect must be that of a "facilitator," who makes sure to smooth the implementation of new projects with business teams.
Here are some insights from enterprise architects on their evolving roles and interactions with business stakeholders.
What is an enterprise architect?
An enterprise architect is responsible for the overall design and successful implementation of an organization's technology infrastructure.
Their job is to analyze the current state of the company's technology, processes, and services to identify areas of improvement and create a plan for future development. Enterprise architects must have excellent communication skills as they must collaborate with multiple contributors to ensure that the architecture meets the needs of all departments within the organization.
They must also possess strong technical skills to evaluate systems properly and develop cost-effective and efficient solutions. A good enterprise architect should also have a knowledge base covering various technologies such as distributed computing, software engineering, databases, virtualization, cloud computing, security, networks, and storage.
Enterprise Architect Job Description Demystified
Enterprise Architects are responsible for designing, developing, and implementing a company's IT strategy. As such, they must possess a unique set of skills to be successful in this role. To become an Enterprise Architect, one must have strong problem-solving and analytical skills to identify opportunities for improvement and streamline processes.
They should also have excellent communication skills to effectively explain their plans to allies and straightforwardly present their solutions. Additionally, they must have deep knowledge of enterprise software development and the latest technology trends. Enterprise Architects should also be knowledgeable in governance models such as ITIL or COBIT and have expertise in project management methodologies like Agile or Scrum.
Furthermore, having experience with cloud computing or cybersecurity will help them create cost-effective, secure systems. All of these skills are essential for any aspiring Enterprise Architect to possess.
Exploring the Roles and Responsibilities of an Enterprise Architect
Enterprise Architect (EA) is one of the most senior positions in the IT department. According to Frédéric Jauffret, Head of IS Architecture at AP-HP (Public hospital), the enterprise architect is first a “regulator, the one who puts in place principles so that everything goes well,” and a “facilitator, the one making sure to facilitate the implementation of new projects regarding applications and systems.”
The primary enterprise architect skills are based on integrating the companies' information applications and programs. To play a crucial role and align with the evolution of the business, an enterprise architect needs “to be an advocate for IT, to move from an IT framework to providing services and to be a Business Partner of businesses, to reverse the trend, to be a source of advice and to influence the path of the organization,” says Frédéric Girardeau, Enterprise Architect at Société du Grand Paris (Public sector).
In this new role, enterprise architects are expected to make strategic recommendations, assess business opportunities related to emerging technologies, and evaluate the impact of business change on IT systems, considering how to adjust the IT ecosystem.
They will clearly show the value generated by the connections between people, processes, applications, and infrastructure by:
- Bringing the strategic vision to organizations that often work in silos and lack an overarching view.
- Engaging with the business to refine its needs, showing how a business capability should evolve in the next three years, or whether the company can address new customer segments or services
- Contributing to an improved IT roadmap that efficiently and proactively supports business needs and better plans for future IT investments.
Enterprise architects: New influential partners in organizations
In the past, enterprise architecture (EA) was often seen as an intrusive cost center that builds architecture for the sake of architecture, delivering nothing more than noise throughout the organization.
Even if enterprise architect is still a “shadow job,” “Now, we are going into influencer mode. People have understood that what we do is paying off, and they come to see us. They listen to our advice and the influences we can have on the information system,” says Dorine Periolat, IT Architect at Bordeaux Métropole (Public sector).
“It is about understanding that architecture is not an ivory tower that lacks transparency about its activities. We are trying to be accessible, to make our role better understood and useful”, says Frédéric Jauffret, Head of IS Architecture at AP-HP (Public hospital sector)
Enterprise architects lead critical change initiatives by leveraging company assets and exploring new business opportunities, such as those delivered by emerging technologies.
The main steps that an enterprise architect can take to accelerate and elevate the value they bring to their organization and become influential are the following:
- Initial - When starting an initiative, Enterprise Architecture has not perceived value and requires extra effort to implement it.
- Valuable - EA is perceived as applicable and has started to produce value for some stakeholders.
- Trusted – Enterprise architecture is trusted and has a reputation for delivering value.
- Influential - EA has become truly influential and is perceived as an internal consultancy by business leaders.
But there is a way to move from “Initial” to “Influential.”
To create success in digital transformation, we recommend the following actions:
- From Initial to Useful. To gain influence in their organization, enterprise architects can build an enterprise architecture baseline that consists of creating an inventory of applications and technology, setting up some dashboards, and socializing their initiative through an enterprise portal. At this stage, it is vital to show quick results by automating the inventory and focusing on the portal.
- From Useful to Trusted. Enterprise architects can leverage this new confidence as a catalyst for more significant projects with more visibility throughout the organization, expanding the audience that recognizes the value of enterprise architecture. At this stage, they can implement additional use cases focused on business outcomes and establish a Center of Excellence that strengthens the discipline.
- From Trusted to Influential. Once enterprise architects are trusted, they’ll be seen as a source of truth for reliable information, and the business will ask for their help. As true experts and internal consultants, the C-suite will soon become their key stakeholders. To foster innovation, they should establish a governance process and have a comprehensive view of the enterprise. This supports “what if” scenario decision-making that drives transformation. To remain in this stage, enterprise architects can continue focusing on new business related to Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) use cases, providing tangible business value and driving transformation and innovation.
In a research note published in 2020, Gartner identifies five steps to demonstrate EA’s value to business leaders:
- Position Enterprise Architecture as an internal management consultancy by defining consulting services that better-fit business strategies, innovation, and operationalization.
- Utilize value-based selling to promote enterprise architecture inside the organization.
- Conduct diligence to build relationships by interacting with business leaders and understanding how the EA practice can help them make smarter investment decisions to build the value proposition.
- Construct a value proposition document specifically tailored to the organization.
- Pitch the Enterprise Architecture value proposition by first practicing and soliciting feedback and identifying the right person to deliver the value proposition.
Main challenges to be faced by enterprise architects in the future
Because the role of enterprise architects has evolved significantly, they know they need to help transform projects by aligning IT approaches and business objectives.
With their expertise in business processes and technology solutions, enterprise architects are critical players in ensuring that organizations stay ahead of the competition and remain competitive in an ever-changing marketplace. They can identify potential problems or opportunities by analyzing data and trends and recommend how best to capitalize on them. Many other challenges must be addressed in the current context of multiple transformations.
Demonstrate business value
Enterprise architecture is more of a long-term process based on transformation projects, but economic players demand to go ever faster. That is why "the ability to demonstrate their contribution of value in an extreme change is key” for enterprise architects, points Christophe Robin, Global IS Architecture and Projects Senior Manager at Nexans (Optical fiber industry).
Adopt a risk prevention approach and be agile
The other challenges are “innovation,” “agility,” and “cybersecurity,” meaning that “We must move from a business value approach to a risk prevention approach, which is rather good for our activity because it helps to make us visible,” explains Christophe Robin.
Get a better understanding of data usage.
According to Frédéric Jauffret, “Many things are driven by data. The challenge is understanding that data often drives IT to ensure we work on data lineage, for example. The challenge for enterprise architects is also to be able to collect information and to be able to interconnect everything.
“In an organization, there is much information, flows, data: the most difficult thing is to capture all that and make it into something that has value and on which we can build,” says Frédéric Girardeau. “The most important challenge is to be as versatile as possible, trying to have an analytical view of the information system with specific indicators (ESG or obsolescence indicators, for example),” adds Fethi Bounaas – Enterprise Architect, Credit Agricole Corporate & Investment Bank.
Integrate sustainability in enterprise architecture
One of the significant issues of the times is how to deal with global climate change, enable sustainable transformation to limit environmental impact, and contribute to a sustainable world. Enterprise architects need to promote best practices for green IT and eco-design actively. "I think that eco-design has a role to play so that we can build a future in which we can all live peacefully," concludes Dorine Periolat.
Enterprise architecture training and certification
Enterprise architecture training is designed to help organizations create an enterprise-wide view of their IT infrastructure, business processes, and information systems. This training helps enterprise architects and organizations identify and analyze strategic and tactical opportunities for improvement and develop plans to optimize the use of resources.
It provides a comprehensive look at how business processes are linked, allowing organizations to better align technology investments with strategic goals. It also helps understand current business processes and their impact on customer satisfaction, cost reduction, and organizational agility.
With the proper Enterprise Architecture training, Enterprise architects can identify potential areas of improvement, create change initiatives, and implement solutions that will have a long-term positive impact on the organization.
In conclusion, enterprise architects are vital to any organization's success.
They are responsible for ensuring that the IT infrastructure is aligned with the company's goals and objectives and providing technical guidance and expertise to all stakeholders. Moreover, enterprise architects must be adept at developing IT solutions that meet customer needs and business objectives.
Their ability to collaborate effectively with other teams within the organization is essential for achieving desired outcomes. With their unique skills, enterprise architects are an indispensable asset to organizations everywhere.
Overcome digital transformation challenges with Enterprise Architecture

Discover how EA helps you tackle digital transformation challenges and optimize all areas of business.
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.

Benefits of Application Portfolio Management

Benefits of Application Portfolio Management
The benefits of application portfolio management are tremendous! This article will explain why application portfolio management tools are necessary and how they can give businesses a competitive edge.
IT departments are confronted with an increasing number of applications to manage. They often need more visibility into these applications, especially how they support the business. By understanding and utilizing the advantages of portfolio management, companies can gain an edge in their industry.
APM provides organizations with organizations' inventory applications and assesses their technical and business value so that organizations can determine which ones to keep, modernize, or eliminate. IT departments use a proven methodology to reorganize their IT systems successfully.
If you're looking for ways to improve your business organization, you will take advantage of these benefits of portfolio management. Managing a business's applications is complex, but the benefits are undeniable.
Benefits of application portfolio management (benefits of APM)
Application Portfolio Management (APM) is a great way to track all the organization's applications. It allows easy tracking of which applications are used, how frequently, and by whom.
This information can be handy for decision-makers who need to understand what is currently being used within their organization and how it affects overall productivity. Additionally, the APM system provides organizations with valuable insight into application performance and usage trends, giving them a better understanding of their technology investments' performance over time.
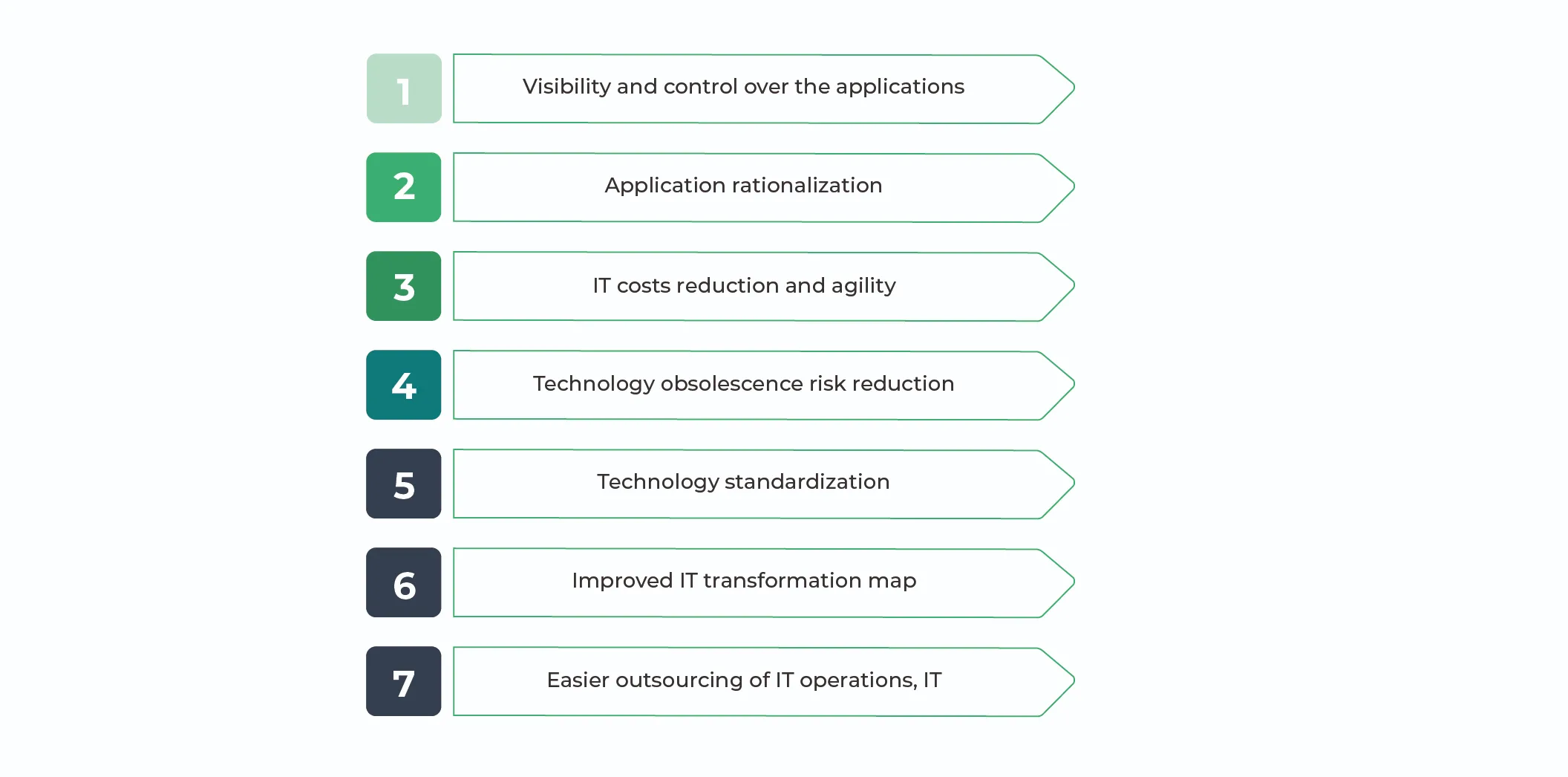
1. Visibility and control over the applications /IT system
Over the last few decades, many IT departments have witnessed increasing applications. This increase is often due to past mergers & acquisitions, globalization, or organic growth.
Thus, IT departments are facing increasing complexity as well as multiple redundancies. They need more visibility into their applications, and integrating new resources into their legacy systems can take time and effort.
Application Portfolio Management helps companies perform an application inventory under multiple perspectives, such as lifecycle, costs, deployments, or the business capabilities they support. IT portfolio managers can also link applications to technologies and business capabilities to understand an IT asset's impact on the business and perform what-if analysis to rationalize applications.
It is possible to call on application owners, who will update their application information to streamline the application inventory.
It can be crowdsourced to application owners, who will update their applications' information to speed up the application inventory. Overall, this inventory will provide greater visibility and a better knowledge of the IT systems, enabling IT leaders to embrace new business projects readily.
2. Application rationalization, IT cost reduction, and IT agility
Application portfolio management provides many dashboards to understand the state of the portfolio. Dashboards on application lifecycles provide information about when applications will be retired or replaced by another version.
Other critical information, such as data flows between applications, clarifies the impacts of removing an application or the possibility of exchanging data with another one. However, the strength of an application portfolio management practice resides from the business perspective.
IT leaders clearly understand how applications support business capabilities, and therefore, they know which applications are critical to the business. Application Portfolio Management tools also include questionnaires that enable business users to provide satisfaction feedback on their applications.
Not only do these dashboards highlight potential inconsistencies, but they also help better plan the IT transformation. Using these dashboards, IT managers can rationalize applications, reduce IT costs , and increase IT flexibility because they better understand their applications' business value.
3. Technology obsolescence risk reduction and standardization
IT departments often manage a vast number of software technology components that represent a threat to organizations. By limiting the variety of technology products, IT departments can perform essential economies of scale, and dev teams are better trained to use these technologies.
APM software can be connected to external libraries containing lifecycle information, including end-of-life dates, to determine technology obsolescence. Based on this information, dashboards are available that show how applications are affected by technologies’ end-of-life.
Once this assessment is complete, technology portfolio managers can decide whether technologies comply with the company's standards.
By defining technology standards, technology portfolio managers help companies reduce the number of technologies – and their costs, while ensuring projects don't use rogue technologies.
4. Improved IT transformation roadmap
If application portfolio management solutions help provide the whole picture of IT systems, they also help IT managers plan their IT systems' transformation.
Based on application lifecycles and cost assumptions, IT managers can simulate future IT projects and analyze the outcome of their premises. To do so, they create a mix of initiatives based on different assumptions, such as extending or phasing out an application, and compile these initiatives into different scenarios.
Then, they can see the impact on their IT systems and compare the different scenarios.
By planning and executing the IT transformation, IT departments can allocate more resources to new business initiatives and focus on innovation.
5. Facilitates outsourcing of IT operations, IT audits, and compliance.
If an organization decides to outsource one part of its IT, it needs to make a detailed inventory of its assets and potentially eliminate irrelevant applications. Therefore, an assessment is required before deciding which applications to keep or outsource.
Streamlining IT audits or IT certifications is another benefit. External consulting companies or governmental organizations recommend or require companies to monitor their IT assets properly. Here, an application portfolio management practice will help organizations better support the IT roadmap, or reduce capital allocation to cover IT risk, for example.
In conclusion, Application Portfolio Management is an essential tool for any company. It provides an efficient and effective way to organize, manage, and update their applications. It significantly reduces complexity, simplifies IT management, and eliminates redundant applications. Furthermore, it helps organizations stay on top of the latest trends and technologies and provides a comprehensive view of the entire application landscape. Lastly, it can help improve operational efficiency by reducing costs and improving performance.
Learn more about:
Increase visibility and rationalize your IT portfolio with APM

Get an effective methodology to set up and achieve a successful application rationalization initiative.
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.

Business Capabilities Guide - Everything you need to know

Business Capabilities Guide - Everything you need to know
At a time when the digitization of the business has accelerated, when every business project is an IT project, there's pressure on IT to enable and support business transformation. By defining what the organization does, business capabilities are a key concept that allows business and IT teams to speak the same language.
Business capability definition
A Business capability is defined as a representation of an organization's needs.
Business capabilities represent an organization's needs and what it does and can do. They depict the core functions of the business and break down the industry into building blocks, which are laid out in a business capability diagram called business capability maps. If needed, they can be broken down into sub-capabilities.
Their regular assessment will help enterprise or business architects identify and prioritize the corresponding IT initiatives with business needs.
Of course, since they depict an organization, business capabilities are not static and evolve; some might even become irrelevant and be replaced or consolidated by another capability. Business capabilities assessment can be based on various parameters, including efficiency, priority, and complexity.
What is a business capability example?
Take a car rental company, for example. An excellent example of business capability might be an "online booking" capability. This competence is supported by one or multiple applications, like the car rental mobile app.
Another example would be a "mortgage loan" capability for a bank supported by an in-house application that computes loans.
The example below shows the capability map of an airport, including applications. Each application has been assessed using color-coded icons to understand better how applications support business capabilities.
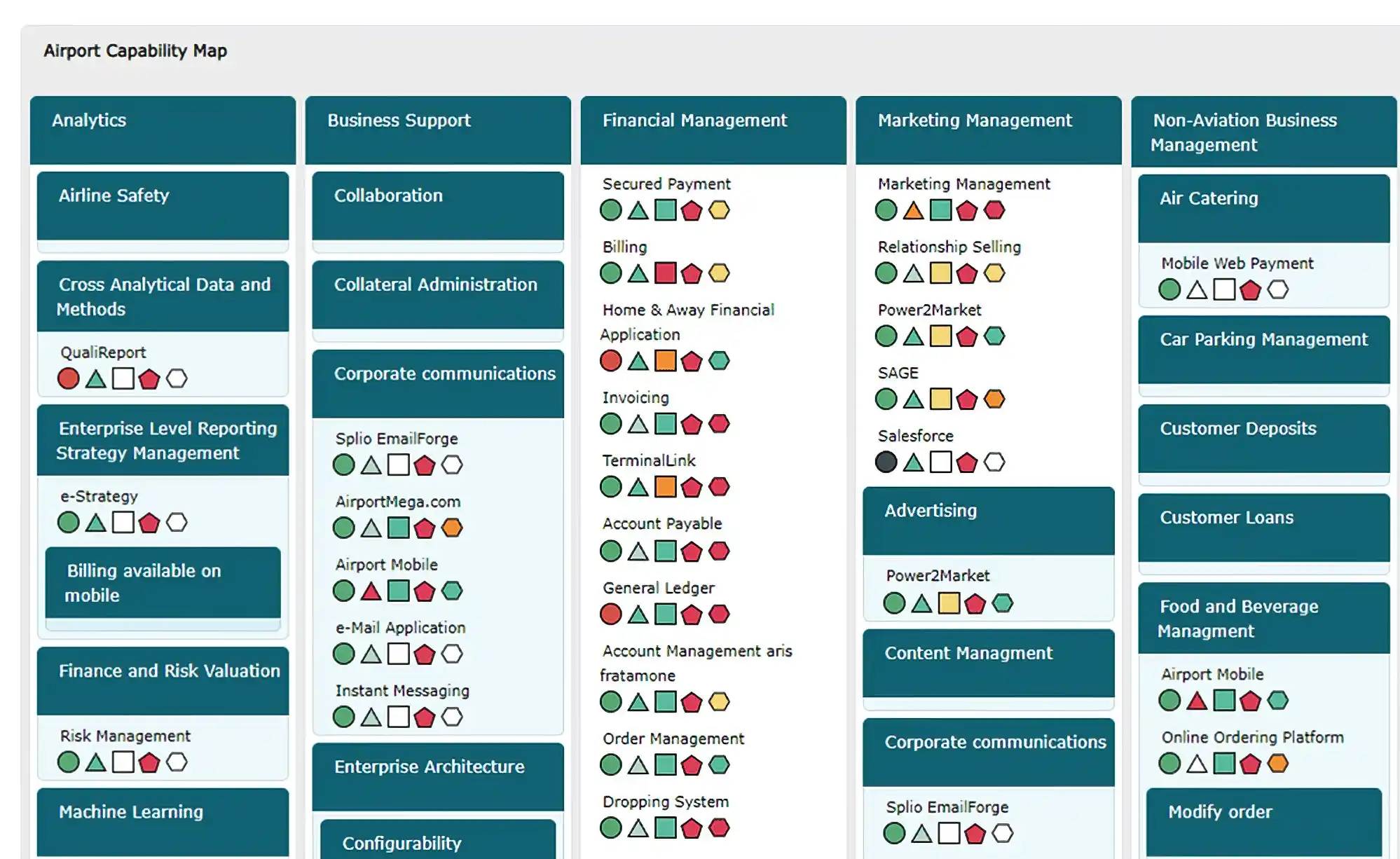
Business capability map with applications
Business capability mapping helps IT leaders shape the IT architecture to meet business needs.
Business capabilities are an essential concept that enables enterprise architects to link IT operations to the business.
Through business capability planning, organizations can figure out how to outline strategic plans with IT investments and prioritize projects.
Business Capability mapping allows companies to see what is done to reach their objectives.
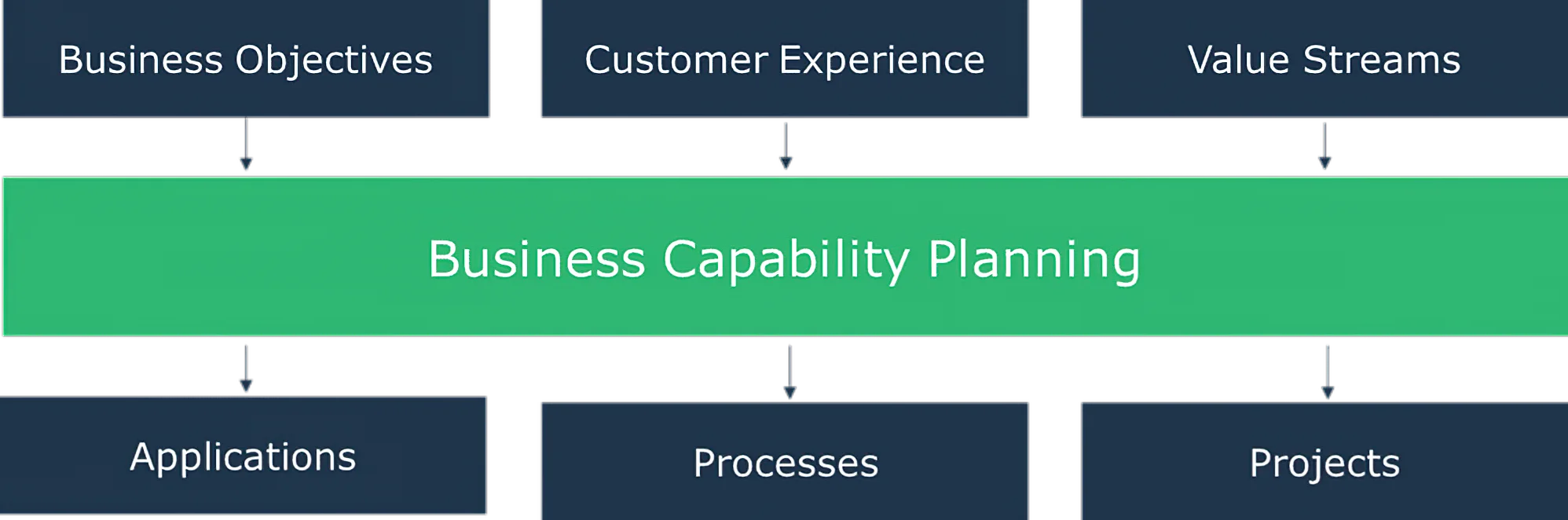
To help shape the map of an organization, there is a list of concepts that "business people" connect to:
Business objectives
From the business side, capabilities connect objectives as defined by the business. By doing so, enterprise architects ensure that the company’s goals are well supported by capabilities and reciprocally that a business capability is not unreliable to the organization's needs.
Customer Experience
One can identify the business capabilities necessary to support the desired customer experience. Customer journey maps describe the customer experience, designing the buying cycle (research, evaluate, purchase), and the various channels available to customers, such as a company website, a mobile app, or a store.
During their journey, customers follow various touchpoints to interact with the organization.
Each touchpoint is linked to business capabilities, providing an outside-in perspective on the capabilities needed to support the customer experience.
Map customer experience in customer journey maps
Value Streams
In today’s world, especially in Agile environments, a customer-centric approach is critical to ensuring that released products deliver value and match customers' needs.
By describing the stages needed to deliver value to customers, value streams translate to IT customers' needs thanks to business capabilities.
Each stage is enabled by business capabilities so that enterprise architects can identify the required capabilities and the missing ones and plan the related IT projects.
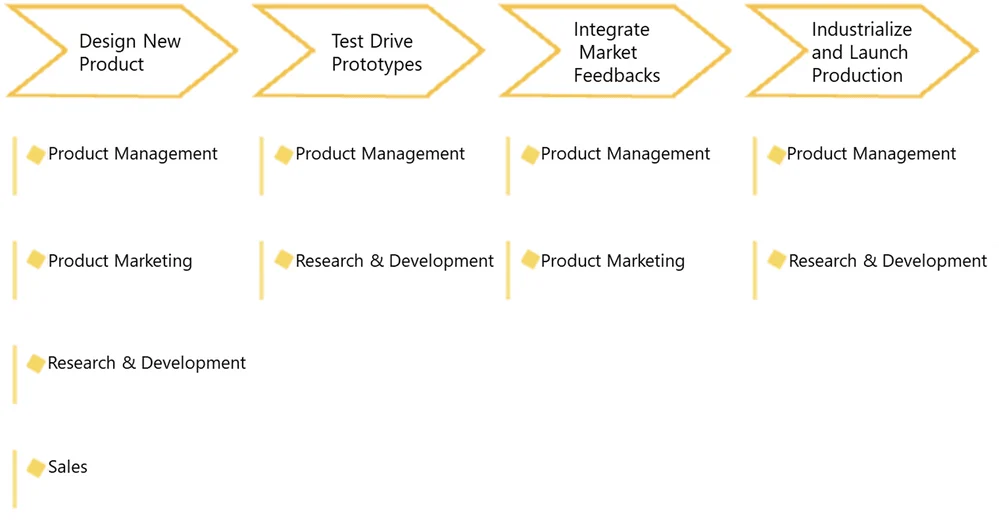
Value stream with supporting business capabilities
To map an organization, here is a list of concepts that the "IT side" can link to business capabilities:
Applications
As we mentioned previously in our examples, business capabilities are supported by one or multiple applications.
The link between applications and business capabilities enables enterprise architects to understand the business value of applications and whether an application supports a critical capability.
Projects
Organizations must build the corresponding strategic projects and link them to business capabilities to transform or create new business capabilities.
By doing so, enterprise architects understand how projects impact business capabilities and their related applications.

Business capabilities, along with projects displayed in a business capability map
Business Processes
Finally, the organizational view with business process mapping brings the perspective on the different organizational tasks people must perform to support business capabilities.
The importance of business capabilities and business capability mapping
The ability of a business to achieve its objectives depends on its capabilities. Business capability mapping is essential to identify the capabilities required to achieve specific business objectives and to track progress over time. This helps businesses focus on the right things, invest in the right areas, and make better resource allocation decisions.
Strategic planning
Business capabilities are the foundation for strategic planning. An organization's strategic plan provides long-term visibility on a company's direction and includes action plans and resources to achieve these goals.
By associating strategy with capabilities, an enterprise architect can view the impact of business projects on their application and the IT landscape.
It will help them plan future architecture to support these business capabilities.
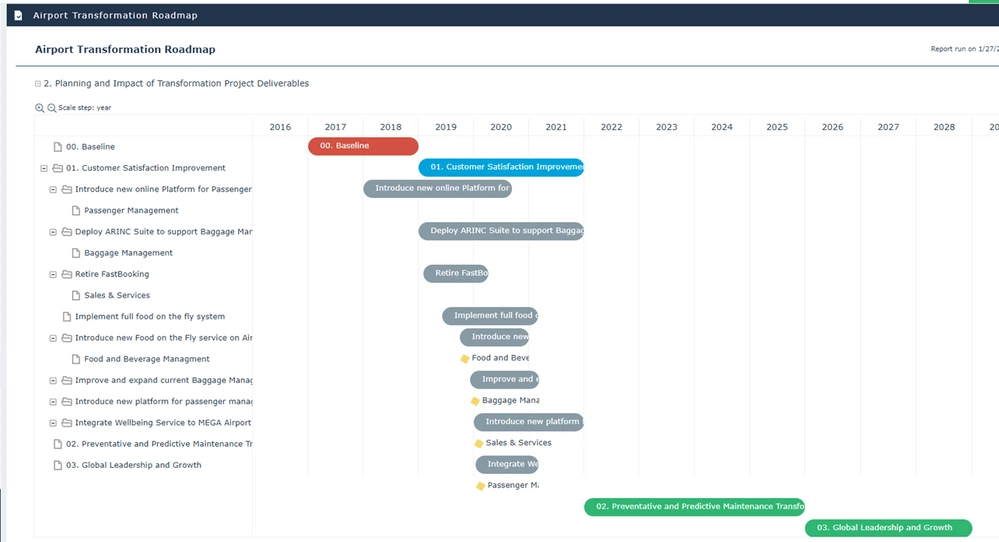
Strategic roadmap with supporting business capabilities
Customer experience in Agile developments.
Agile enterprises are organized around the customer. Even though product owners translate business requirements into user stories and hence, software developments, they don't necessarily have the complete picture of the value delivered to the customer or the customer experience. Using value streams, enterprise architects can formalize the delivered value.
They also use customer journey maps to describe the desired customer experience. Enterprise architects plan the required business capabilities by connecting touchpoints and stages of the value streams to business capabilities. Most importantly, they can link these business capabilities to Epics and user stories so that software developments are directly tied to customer experience!
Application Rationalization
Organizations have often accumulated many applications and other IT assets due to company growth or past mergers and acquisitions.
Many IT organizations fail to rationalize their application portfolio because they only have a cost perspective.
Indeed, organizations won't eliminate a business-critical application simply because it costs too much!
By linking applications to business capabilities, IT organizations can clearly see how an application supports the business, whether it supports a critical or minor capability.
Using business capabilities also helps identify redundant applications, especially in the case of mergers and acquisitions, where the new company gains applications from the acquired company.
Technology Risk Management
In EA repositories, underlying technology components supporting applications, such as databases or software frameworks, are linked to applications linked to business capabilities and objectives.
By monitoring the end-of-life of these technology components, enterprise architects can easily understand the impact of an obsolete technology component on strategic goals.
This is also the case for an application that would use a technology that has been prohibited, as set by the company policy.
Reciprocally, enterprise architects can monitor critical business capabilities and view if they are not being put at risk due to obsolete or prohibited technology.
Benefits of business capabilities
There are many benefits to having well-defined business capabilities. The main advantages are listed below.
Increased visibility of the business value of an IT asset
Capabilities are a great way to organize IT assets from a business standpoint. CMDBs are a critical component when managing IT assets, but they are often difficult to maintain and do not provide visibility into the business value of IT assets.
Business capabilities give an immediate understanding of the value for the business by linking IT assets to capabilities.
They enable IT departments to focus on critical assets. It is also a communication tool that offers a common language between business and IT.
Reduce IT Costs
By mapping applications to business capabilities, redundancies are more accessible to analyze and reduce costs. If two applications support the same business capability, they are likely to provide the same functionalities or functional overlaps.
Adding other information, such as application cost, end-of-life, or technology obsolescence, also helps improve decision-making to remove or modernize an application.
Greater flexibility
IT departments are often swamped with existing projects or assets when managing IT projects. Don’t they clearly see how new projects or applications fit into their existing IT systems? How will the new project impact the IT landscape? Is it redundant with another project or application? Thanks to business capabilities, IT departments increase their ability to embrace new projects by streamlining the IT landscape.
They can also focus their resources on projects critical to the business and work on what matters the most.
Improved IT investments
Business capabilities are crucial to linking strategy to execution. Business capabilities are planned in time, with strategic objectives forming the strategic roadmap.
Based on this roadmap, IT leaders determine the related IT projects, the applications, and the impacted architecture.
By aligning projects with business needs, IT departments ensure that resources are spent on suitable projects and that investments are better planned through greater visibility into upcoming projects.
It is also easier to reprioritize projects as strategic objectives change, especially in agile environments.
How do you map business capabilities?
Business capabilities link business needs to IT assets so that IT assets genuinely support the business. Additionally, business-capability planning helps enterprise architects map strategic plans and ensure that projects are aligned with business objectives.
To make sure capability maps are named and defined in business terms. Here are our guidelines for doing so:
1 - Understand your organization’s strategic goals
Understanding where your organization is heading and the strategic goals defined by the executive team is crucial.
Define the mission, vision, strategies, tactics, objectives, and goals using the business motivation model to help you with this task.
Enterprise architects must work closely with the business to get insights into the organization's strategy and ensure that the business's capabilities are comprehensive.
Map out business strategy, including tactics, objectives, goals, mission, and vision
2 - Break down the business into building blocks
Meet with business leaders to understand the relevant level of detail that fits your organization’s needs and then break down capabilities into sub-business capabilities.
Note that business capability templates are available to speed up this step. They are either generic or industry-specific.
Standards bodies such as BIAN for the banking sector or the Business Architecture Guild provide generic or industry-specific templates. These business capability frameworks help accelerate business capability modeling.
Review your findings with business leaders and adjust if necessary. Establish a process for regularly reviewing business capability mapping.
3 - Link business capabilities to applications and impact analysis
In this step, enterprise architects will link the business and IT by connecting applications to business capabilities and performing a business capability analysis.
Since technology components are also tied to applications in the EA repository, you can quickly impact analysis from a technology component up to business objectives.
Applications and business capabilities are viewed in business capability maps. Using indicators on applications and business capabilities, such as application lifecycle and business criticality, you can make better decisions on the evolution of the application portfolio.
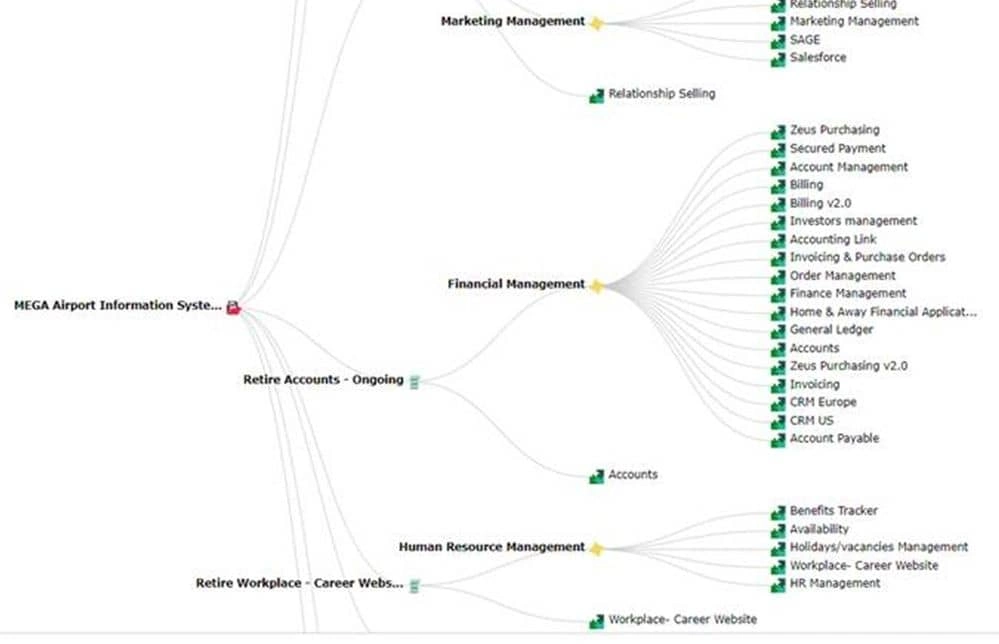
Impact analyses on projects, business capabilities, and applications
4 - Integrate the customer perspective
To plan initiatives that focus on customer needs, it is essential to connect business capabilities to the customer’s experience.
Work with epic owners or business leaders to create value streams that depict the value delivered to customers.
Work with marketing and product teams on customer journey maps to design optimal customer journeys. Identify the related business capabilities required to fulfill customer needs.
5 - Prioritize and assess business capabilities to plan project
Assess business capabilities based on priority, complexity, and efficiency to prioritize and plan business capabilities. Identify the related projects to create or transform business capabilities.
The identified projects are then planned and put into a strategic roadmap. It's important to share the strategic roadmap with your organization to review the strategic roadmap.
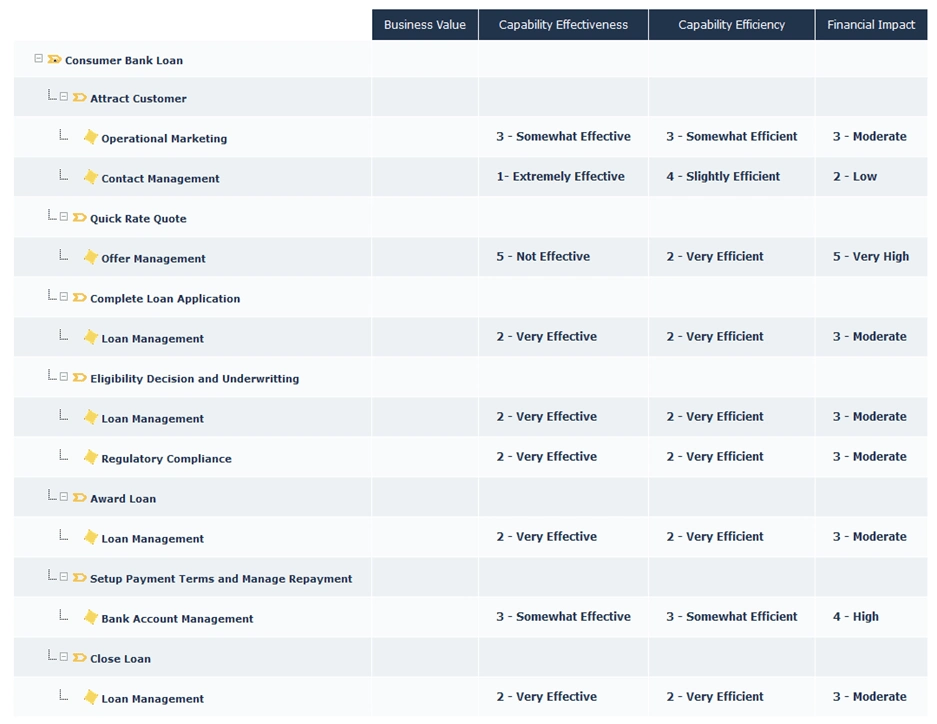
Assess business capabilities on various criteria
Summary
With the help of business capabilities and Business capability maps, enterprise architects can act as strategic advisors to the business by explaining what can or cannot be done from an IT perspective.
Business capability planning will also help CIOs communicate how IT value will be delivered to the business.
FAQs
In business, a capability is defined as a combination of skills, knowledge, experience, and resources that allow an organization to perform a particular task or set of tasks. A capability can be considered an organization's "secret sauce" - the unique combination of capabilities that gives it the ability to succeed at something others cannot. Capabilities are often described in terms of processes or functions; for example, a manufacturing organization might be capable of designing and producing products. However, it is important to remember that a capability is more than just a process or function - it is the combination of skills, knowledge, experience, and resources that allow an organization to perform that process or function in a way that is unique and successful.
Business capability planning is the process of identifying, documenting, and tracking the capabilities of an organization. This includes developing new products or services, entering new markets, responding to customer needs, or taking advantage of new technology. Business capability planning aims to ensure that the organization has the right mix of capabilities to achieve its strategic objectives.
A business capability heat map is a visual tool that helps organizations understand the relationships between their capabilities and other factors, such as business goals, processes, and organizational structures. The heat map allows organizations to identify high or low-performance areas and decide where to focus their resources.
The Togaf IT business capability map is a tool used to help organizations understand and manage their IT capabilities. It provides a common language for discussing and analyzing IT capabilities and can be used to identify gaps and areas for improvement. The Togaf map is based on the Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF), a framework for enterprise architecture.
To map business capabilities, you need first to identify the different areas or functions of the business. Once these are identified, you can start mapping out how they work together and what dependencies are between them. This can be done using various methods, such as process mapping or creating a value stream map.
Achieve Business-IT Alignment with IT portfolio management methods

Provide key steps for ensuring an aligned business architecture and IT architecture.
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.

How Enterprise Architecture strengthens Agile development

How Enterprise Architecture strengthens Agile development
SAFe, scrum, domain-driven design, Spotify… Agile project frameworks & methodologies have made their way into the enterprise, especially IT software project management. In this dynamic environment, it’s important for a company not to lose sight of its enterprise architecture, as it’s essential to understanding how business transformation initiatives can succeed.
Let’s explore how and why companies must ensure their enterprise architecture discipline can fuel SAFe and Agile productivity when applying the right methods.
Enterprise Architecture is an enabler for Agile
Enterprise architecture (EA) is designing, planning, and managing enterprise-level structures and systems. It helps organizations achieve their desired outcomes by aligning their strategies, processes, and technologies.
Enterprise architecture (EA) needs to adapt and evolve to support a company’s ecosystem in becoming an enabler. It enables an organization to scale its business transformation goals as needed. Scaling down is especially important to helping Agile delivery teams quickly understand where the enterprise needs to adapt as the market evolves.
How does Enterprise Architecture work with Agile?
In recent years, EA has been increasingly used to support agile development processes. This is because agile development relies on several architectural decisions that must be made early in the project. For example, decisions about technology platforms, application integration, and data management must be made before development begins.
EA provides a framework for making these decisions systematically and consistently. This ensures that the resulting architecture is aligned with the organization's strategy and can effectively support the agile process. In addition, EA can help identify potential risks and issues early on, saving time and money in the long run.
In Figure 1 below, you can see this concept in action. It shows how enterprise architecture can interpret the enterprise's vision and goals into a roadmap and strategy. Then it can be scaled as needed and embedded into Agile sprints. This ability to change and adapt creates the flexibility necessary to fuel Agile and ensure a successful and aligned output.
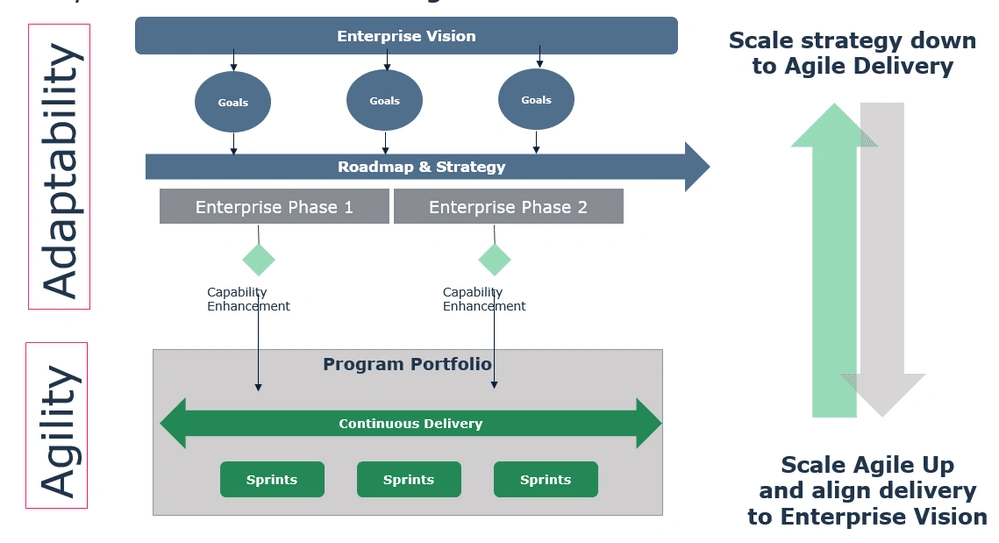
Figure 1: Enterprise architecture and Agile-at-scale
An Agile mindset provides many benefits to companies. However, it also has some downfalls. This becomes evident when Agile’s suggested improvements may not align with overall business goals. Agile methods are activity-focused because they focus on executing a project.
Companies must ensure that programs are executed to help the business achieve sustainable growth. Aligning these results to the company’s strategy is crucial. This is where the enterprise architecture discipline shines.
How Enterprise Architecture strengthens Agile development
10 Key Moments in this video
Agile Enterprise Architecture Principles
Several agile enterprise architecture principles can help organizations become more agile and responsive to change. These include:
- Creating a lean and modular architecture involves creating a simpler and more streamlined architecture that is easy to change and adapt as needed.
- Developing in short cycles: This helps ensure that changes can be quickly implemented and tested and that feedback is continuously incorporated into the development process.
- Automating key processes: This helps free up resources to be focused on more strategic tasks.
- Encouraging collaboration: This ensures that all stakeholders are involved in the development process and that ideas can be quickly shared and implemented.
- Focusing on business value means prioritizing features and functionality that will impact the business more than simply nice ones.
Enterprise architecture is about aligning Agile outputs to strategy.
Enterprise architecture is all about aligning the outputs of an Agile software development process with an organization's overall strategy. This means creating a blueprint for how the software will support business goals and objectives.
The enterprise architect ensures the software development team understands the big picture and how their work fits it.
This can be challenging, but the new and modern enterprise architect needs to be business outcome-driven. Simply put, the primary outcome he/she needs to look for is aligning the business architecture (objectives, regulations, capability planning, strategy, value stream mapping) to the IT architecture and portfolios.
Understanding how the company's architecture works today and whether it will support the business objectives is key, especially for Agile developments to be successful.
An enterprise architect plays a key role in aligning the enterprise roadmap(s) to the IT roadmap(s) by answering a crucial question:
Will we adapt quickly enough to meet our market in time?
The key to reconciling Agile design
The key to reconciling Agile design is understanding the differences between the two approaches. Agile focuses on iterative development, meaning requirements constantly evolve and change. On the other hand, design is a more linear process, focusing on creating a detailed plan upfront.
One way to reconcile these two approaches is to start with a high-level design that outlines the overall architecture and framework.
This can be done using Agile techniques such as user stories and storyboards. Once the high-level design is complete, you can flesh out the details using a more traditional approach.
Another way to reconcile Agile and design is to use a hybrid approach that combines elements of both.
For example, you could start with a detailed design for the core functionality and then use an Agile approach for the remaining features. This allows you to get the best of both worlds – a well-designed core with the flexibility to adapt to changing requirements quickly.
Agile Development projects create emergent designs, and architects designing “to be” architecture cannot keep up. In that spirit, the concept of intentional architecture becomes key.
Intentional architecture represents the intent or the plan the organization wants to achieve.
It includes documenting business goals, value streams, capabilities, applications, new technologies, data, and APIs for each phase of the company’s roadmap. An enterprise architect can do this in two steps:
- The first objective of an enterprise architect should be to align the business objectives to the intentional architecture. Of course, even the best-laid plans change as an organization adapts to changing market conditions, so an enterprise architect needs to be mindful of how the guardrails must be adjusted.
- The second objective of an enterprise architect is to reconcile the intentional architecture to the new designs created by the Agile Development teams. In this context, the EA team’s reaction often engages “force” to make the Agile Development team and operation follow their vision. However, this is the exact opposite of what EA can and should do. Rather, the EA team should focus on reconciling the agile development to the intentional architecture and understand the impact on the strategy, if any.
In this scenario, enterprise architects play a crucial role in ensuring the ability to scale the strategy down to Agile Delivery and deliver the enterprise vision.
Today’s enterprise architect can now focus on business outcomes, enabling the enterprise to marry business adaptability to project agility.
Figure 2 below shows how this comes to life in a walk, jog, run analogy.
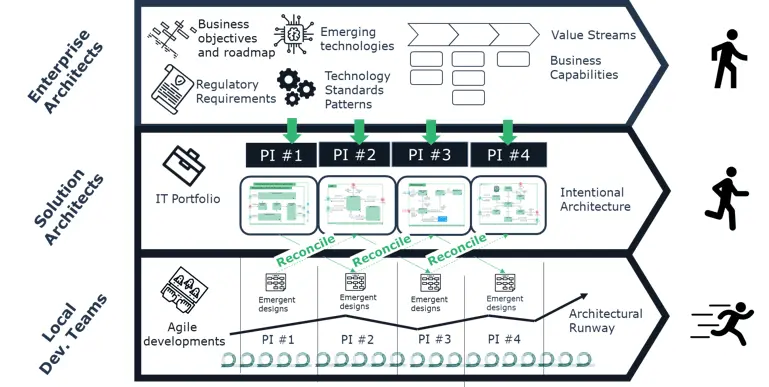
Figure 2: Agile Support Developments with intentional architecture at different paces
Regardless of your chosen approach, it’s important to remember that communication and collaboration are essential for success. Make sure all stakeholders are involved from the beginning and that there is a clear understanding of what each team is responsible for.
What are some of the key benefits of enterprise agile?
Enterprise agile has many benefits, but some key benefits are improved communication, better quality products, and faster delivery times.
Enterprise agile helps improve communication by breaking down barriers between departments and allowing for more collaboration. This improved communication leads to better quality products because everyone is on the same page and working together towards a common goal. Enterprise agile also results in faster delivery times because there is less red tape and more flexibility to make changes quickly.
Overall, enterprise agile leads to better communication, higher quality products, and faster delivery times – all of which benefit businesses.
Agile Methodology and Enterprise Architecture crucial for Business Success
Agile methodology can co-exist with enterprise architecture. They can complement each other very well. Enterprise architecture provides the framework and foundation for an organization, while agile methodology provides flexibility and adaptability to meet changing needs. Together, they can help an organization be more responsive to change and be more successful.
Enterprise architect's role in an Agile environment
In an Agile environment, the role of enterprise architects is pivotal as it provides strategic direction to development teams. Without this intentional architecture, emergent design alone cannot handle the complexity of large-scale system development.
Using HOPEX, companies can manage comprehensive enterprise architecture disciplines within one repository and connect business architecture, solution architecture, IT & technology architecture, portfolio management, and GRC.
This single source of truth helps organizations break down silos, avoid rework, and ensure the Agile development team’s outputs are immediately viable and successful.
For more tactics on this topic, check out our e-Book, “How enterprise architecture can scale Agile development.”
Support Agile developments with just-in-time intentional architecture
Enterprise Architecture Related Content
Shift from a documentation tool to an operational tool and accelerate business transformation
MEGA HOPEX for Enterprise Architecture
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for EA, and see how you can have immediate value of your projects.